|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
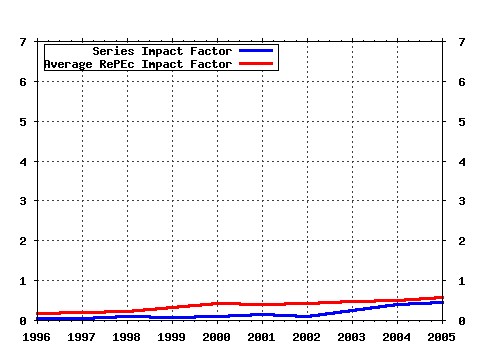
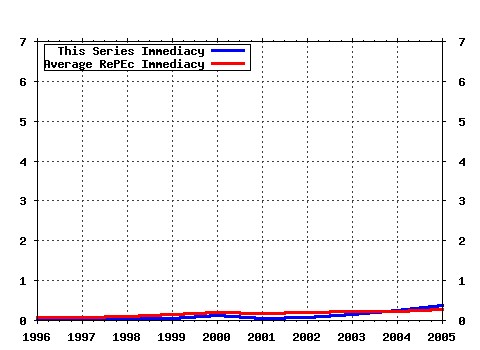
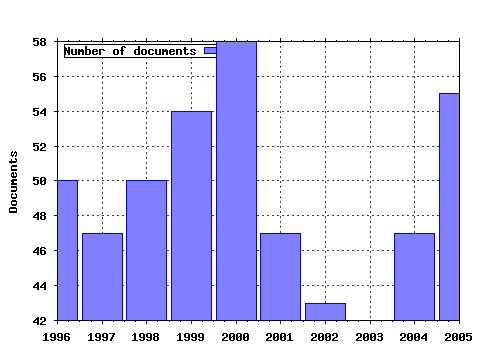
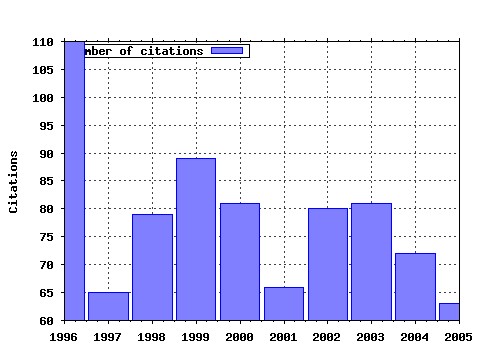
Journal of Mathematical Economics Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Latest citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:18:y:1989:i:2:p:141-153 Maxmin expected utility with non-unique prior (1989). (2) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:19:y:1990:i:3:p:305-321 Nash equilibrium with strategic complementarities (1990). (3) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:1:y:1974:i:1:p:67-96 Subjectivity and correlation in randomized strategies (1974). (4) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:1:y:1974:i:1:p:23-37 On cores and indivisibility (1974). (5) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:16:y:1987:i:1:p:65-88 Expected utility with purely subjective non-additive probabilities (1987). (6) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:10:y:1982:i:1:p:67-81 Optimal coordination mechanisms in generalized principal-agent problems (1982). (7) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:14:y:1985:i:3:p:285-300 Equilibrium in incomplete markets: I : A basic model of generic existence (1985). (8) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:1:y:1974:i:1:p:15-21 Excess demand functions (1974). (9) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:23:y:1994:i:1:p:45-58 Intermediate preferences and stable coalition structures (1994). (10) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:4:y:1977:i:2:p:131-137 Weak versus strong domination in a market with indivisible goods (1977). (11) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:20:y:1991:i:4:p:371-395 Asset pricing for general processes (1991). (12) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:11:y:1983:i:2:p:161-169 Competitive bidding and proprietary information (1983). (13) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:26:y:1996:i:1:p:133-170 Incomplete markets over an infinite horizon: Long-lived securities and speculative bubbles (1996). (14) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:31:y:1999:i:4:p:493-522 Which one should I imitate? (1999). (15) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:2:y:1975:i:3:p:345-348 Equilibrium in abstract economies without ordered preferences (1975). (16) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:18:y:1989:i:2:p:129-139 An equivalence theorem for a bargaining set (1989). (17) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:2:y:1975:i:1:p:9-15 An equilibrium existence theorem for a general model without ordered preferences (1975). (18) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:2:y:1975:i:2:p:263-295 A model of equilibrium with differentiated commodities (1975). (19) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:10:y:1982:i:2-3:p:233-267 An integration of equilibrium theory and turnpike theory (1982). (20) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:11:y:1983:i:3:p:277-300 The epsilon core of a large replica game (1983). (21) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:17:y:1988:i:1:p:77-87 Anonymous sequential games (1988). (22) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:19:y:1990:i:1-2:p:1-38 An introduction to general equilibrium with incomplete asset markets (1990). (23) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:38:y:2002:i:3:p:329-339 Strategy-proofness and population-monotonicity for house allocation problems (2002). (24) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:26:y:1996:i:1:p:103-131 Debt constraints and equilibrium in infinite horizon economies with incomplete markets (1996). (25) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:8:y:1981:i:1:p:15-35 Arbitrage and equilibrium in economies with infinitely many commodities (1981). (26) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:21:y:1992:i:5:p:461-481 Benefit functions and duality (1992). (27) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:21:y:1992:i:5:p:483-508 Optimal licensing of cost-reducing innovation (1992). (28) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:25:y:1996:i:1:p:123-141 Sensitivity analysis of multisector optimal economic dynamics (1996). (29) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:20:y:1991:i:5:p:465-487 A variational problem arising in financial economics (1991). (30) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:21:y:1992:i:4:p:301-342 Real effects of money in general equilibrium (1992). (31) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:39:y:2003:i:5-6:p:619-655 Equilibrium analysis, banking and financial instability (2003). (32) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:1:y:1974:i:1:p:51-62 Random economies with many interacting agents (1974). (33) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:21:y:1992:i:3:p:271-299 The market game: existence and structure of equilibrium (1992). (34) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:19:y:1990:i:1-2:p:113-151 Generic inefficiency of stock market equilibrium when markets are incomplete (1990). (35) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:23:y:1994:i:1:p:1-19 Generalized urn schemes and technological dynamics (1994). (36) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:41:y:2005:i:1-2:p:7-42 Evolutionary dynamics in markets with many trader types (2005). (37) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:9:y:1982:i:1-2:p:83-97 Simplicial approximation of unemployment equilibria (1982). (38) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:3:y:1976:i:2:p:107-120 A convergent process of price adjustment and global newton methods (1976). (39) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:10:y:1982:i:1:p:105-114 The value of information in a sealed-bid auction (1982). (40) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:10:y:1982:i:1:p:115-145 Cores of effectivity functions and implementation theory (1982). (41) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:12:y:1983:i:1:p:63-101 Neighboring information and distributions of agents characteristics under uncertainty (1983). (42) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:21:y:1992:i:2:p:185-197 A model of random matching (1992). (43) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:33:y:2000:i:1:p:35-55 The evolution of Walrasian behavior in oligopolies (2000). (44) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:27:y:1997:i:2:p:163-193 A globally and universally stable price adjustment process (1997). (45) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:34:y:2000:i:1:p:77-97 Consistency in house allocation problems (2000). (46) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:31:y:1999:i:1:p:49-79 Behavioral heterogeneity and structural properties of aggregate demand (1999). (47) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:19:y:1990:i:1-2:p:153-165 Observability and optimality (1990). (48) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:38:y:2002:i:1-2:p:1-41 Incentives and the core of an exchange economy: a survey (2002). (49) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:3:y:1976:i:2:p:131-134 How to discard `free disposability - at no cost (1976). (50) RePEc:eee:mateco:v:40:y:2004:i:1-2:p:191-206 Testable implications of consumption-based asset pricing models with incomplete markets (2004). Latest citations received in: | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 | 2002 Latest citations received in: 2005 (1) RePEc:att:wimass:200511 Optimal control and spatial heterogeneity : pattern formation in economic-ecological models (2005). Wisconsin Madison - Social Systems / Working papers (2) RePEc:ces:ceswps:_1462 Putting Risk in its Proper Place (2005). CESifo GmbH / CESifo Working Paper Series (3) RePEc:cla:levarc:784828000000000422 Economic Survival when Markets are Incomplete (2005). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Working Paper Archive (4) RePEc:cla:levrem:122247000000000935 Bargaining Sets of Majority Voting Games (2005). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (5) RePEc:dgr:uvatin:20050055 Heterogeneous Agent Models: Two Simple Case Studies (2005). Tinbergen Institute / Tinbergen Institute Discussion Papers (6) RePEc:fip:fedbwp:05-16 Heterogeneous beliefs and inflation dynamics: a general equilibrium approach (2005). Federal Reserve Bank of Boston / Working Papers (7) RePEc:hal:papers:halshs-00173787_v1 Asset market equilibrium with short-selling and differential information (2005). HAL, CCSd/CNRS / Pre- and Post-Print documents (8) RePEc:hhs:nhhfms:2005_017 Globally Evolutionarily Stable Portfolio Rules (2005). Department of Finance and Management Science, Norwegian School of Economics and Business Administration / Discussion Papers (9) RePEc:huj:dispap:dp410 Bargaining Sets of Majority Voting Games (2005). Center for Rationality and Interactive Decision Theory, Hebrew University, Jerusalem / Discussion Paper Series (10) RePEc:mse:wpsorb:b05098 Asset market equilibrium with short-selling and differential information. (2005). Université Panthéon-Sorbonne (Paris 1) / Cahiers de la Maison des Sciences Economiques (11) RePEc:pra:mprapa:190 On the neutrality of redistribution in a general equilibrium model with public goods (2005). University Library of Munich, Germany / MPRA Paper (12) RePEc:rio:texdis:513 Bubbles, collateral and monetary equilibrium (2005). Department of Economics PUC-Rio (Brazil) / Textos para discussão (13) RePEc:sap:wpaper:88 Asset Price Dynamics in a Financial Market with Heterogeneous Trading Strategies and Time Delays (2005). University of Rome La Sapienza, Department of Public Economics / Working Papers (14) RePEc:ssa:lemwps:2005/06 Price and Wealth Dynamics in a Speculative Market with an Arbitrary Number of Generic Technical Traders (2005). Laboratory of Economics and Management (LEM), Sant'Anna School of Advanced Studies, Pisa, Italy / LEM Papers Series (15) RePEc:ssa:lemwps:2005/27 Wealth-Driven Competition in a Speculative Financial Market: Examples with Maximizing Agents (2005). Laboratory of Economics and Management (LEM), Sant'Anna School of Advanced Studies, Pisa, Italy / LEM Papers Series (16) RePEc:uts:rpaper:162 Market Mood, Adaptive Beliefs and Asset Price Dynamics (2005). Quantitative Finance Research Centre, University of Technology, Sydney / Research Paper Series (17) RePEc:wpa:wuwpco:0506001 Breeds of risk-adjusted fundamentalist strategies in an order- driven market (2005). EconWPA / Computational Economics (18) RePEc:wpa:wuwpfi:0504019 Simple market protocols for efficient risk sharing (2005). EconWPA / Finance (19) RePEc:wpa:wuwpfi:0510026 Asset Price Dynamics in a Financial Market with Heterogeneous Trading Strategies and Time Delays (2005). EconWPA / Finance (20) RePEc:zbw:cauewp:3559 A Noise Trader Model as a Generator of Apparent Financial Power Laws and Long Memory (2005). Christian-Albrechts-University of Kiel, Department of Economics / Economics working papers (21) RePEc:zbw:cauewp:3560 Time-Variation of Higher Moments in a Financial Market with Heterogeneous Agents: An Analytical Approach (2005). Christian-Albrechts-University of Kiel, Department of Economics / Economics working papers Latest citations received in: 2004 (1) RePEc:bro:econwp:2004-08 Welfare Cost of Business Cycles When Markets Are Incomplete (2004). Brown University, Department of Economics / Working Papers (2) RePEc:bro:econwp:2004-18 The Type-Agent Core for Exchange Economies with Asymmetric Information (2004). Brown University, Department of Economics / Working Papers (3) RePEc:clt:sswopa:1190 The Relevance of a Choice of Auction Format in a Competitive Environment (2004). California Institute of Technology, Division of the Humanities and Social Sciences / Working Papers (4) RePEc:dgr:kubcen:200476 The collective model of household consumption : a nonparametric characterization (2004). Tilburg University, Center for Economic Research / Discussion Paper (5) RePEc:ecm:nasm04:283 welfare cost of business cycles when markets are incomplete (2004). Econometric Society / Econometric Society 2004 North American Summer Meetings (6) RePEc:hol:holodi:0428 Testable Restrictions of General Equilibrium Theory in Exchange Economies with Externalities (2004). Department of Economics, Royal Holloway University of London / Royal Holloway, University of London: Discussion Papers in Economics (7) RePEc:hol:holodi:0430 Global identification from the equilibrium manifold under incomplete markets (2004). Department of Economics, Royal Holloway University of London / Royal Holloway, University of London: Discussion Papers in Economics (8) RePEc:mse:wpsorb:b04116 Equilibria in production economies (2004). Université Panthéon-Sorbonne (Paris 1) / Cahiers de la Maison des Sciences Economiques (9) RePEc:mse:wpsorb:b04123 Existence of competitive equilibrium in a single-sector growth model with elastic labor (2004). Université Panthéon-Sorbonne (Paris 1) / Cahiers de la Maison des Sciences Economiques (10) RePEc:mse:wpsorb:v04056 Coping with imprecise information : a decision theoretic approach (2004). Université Panthéon-Sorbonne (Paris 1) / Cahiers de la Maison des Sciences Economiques (11) RePEc:nuf:econwp:0418 The aggregate weak axiom in a financial economy through dominant substitution effects (2004). Economics Group, Nuffield College, University of Oxford / Economics Papers (12) RePEc:upf:upfgen:785 Noise and Aggregation of Information in Large Markets (2004). Department of Economics and Business, Universitat Pompeu Fabra / Economics Working Papers Latest citations received in: 2003 (1) RePEc:bon:bonedp:bgse26_2003 Perfect Competition in a Bilateral Monopoly (2003). University of Bonn, Germany / Bonn Econ Discussion Papers (2) RePEc:icr:wpmath:13-2003 Ultramodular functions. (2003). ICER - International Centre for Economic Research / ICER Working Papers - Applied Mathematics Series (3) RePEc:nwu:cmsems:1383 Foundations of Markov-Perfect Industry Dynamics. Existence, Purification, and Multiplicity (2003). Northwestern University, Center for Mathematical Studies in Economics and Management Science / Discussion Papers (4) RePEc:sbs:wpsefe:2003fe08 Equilibrium Analysis, Banking and Financial Instability (2003). Oxford Financial Research Centre / OFRC Working Papers Series (5) RePEc:sbs:wpsefe:2003fe13 A Model to Analyse Financial Fragility (2003). Oxford Financial Research Centre / OFRC Working Papers Series (6) RePEc:wpa:wuwpma:0312006 A Unified Approach to Credit Crunches, Financial Instability, and Banking Crises (2003). EconWPA / Macroeconomics Latest citations received in: 2002 (1) RePEc:aub:autbar:554.02 Efficient Priority Rules (2002). Unitat de Fonaments de l'Anà lisi Econòmica (UAB) and Institut d'Anà lisi Econòmica (CSIC) / UFAE and IAE Working Papers (2) RePEc:dgr:kubcen:200247 Divestment, entrepreneurial incentives and the decision to go public (2002). Tilburg University, Center for Economic Research / Discussion Paper (3) RePEc:mlb:wpaper:830 THE AUSTRALIAN BOOK AUCTION RECORDS (2002). The University of Melbourne / Department of Economics - Working Papers Series Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |