|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
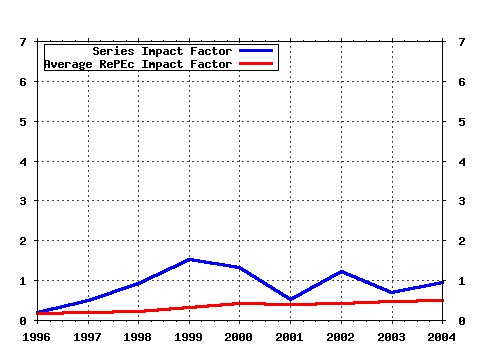
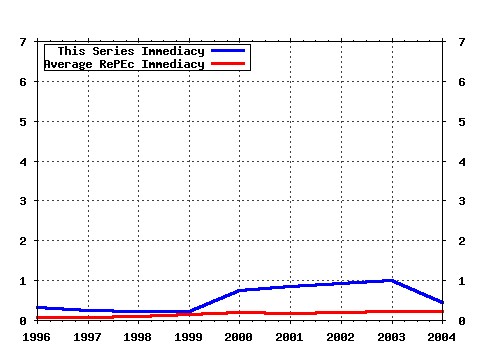
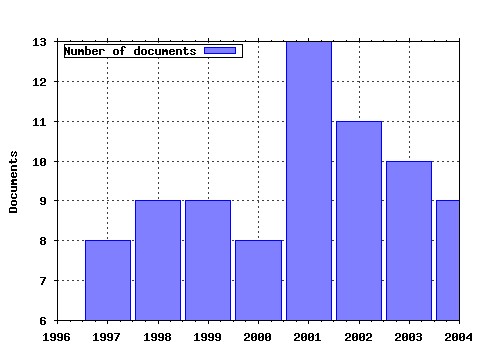
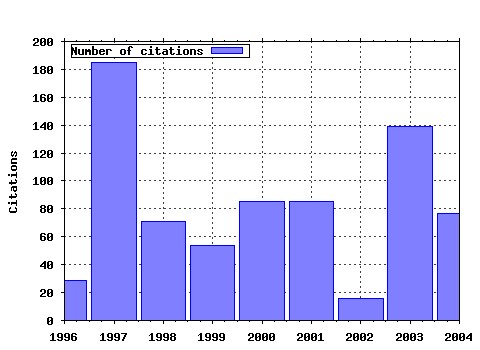
Proceedings Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Latest citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1997:p:653-686 Inflation forecasts and monetary policy (1997). (2) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1988:p:559-596 Financial structure and aggregate economic activity: an overview (1988). (3) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1991:p:519-546 Optimal fiscal and monetary policy: some recent results (1991). (4) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2003:p:1119-1215 The Great Depression and the Friedman-Schwartz hypothesis (2003). (5) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1993:p:475-520 Inflation regimes and the sources of inflation uncertainty (1993). (6) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1991:p:483-518 The welfare costs of moderate inflations (1991). (7) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2003:p:1045-1084 Adaptive learning and monetary policy design (2003). (8) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1998:i:aug:p:596-620 The legal environment, banks, and long-run economic growth (1998). (9) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1999:p:443-468 Inside and outside money as alternative media of exchange (1999). (10) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2000:p:611-640 Systemic risk, interbank relations, and liquidity provision by the central bank (2000). (11) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2001:p:482-517 Stabilization policy and the costs of dollarization (2001). (12) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2000:p:641-670 Comparing market and supervisory assessments of bank performance: who knows what when? (2000). (13) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2004:p:511-542 How foreign participation and market concentration impact bank spreads: evidence from Latin America (2004). (14) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2004:p:563-592 What drives bank competition? Some international evidence (2004). (15) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2001:p:312-338 Capital markets and the exchange rate with special reference to the dollarization debate in Latin America (2001). (16) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2000:p:580-610 Who should act as lender of last resort? an incomplete contracts model (2000). (17) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1991:p:439-461 The genesis of inflation and the costs of disinflation (1991). (18) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2001:p:597-625 Fiscal consequences for Mexico of adopting the dollar (2001). (19) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2001:p:440-481 The benefits of dollarization when stabilization policy lacks credibility and financial markets are imperfect (2001). (20) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2004:p:593-626 Regulations, market structure, institutions, and the cost of financial intermediation (2004). (21) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1993:p:681-708 Long-memory inflation uncertainty: evidence from the term structure of interest rates (1993). (22) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1997:i:nov:p:568-623 Money in a real business cycle model (1997). (23) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1996:i:aug:p:426-451 The behavior of interest rates implied by the term structure of Eurodollar future (1996). (24) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2003:p:1425-1483 How forward-looking is optimal monetary policy? (2003). (25) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2000:p:671-705 Incentives for banking megamergers: what motives might regulators infer from event-study evidence? (2000). (26) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1997:p:687-724 The optimum quantity of money: theory and evidence (1997). (27) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2004:p:453-486 Competition and financial stability (2004). (28) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1998:i:aug:p:524-550 The past and future of commercial banking viewed through an incomplete contract lens (1998). (29) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1999:p:469-499 Private money (1999). (30) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2003:p:1319-1377 Taking intermediation seriously (2003). (31) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2001:p:370-403 The costs of losing monetary independence: the case of Mexico (2001). (32) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1993:p:521-557 Inflation uncertainty, relative price uncertainty, and investment in U.S. manufacturing (1993). (33) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1994:p:1241-1289 The quantitative analysis of the basic neomonetarist model (1994). (34) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1998:i:aug:p:426-471 Moral hazard under commercial and universal banking (1998). (35) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2004:p:627-654 Bank competition and access to finance: international evidence (2004). (36) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1991:p:625-631 Panel discussion: price stability ; How should long-term monetary policy be determined? (1991). (37) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1989:p:201-213 Macroeconomic implications (1989). (38) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2003:p:1217-1264 Putting M back in monetary policy (2003). (39) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1994:p:585-633 Did risk-based capital allocate bank credit and cause a credit crunch in the United States? (1994). (40) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2002:p:848-886 The conduct of monetary policy with a shrinking stock of government debt (2002). (41) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1994:p:1354-1401 Inside money, outside money and short-term interest rates (1994). (42) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2003:p:1379-1423 Backward-looking interest-rate rules, interest-rate smoothing, and macroeconomic instability (2003). (43) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1994:p:634-678 Housing-finance intervention and private incentives: helping minorities and the poor (1994). (44) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1999:p:531-567 Financial fragility with rational and irrational exuberance (1999). (45) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1991:p:580-612 The sustainability of budget deficits with lump-sum and with income-based taxation (1991). (46) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1999:p:624-667 Private money creation and the Suffolk Banking System (1999). (47) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1991:p:462-482 Seigniorage as a tax: a quantitative evaluation (1991). (48) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2003:p:1085-1117 Search, money, and capital: a neoclassical dichotomy (2003). (49) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:1991:p:547-579 Inflation, personal taxes, and real output: a dynamic analysis (1991). (50) RePEc:fip:fedcpr:y:2000:p:518-579 Deposit insurance and lender-of-last-resort functions (2000). Latest citations received in: | 2004 | 2003 | 2002 | 2001 Latest citations received in: 2004 (1) RePEc:bca:bocawp:04-24 Competition in Banking: A Review of the Literature (2004). Bank of Canada / Working Papers (2) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:10832 Finance as a Barrier to Entry: Bank Competition and Industry Structure in Local U.S. Markets (2004). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (3) RePEc:trf:wpaper:8 Banks without Parachutes - Competitive Effects of Government Bail-out Policies (2004). SFB/TR 15 Governance and the Efficiency of Economic Systems, University of Mannheim / Discussion Papers (4) RePEc:wbk:wbrwps:3210 How Foreign Participation and Market Concentration Impact Bank Spreads: Evidence from Latin America (2004). The World Bank / Policy Research Working Paper Series Latest citations received in: 2003 (1) RePEc:cfs:cfswop:wp200339 Performance of Inflation Targeting Based On Constant Interest Rate Projections (2003). Center for Financial Studies / CFS Working Paper Series (2) RePEc:ehu:dfaeii:200307 The role of the term spread in an augmented Taylor rule: An empirical investigation. (2003). University of the Basque Country - Department of Foundations of Economic Analysis II / DFAEII Working Papers (3) RePEc:fip:fedcwp:0317 Inflation and financial market performance: what have we learned in the last ten years (2003). Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland / Working Paper (4) RePEc:fip:fedkrw:rwp03-02 The social value of risk-free government debt (2003). Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City / Research Working Paper (5) RePEc:fip:fedkrw:rwp03-03 Optimality of the Friedman rule in overlapping generations model with spatial separation (2003). Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City / Research Working Paper (6) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2000-030 Determinacy, learnability, and monetary policy inertia (2003). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (7) RePEc:ime:imemes:v:21:y:2003:i:4:p:1-20 Monetary Implications of the Hayashi-Prescott Hypothesis for Japan (2003). Monetary and Economic Studies (8) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:10089 An Inflation Reports Report (2003). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (9) RePEc:umc:wpaper:0306 Optimality of the Friedman Rule in Overlapping Generations Model with Spatial Separation (2003). Department of Economics, University of Missouri-Columbia / Working Papers (10) RePEc:upf:upfgen:659 Incomplete Markets, Labor Supply and Capital Accumulation (2003). Department of Economics and Business, Universitat Pompeu Fabra / Economics Working Papers Latest citations received in: 2002 Latest citations received in: 2001 (1) RePEc:boc:bocoec:476 Monetary Rules for Emerging Market Economies (2001). Boston College Department of Economics / Boston College Working Papers in Economics (2) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:2688 Optimal Fiscal and Monetary Policy under Imperfect Competition (2001). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (3) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:2942 Optimal Fiscal and Monetary Policy Under Sticky Prices (2001). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (4) RePEc:fip:fedfpr:y:2001:i:jun:x:1 Optimal fiscal and monetary policy under sticky prices (2001). Proceedings (5) RePEc:fip:fedfpr:y:2001:i:jun:x:2 Sticky information versus sticky prices: a proposal to replace the new Keynesian Phillips curve (2001). Proceedings (6) RePEc:fip:fedlrv:y:2001:i:nov.:p:29-40:n:v.83no.6 Dollarization as a monetary arrangement for emerging market economies (2001). Review (7) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:8671 Dollarization, Inflation and Growth (2001). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (8) RePEc:rut:rutres:200101 Optimal Fiscal and Monetary Policy under Imperfect Competition (2001). Rutgers University, Department of Economics / Departmental Working Papers (9) RePEc:rut:rutres:200105 Optimal Fiscal and Monetary Policy Under Sticky Prices (2001). Rutgers University, Department of Economics / Departmental Working Papers (10) RePEc:rut:rutres:200115 Closing Small Open Economy Models (2001). Rutgers University, Department of Economics / Departmental Working Papers (11) RePEc:uct:uconnp:2001-06 Official Dollarization in Latin America: Could it Work? (2001). University of Connecticut, Department of Economics / Working papers Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |