|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
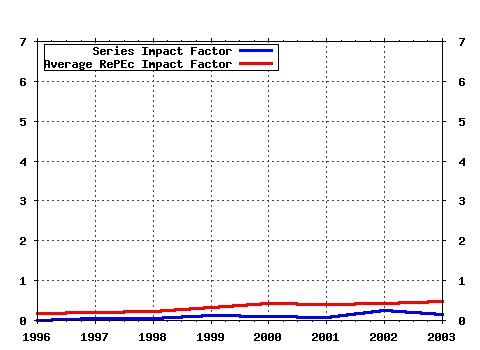
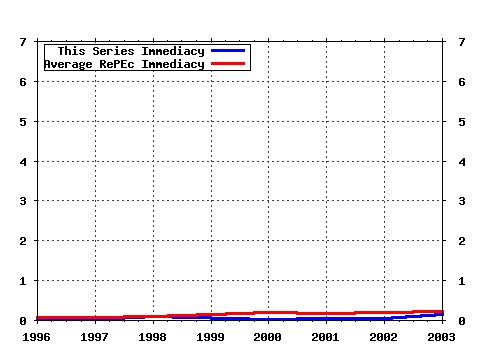
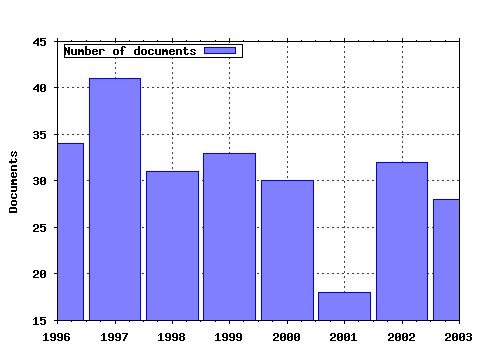
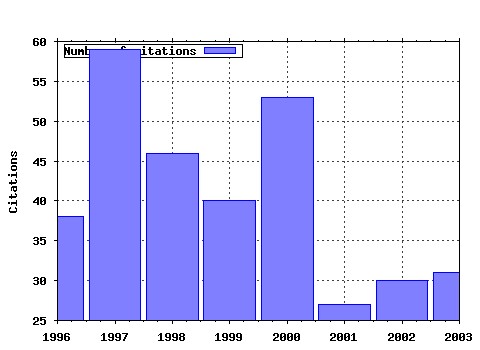
International Review of Law and Economics Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Latest citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:6:y:1986:i:1:p:45-58 The judgment proof problem (1986). International Review of Law and Economics (2) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:20:y:2000:i:1:p:75-106 Socioeconomic and demographic factors of crime in Germany: Evidence from panel data of the German states (2000). International Review of Law and Economics (3) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:15:y:1995:i:1:p:109-126 The effects of criminality and conviction on the labor market status of young British offenders (1995). International Review of Law and Economics (4) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:17:y:1997:i:1:p:75-87 Casual police corruption and the economics of crime (1997). International Review of Law and Economics (5) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:13:y:1993:i:2:p:217-224 Optimal sanctions and differences in individuals likelihood of avoiding detection (1993). International Review of Law and Economics (6) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:22:y:2002:i:2:p:193-216 Rent-seeking through litigation: adversarial and inquisitorial systems compared (2002). International Review of Law and Economics (7) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:6:y:1986:i:1:p:101-105 Optimal subsidies and damages in the presence of judicial error (1986). International Review of Law and Economics (8) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:14:y:1994:i:4:p:393-409 The capture of wealth by monopolists and the protection of property rights (1994). International Review of Law and Economics (9) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:16:y:1996:i:1:p:81-99 The political economy of immigration policies (1996). International Review of Law and Economics (10) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:20:y:2000:i:1:p:35-51 Casual police corruption and the economics of crime:: Further results (2000). International Review of Law and Economics (11) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:20:y:2000:i:3:p:371-382 On the joint use of liability and safety regulation (2000). International Review of Law and Economics (12) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:10:y:1990:i:3:p:233-239 Re-examining liability rules when injurers as well as victims suffer losses (1990). International Review of Law and Economics (13) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:21:y:2001:i:3:p:287-307 Collective wage setting when wages are generally binding An antitrust perspective (2001). International Review of Law and Economics (14) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:14:y:1994:i:3:p:341-350 Deterrence effects of sequential punishment policies: Should repeat offenders be more severely punished? (1994). International Review of Law and Economics (15) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:23:y:2003:i:3:p:253-259 A note on the optimal punishment for repeat offenders (2003). International Review of Law and Economics (16) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:2:y:1982:i:1:p:47-65 Evaluating choice (1982). International Review of Law and Economics (17) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:17:y:1997:i:4:p:509-520 Judicial detection skill and contractual compliance (1997). International Review of Law and Economics (18) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:11:y:1991:i:1:p:3-10 Optimal criminal procedure: Fairness and deterrence (1991). International Review of Law and Economics (19) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:17:y:1997:i:3:p:431-447 The burden of proof in civil litigation: A simple model of mechanism design (1997). International Review of Law and Economics (20) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:14:y:1994:i:1:p:103-119 Does conviction have a persistent effect on income and employment? (1994). International Review of Law and Economics (21) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:19:y:1999:i:3:p:295-317 Contingent fees and litigation settlement1 (1999). International Review of Law and Economics (22) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:13:y:1993:i:3:p:239-257 Should employees be subject to fines and imprisonment given the existence of corporate liability? (1993). International Review of Law and Economics (23) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:18:y:1998:i:3:p:341-359 Dissolving the relationship between divorce laws and divorce rates (1998). International Review of Law and Economics (24) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:19:y:1999:i:1:p:1-21 A contractual approach to the gray market (1999). International Review of Law and Economics (25) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:14:y:1994:i:1:p:21-34 Efficient standards of due care: Should courts find more parties negligent under comparative negligence? (1994). International Review of Law and Economics (26) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:20:y:2000:i:1:p:21-33 Expertise, contingent fees, and insufficient attorney effort (2000). International Review of Law and Economics (27) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:8:y:1988:i:2:p:127-143 Judicial decisionmaking and litigation expenditure (1988). International Review of Law and Economics (28) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:19:y:1999:i:2:p:275-293 Using decoupling and deep pockets to mitigate judgment-proof problems1 (1999). International Review of Law and Economics (29) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:23:y:2003:i:1:p:1-29 Voting control in German corporations (2003). International Review of Law and Economics (30) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:20:y:2000:i:1:p:127-140 Punishing repeat offenders more severely (2000). International Review of Law and Economics (31) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:5:y:1985:i:1:p:91-106 Why did inheritance laws change? (1985). International Review of Law and Economics (32) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:5:y:1985:i:1:p:3-13 A model in which suits are brought for their nuisance value (1985). International Review of Law and Economics (33) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:25:y:2005:i:1:p:75-88 Formal Markets and Informal Insurance (2005). International Review of Law and Economics (34) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:8:y:1988:i:1:p:109-116 The deterrent effects of settlements and trials (1988). International Review of Law and Economics (35) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:18:y:1998:i:3:p:305-324 On offense history and the theory of deterrence (1998). International Review of Law and Economics (36) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:9:y:1989:i:2:p:149-164 A method for estimating injury caused by unfair trade practices (1989). International Review of Law and Economics (37) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:25:y:2005:i:2:p:209-228 Law and Economics of Obligations (2005). International Review of Law and Economics (38) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:16:y:1996:i:2:p:259-276 Limited liability and the requirement to purchase insurance (1996). International Review of Law and Economics (39) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:21:y:2001:i:3:p:309-327 Trial procedures and optimal limits on proof-taking10 (2001). International Review of Law and Economics (40) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:10:y:1990:i:1:p:3-27 The effect of frivolous lawsuits on the settlement of litigation (1990). International Review of Law and Economics (41) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:17:y:1997:i:1:p:31-61 Mandatory rotation of company auditors: A critical examination (1997). International Review of Law and Economics (42) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:12:y:1992:i:2:p:263-279 A positive theory of statutory interpretation (1992). International Review of Law and Economics (43) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:3:y:1983:i:1:p:3-26 Legal fees contracts and alternative cost rules: An economic analysis (1983). International Review of Law and Economics (44) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:17:y:1997:i:4:p:589-608 Tort law and internalization: The gap between private loss and social cost (1997). International Review of Law and Economics (45) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:10:y:1990:i:2:p:161-171 The influence of litigation costs on deterrence under strict liability and under negligence (1990). International Review of Law and Economics (46) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:2:y:1982:i:1:p:3-27 The optimum enforcement of laws and the concept of justice: A positive analysis (1982). International Review of Law and Economics (47) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:19:y:1999:i:1:p:47-68 Do punitive damages promote deterrence?1 (1999). International Review of Law and Economics (48) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:12:y:1992:i:3:p:345-355 A note on marginal deterrence (1992). International Review of Law and Economics (49) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:11:y:1991:i:2:p:223-232 The initiation problem in bankruptcy (1991). International Review of Law and Economics (50) RePEc:eee:irlaec:v:15:y:1995:i:3:p:323-345 Predictable and unpredictable error in tort awards: The effect of plaintiff self-selection and signaling (1995). International Review of Law and Economics Latest citations received in: | 2003 | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 Latest citations received in: 2003 (1) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:4131 Escalating Penalties for Repeat Offenders (2003). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (2) RePEc:dgr:kubcen:200378 Do corporate control and product market competition lead to stronger productivity growth? : Evidence from market-oriented and blockholder-based governance regimes (2003). Tilburg University, Center for Economic Research / Discussion Paper (3) RePEc:ube:dpvwib:dp0315 Escalating Penalties for Repeat Offenders (2003). Universitat Bern, Volkswirtschaftliches Institut / Diskussionsschriften (4) RePEc:use:tkiwps:0313 The Economics of Tort Law: A Précis (2003). Utrecht School of Economics / Working Papers Latest citations received in: 2002 (1) RePEc:aea:jecper:v:16:y:2002:i:4:p:67-90 Pharmaceuticals and the Developing World (2002). Journal of Economic Perspectives (2) RePEc:upf:upfgen:639 Cashing by the Hour: Why Large Law Firms Prefer Hourly Fees Over Contingent Fees (2002). Department of Economics and Business, Universitat Pompeu Fabra / Economics Working Papers Latest citations received in: 2001 (1) RePEc:hhs:ifauwp:2001_011 Now and forever? Initial and subsequent location choices of immigrants (2001). IFAU - Institute for Labour Market Policy Evaluation / Working Paper Series Latest citations received in: 2000 (1) RePEc:cdl:oplwec:1057 The Virtuous Circle of Distrust: A Mechanism to Deter Bribes and Other Cooperative Crimes (2000). Berkeley Olin Program in Law & Economics / Berkeley Olin Program in Law & Economics, Working Paper Series Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |