|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
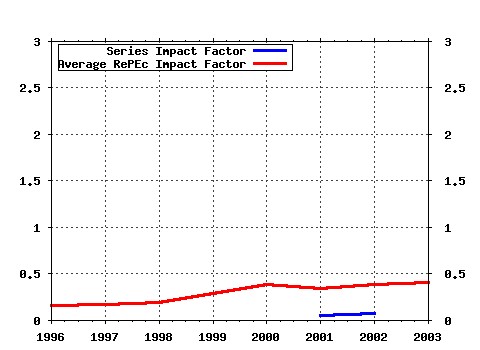
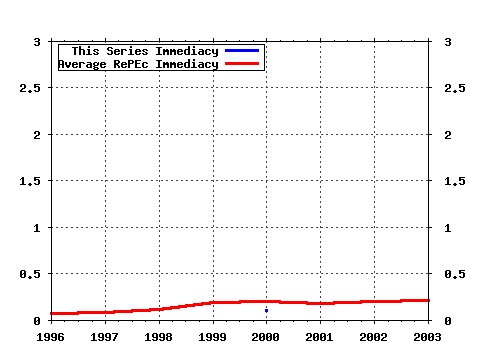
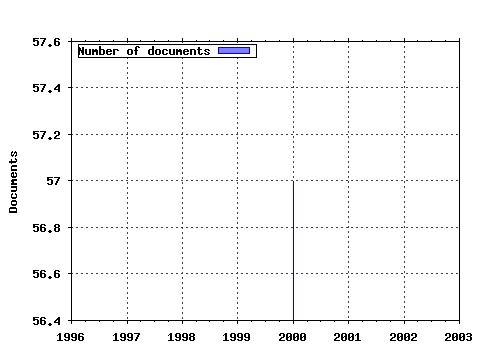
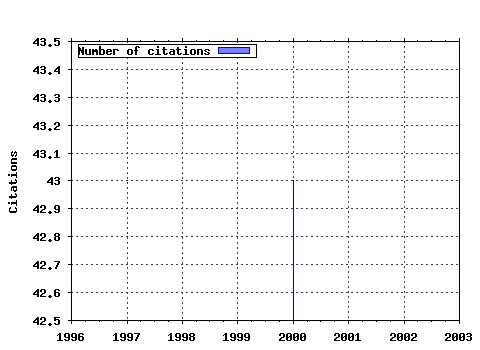
ESRC Centre on Economics Learning and Social Evolution / ELSE working papers Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Latest citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:els:esrcls:028 Why Imitate, and if so, How? A Bounded Rational Approach to Multi-
Armed Bandits (2000). ESRC Centre on Economics Learning and Social Evolution / ELSE working papers (2) RePEc:els:esrcls:002 Continuous Approximations of Stochastic Evolutionary Game Dynamics (2000). ESRC Centre on Economics Learning and Social Evolution / ELSE working papers (3) RePEc:els:esrcls:024 CYCLES OF LEARNING IN THE CENTIPEDE GAME (2000). ESRC Centre on Economics Learning and Social Evolution / ELSE working papers (4) RePEc:els:esrcls:033 Learning, Matching and Aggregation (2000). ESRC Centre on Economics Learning and Social Evolution / ELSE working papers (5) RePEc:els:esrcls:023 Learning with Hazy Beliefs (2000). ESRC Centre on Economics Learning and Social Evolution / ELSE working papers (6) RePEc:els:esrcls:037 Naive Reinforcement Learning With Endogenous Aspiration (2000). ESRC Centre on Economics Learning and Social Evolution / ELSE working papers (7) RePEc:els:esrcls:012 Neutrally Stable Outcomes in Cheap Talk Coordination Games (2000). ESRC Centre on Economics Learning and Social Evolution / ELSE working papers (8) RePEc:els:esrcls:035 Monopoly Pricing with Social Learning (2000). ESRC Centre on Economics Learning and Social Evolution / ELSE working papers (9) RePEc:els:esrcls:026 When Does Evolution Lead to Efficiency in Communication Games? (2000). ESRC Centre on Economics Learning and Social Evolution / ELSE working papers (10) RePEc:els:esrcls:049 EVOLUTIONARY DRIFT AND EQUILIBRIUM SELECTION (2000). ESRC Centre on Economics Learning and Social Evolution / ELSE working papers (11) RePEc:els:esrcls:011 Evolutionary Drift and Equilibrium Selection (2000). ESRC Centre on Economics Learning and Social Evolution / ELSE working papers (12) RePEc:els:esrcls:034 Conventions and Social Mobility in Bargaining Situations (2000). ESRC Centre on Economics Learning and Social Evolution / ELSE working papers (13) RePEc:els:esrcls:045 How Proper is Sequential Equilibrium (2000). ESRC Centre on Economics Learning and Social Evolution / ELSE working papers (14) RePEc:els:esrcls:009 Adaptive Dynamics and the Implementation Problem with Complete
Information (2000). ESRC Centre on Economics Learning and Social Evolution / ELSE working papers Latest citations received in: | 2003 | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 Latest citations received in: 2003 Latest citations received in: 2002 Latest citations received in: 2001 Latest citations received in: 2000 (1) RePEc:els:esrcls:043 Price Dispersion: an Evolutionary Approach (2000). ESRC Centre on Economics Learning and Social Evolution / ELSE working papers (2) RePEc:ivi:wpasad:2000-08 SPLITTING THE BABY IN TWO: HOW TO SOLVE SOLOMONS DILEMMA WHEN AGENTS ARE BOUNDEDLY RATIONAL (2000). Instituto Valenciano de Investigaciones Económicas, S.A. (Ivie) / Working Papers. Serie AD (3) RePEc:oxf:wpaper:033 Stochastic Evolution with Slow Learning (2000). University of Oxford, Department of Economics / Economics Series Working Papers (4) RePEc:red:issued:v:3:y:2000:i:2:p:247-282 Implementation, Elimination of Weakly Dominated Strategies and Evolutionary Dynamics (2000). Review of Economic Dynamics (5) RePEc:tky:fseres:2000cf79 Stability of Spatial Equilibrium (2000). CIRJE, Faculty of Economics, University of Tokyo / CIRJE F-Series (6) RePEc:wpa:wuwpmi:0004007 Learning in Economics: Where Do We Stand? (2000). EconWPA / Microeconomics Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |