|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
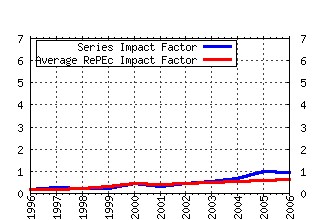
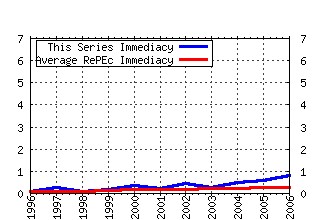
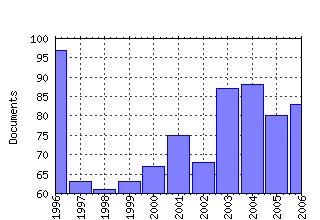
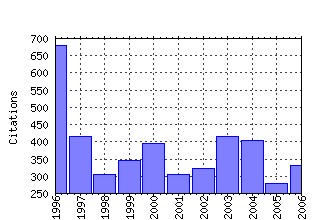
Games and Economic Behavior Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Recent citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:10:y:1995:i:1:p:122-142 Trust, Reciprocity, and Social History (1995). (2) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:10:y:1995:i:1:p:6-38 Quantal Response Equilibria for Normal Form Games (1995). (3) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:47:y:2004:i:2:p:268-298 A theory of sequential reciprocity (2004). (4) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:14:y:1996:i:1:p:124-143 Potential Games (1996). (5) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:54:y:2006:i:2:p:293-315 A theory of reciprocity (2006). (6) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:7:y:1994:i:3:p:346-380 Preferences, Property Rights, and Anonymity in Bargaining Games (1994). (7) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:5:y:1993:i:3:p:387-424 The Statistical Mechanics of Strategic Interaction (1993). (8) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:1:y:1989:i:1:p:60-79 Psychological games and sequential rationality (1989). (9) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:6:y:1994:i:3:p:347-369 Fairness in Simple Bargaining Experiments (1994). (10) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:1:y:1989:i:4:p:327-360 Renegotiation in repeated games (1989). (11) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:2:y:1990:i:1:p:29-46 Endogenous timing in duopoly games: Stackelberg or cournot equilibria (1990). (12) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:10:y:1995:i:1:p:218-254 On Players Models of Other Players: Theory and Experimental Evidence (1995). (13) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:26:y:1999:i:2:p:286-336 A Theory of Endogenous Coalition Structures (1999). (14) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:14:y:1996:i:1:p:90-123 Sequential Formation of Coalitions in Games with Externalities and Fixed Payoff Division (1996). (15) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:16:y:1996:i:2:p:181-191 Altruism in Anonymous Dictator Games (1996). (16) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:46:y:2004:i:2:p:260-281 How to identify trust and reciprocity (2004). (17) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:10:y:1995:i:1:p:95-121 Anonymity versus Punishment in Ultimatum Bargaining (1995). (18) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:1:y:1989:i:2:p:170-190 Approximating common knowledge with common beliefs (1989). (19) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:38:y:2002:i:2:p:201-230 The Stability of Hedonic Coalition Structures (2002). (20) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:20:y:1997:i:2:p:201-237 Stable Coalition Structures with Externalities (1997). (21) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:5:y:1993:i:3:p:320-367 Learning Mixed Equilibria (1993). (22) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:30:y:2000:i:2:p:163-182 Measuring Beliefs in an Experimental Lost Wallet Game (2000). (23) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:1:y:1989:i:4:p:295-326 Collective dynamic consistency in repeated games (1989). (24) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:3:y:1991:i:1:p:82-100 Adaptive and sophisticated learning in normal form games (1991). (25) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:13:y:1996:i:1:p:100-110 Fairness in Ultimatum Games with Asymmetric Information and Asymmetric Payoffs (1996). (26) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:19:y:1997:i:1:p:46-76 Individual Learning in Normal Form Games: Some Laboratory Results (1997). (27) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:15:y:1996:i:2:p:132-148 Cournot Oligopoly and the Theory of Supermodular Games (1996). (28) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:44:y:2003:i:2:p:217-226 The strategic equivalence of rent-seeking, innovation, and patent-race games (2003). (29) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:28:y:1999:i:1:p:13-24 The Indirect Evolutionary Approach to Explaining Fair Allocations (1999). (30) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:9:y:1995:i:1:p:79-109 Social Norms and Random Matching Games (1995). (31) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:6:y:1994:i:3:p:445-468 A Laboratory Investigation of Multiperson Rationality and Presentation Effects (1994). (32) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:12:y:1996:i:2:p:187-218 Cooperation without Reputation: Experimental Evidence from Prisoners Dilemma Games (1996). (33) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:2:y:1990:i:4:p:378-394 Population monotonic allocation schemes for cooperative games with transferable utility (1990). (34) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:7:y:1994:i:1:p:62-91 Learning Behavior in an Experimental Matching Pennies Game (1994). (35) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:59:y:2007:i:1:p:17-45 A tractable model of reciprocity and fairness (2007). (36) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:5:y:1993:i:3:p:425-454 An Evolutionary Analysis of Backward and Forward Induction (1993). (37) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:42:y:2003:i:1:p:172-179 Risk taking in selection contests (2003). (38) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:34:y:2001:i:2:p:331-341 A Dynamic Model of Network Formation (2001). (39) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:41:y:2002:i:2:p:265-291 On the formation of interaction networks in social coordination games (2002). (40) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:5:y:1993:i:4:p:514-531 Meaning and Credibility in Cheap-Talk Games (1993). (41) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:20:y:1997:i:1:p:3-24 On the Interpretation of Decision Problems with Imperfect Recall (1997). (42) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:7:y:1994:i:2:p:295-300 The Set of Nash Equilibria of a Supermodular Game Is a Complete Lattice (1994). (43) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:13:y:1996:i:2:p:141-177 Path Dependence and Learning from Neighbors (1996). (44) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:11:y:1995:i:2:p:111-145 The Statistical Mechanics of Best-Response Strategy Revision (1995). (45) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:21:y:1997:i:1-2:p:40-55 Calibrated Learning and Correlated Equilibrium (1997). (46) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:52:y:2005:i:2:p:460-492 Modeling internal commitment mechanisms and self-control: A neuroeconomics approach to consumption-saving decisions (2005). (47) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:3:y:1991:i:4:p:467-486 Collusion in second price auctions with heterogeneous bidders (1991). (48) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:54:y:2006:i:1:p:1-24 Do non-strategic sanctions obey the law of demand? The demand for punishment in the voluntary contribution mechanism (2006). (49) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:34:y:2001:i:2:p:177-199 Minimum-Effort Coordination Games: Stochastic Potential and Logit Equilibrium (2001). (50) RePEc:eee:gamebe:v:54:y:2006:i:1:p:134-158 An experimental study of price dispersion (2006). Recent citations received in: | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 Recent citations received in: 2006 (1) RePEc:aea:aecrev:v:96:y:2006:i:3:p:602-629 An Efficient Dynamic Auction for Heterogeneous (2006). American Economic Review (2) RePEc:ags:aaea06:21276 Estimating Heterogeneous Primal Capacity and Capacity Utilization Measures in a Multi-Species Fishery (2006). American Agricultural Economics Association (New Name 2008: Agricultural and Applied Economics Association) / 2006 Annual meeting, July 23-26, Long Be (3) RePEc:aub:autbar:664.06 (When) Would I Lie To You? Comment on ?Deception: The Role of Consequences? (2006). Unitat de Fonaments de l'Anà lisi Econòmica (UAB) and Institut d'Anà lisi Econòmica (CSIC) / UFAE and IAE Working Papers (4) RePEc:aub:autbar:668.06 Weighted Approval Voting (2006). Unitat de Fonaments de l'Anà lisi Econòmica (UAB) and Institut d'Anà lisi Econòmica (CSIC) / UFAE and IAE Working Papers (5) RePEc:bbk:bbkefp:0614 Links and Architecture in Village Networks (2006). Birkbeck, School of Economics, Mathematics & Statistics / Birkbeck Working Papers in Economics and Finance (6) RePEc:cdx:dpaper:2006-11 Demand Bargaining and Proportional Payoffs in Legislatures (2006). The Centre for Decision Research and Experimental Economics, School of Economics, University of Nottingham / Discussion Papers (7) RePEc:cdx:dpaper:2006-14 An Experiment on Spatial Price Competition (2006). The Centre for Decision Research and Experimental Economics, School of Economics, University of Nottingham / Discussion Papers (8) RePEc:cdx:dpaper:2006-21 Private-Collective Innovation and the Fragility of Knowledge Sharing (2006). The Centre for Decision Research and Experimental Economics, School of Economics, University of Nottingham / Discussion Papers (9) RePEc:cdx:dpaper:2006-22 Counterintuitive Number Effects in Experimental Oligopolies (2006). The Centre for Decision Research and Experimental Economics, School of Economics, University of Nottingham / Discussion Papers (10) RePEc:ces:ceswps:_1782 The Chopstick Auction: A Study of the Exposure Problem in Multi-Unit Auctions (2006). CESifo GmbH / CESifo Working Paper Series (11) RePEc:ces:ceswps:_1794 Institution Formation in Public Goods Games (2006). CESifo GmbH / CESifo Working Paper Series (12) RePEc:cir:cirwor:2006s-12 Who Gets the Last Word? An Experimental Study of the Effect of a Peer Review Process on the Expression of Social Norms (2006). CIRANO / CIRANO Working Papers (13) RePEc:cir:cirwor:2006s-30 A Simple Test of Learning Theory (2006). CIRANO / CIRANO Working Papers (14) RePEc:cla:levrem:321307000000000042 Pinocchios Pupil: Using Eyetracking and Pupil Dilation to Understand Truth-telling and Deception in Games (2006). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (15) RePEc:cla:levrem:321307000000000092 Moral Norms in a Partly Compliant Society (2006). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (16) RePEc:cla:levrem:321307000000000256 Level-k Auctions: Can a Non-Equilibrium Model of Strategic Thinking Explain the Winners Curse and Overbidding in Private-Value Auctions? (2006). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (17) RePEc:cla:levrem:321307000000000457 The Canonical Type Space for Interdependent Preferences (2006). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (18) RePEc:cla:levrem:321307000000000547 Learning in Games with Unstable Equilibria (2006). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (19) RePEc:cla:levrem:321307000000000724 A Simple Test of Learning Theory (2006). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (20) RePEc:clt:sswopa:1259 The compromise game: Two-sided adverse selection in the laboratory (2006). California Institute of Technology, Division of the Humanities and Social Sciences / Working Papers (21) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5532 Competition and Well-Being (2006). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (22) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5538 On the Evolution of Market Institutions: The Platform Design Paradox (2006). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (23) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5789 Homo Reciprocans: Survey Evidence on Prevalence, Behaviour and Success (2006). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (24) RePEc:cra:wpaper:2006-16 Rewarding Honest Taxpayers? Evidence on the Impact of Rewards from Field Experiments (2006). Center for Research in Economics, Management and the Arts (CREMA) / CREMA Working Paper Series (25) RePEc:cwl:cwldpp:1554 Caller Number Five: Timing Games that Morph from One Form to Another (2006). Cowles Foundation, Yale University / Cowles Foundation Discussion Papers (26) RePEc:dgr:umamet:2006003 On the Evolution of Trading Institutions: The Platform Design Paradox (2006). Maastricht : METEOR, Maastricht Research School of Economics of Technology and Organization / Research Memoranda (27) RePEc:dgr:umamet:2006029 Institution Formation in Public Goods Games (2006). Maastricht : METEOR, Maastricht Research School of Economics of Technology and Organization / Research Memoranda (28) RePEc:dgr:umamet:2006038 Weighted Approval Voting (2006). Maastricht : METEOR, Maastricht Research School of Economics of Technology and Organization / Research Memoranda (29) RePEc:dgr:uvatin:20060037 Gift Exchange and the Separation of Ownership and Control (2006). Tinbergen Institute / Tinbergen Institute Discussion Papers (30) RePEc:dgr:uvatin:20060104 Does Stake Size matter for Cooperation and Punishment? (2006). Tinbergen Institute / Tinbergen Institute Discussion Papers (31) RePEc:edn:esedps:153 A Simple Test of Learning Theory? (2006). Edinburgh School of Economics, University of Edinburgh / ESE Discussion Papers (32) RePEc:esi:discus:2006-01 Are preferences complete? An experimental measurement of indecisiveness under risk (2006). Max Planck Institute of Economics, Strategic Interaction Group / Discussion Papers on Strategic Interaction (33) RePEc:fem:femwpa:2006.80 Inequity Aversion May Increase Inequity (2006). Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei / Working Papers (34) RePEc:gat:wpaper:0604 Punishment, Inequality and Emotions (2006). Groupe d'Analyse et de Théorie Economique (GATE), Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS), Université Lyon 2, Ecole Normale Supérieure / W (35) RePEc:hal:journl:halshs-00142866_v1 Punishment, Inequality and Emotions (2006). HAL / Post-Print (36) RePEc:hal:journl:halshs-00175045_v1 Punishment, Inequality and Emotions (2006). HAL / Post-Print (37) RePEc:hhs:gunwpe:0219 Bridging the Great Divide in South Africa: Inequality and Punishment in the Provision of Public Goods (2006). Göteborg University, Department of Economics / Working Papers in Economics (38) RePEc:hhs:gunwpe:0221 A Note on the Risk Behavior and Death of Homo Economicus (2006). Göteborg University, Department of Economics / Working Papers in Economics (39) RePEc:hhs:hastef:0629 Evolutionary dynamics may eliminate all strategies used in correlated equilibrium (2006). Stockholm School of Economics / Working Paper Series in Economics and Finance (40) RePEc:hhs:hastef:0634 Organizational Structure as the Channeling of Boundedly Rational Pre-play Communication (2006). Stockholm School of Economics / Working Paper Series in Economics and Finance (41) RePEc:hhs:ratioi:0109 Reciprocity and Payment Schemes: When Equality Is Unfair (2006). The Ratio Institute / Ratio Working Papers (42) RePEc:hit:hituec:a473 Axiomatic bargaining theory on opportunity assignments (2006). Institute of Economic Research, Hitotsubashi University / Discussion Paper Series (43) RePEc:inu:caeprp:2006005 The Effect of Rewards and Sanctions in Provision of Public Goods (2006). Center for Applied Economics and Policy Research, Economics Department, Indiana University Bloomington / Caepr Working Papers (44) RePEc:ivi:wpasad:2006-24 AN EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF CONDITIONAL COOPERATION (2006). Instituto Valenciano de Investigaciones Económicas, S.A. (Ivie) / Working Papers. Serie AD (45) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2119 Punishment, Inequality and Emotions (2006). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (46) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2205 Homo Reciprocans: Survey Evidence on Prevalence, Behavior and Success (2006). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (47) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2288 Institution Formation in Public Goods Games (2006). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (48) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2500 Reciprocity and Payment Schemes: When Equality Is Unfair (2006). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (49) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:9:y:2006:i:3:p:193-208 Decomposing trust and trustworthiness (2006). Experimental Economics (50) RePEc:kud:kuiedp:0608 Social Ties and Coordination on Negative Reciprocity: The Role of Affect (2006). University of Copenhagen. Department of Economics (formerly Institute of Economics) / Discussion Papers (51) RePEc:lsu:lsuwpp:2006-05 Existence of Nash Networks in One-Way Flow Models (2006). Department of Economics, Louisiana State University / Departmental Working Papers (52) RePEc:lsu:lsuwpp:2006-18 Heterogeneity in Nash Networks (2006). Department of Economics, Louisiana State University / Departmental Working Papers (53) RePEc:max:cprwps:86 Estimating Heterogeneous Capacity and Capacity Utilization in a Multi-Species Fishery (2006). Center for Policy Research, Maxwell School, Syracuse University / Center for Policy Research Working Papers (54) RePEc:mcl:mclwop:2006-11 WHO GETS THE LAST WORD? AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF A PEER REVIEW PROCESS ON THE EXPRESSION OF SOCIAL NORMS (2006). McGill University, Department of Economics / Departmental Working Papers (55) RePEc:mse:wpsorb:bla06063 Group and individual risk preferences : a lottery-choice experiment. (2006). Université Panthéon-Sorbonne (Paris 1) / Cahiers de la Maison des Sciences Economiques (56) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:12588 Optimal Inequality/Optimal Incentives: Evidence from a Tournament (2006). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (57) RePEc:pse:psecon:2006-38 The strategy structure of some coalition formation games (2006). PSE (Ecole normale supérieure) / PSE Working Papers (58) RePEc:pur:prukra:1181 A Trackable Model of Reciprocity and Fairness. (2006). Purdue University, Department of Economics / Purdue University Economics Working Papers (59) RePEc:pur:prukra:1188 Peer Punishment in Teams: Emotional or Strategic Choice? (2006). Purdue University, Department of Economics / Purdue University Economics Working Papers (60) RePEc:scp:wpaper:06-60 The Compromise Game: Two-sided Adverse Selection in the Laboratory (2006). Institute of Economic Policy Research (IEPR) / IEPR Working Papers (61) RePEc:sef:csefwp:169 Are Disadvantaged Bidders Doomed in Ascending Auctions? (2006). Centre for Studies in Economics and Finance (CSEF), University of Salerno, Italy / CSEF Working Papers (62) RePEc:siu:wpaper:10-2006 Expectations, Animal Spirits, and Evolutionary Dynamics (2006). Singapore Management University, School of Economics / Working Papers (63) RePEc:spr:jeicoo:v:1:y:2006:i:2:p:147-169 Can boundedly rational sellers learn to play Nash? (2006). Journal of Economic Interaction and Coordination (64) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:35:y:2006:i:1:p:129-150 Naive audience and communication bias (2006). International Journal of Game Theory (65) RePEc:use:tkiwps:0611 Social Exchange and Common Agency in Organizations (2006). Utrecht School of Economics / Working Papers (66) RePEc:yca:wpaper:2006_7 Auctions with Almost Homogeneous Bidders (2006). York University, Department of Economics / Working Papers (67) RePEc:zur:iewwpx:288 Environmental Morale and Motivation (2006). Institute for Empirical Research in Economics - IEW / IEW - Working Papers Recent citations received in: 2005 (1) RePEc:ads:wpaper:0050 Information Transmission in Coalitional Voting Games (2005). Institute for Advanced Study, School of Social Science / Economics Working Papers (2) RePEc:ads:wpaper:0059 Minorities and Storable Votes (2005). Institute for Advanced Study, School of Social Science / Economics Working Papers (3) RePEc:ads:wpaper:0060 A Simple Scheme to Improve the Efficiency of Referenda (2005). Institute for Advanced Study, School of Social Science / Economics Working Papers (4) RePEc:aea:aecrev:v:95:y:2005:i:2:p:340-345 The Neuroeconomics of Mind Reading and Empathy (2005). American Economic Review (5) RePEc:bon:bonedp:bgse33_2005 Stationary Concepts for Experimental 2x2 Games (2005). University of Bonn, Germany / Bonn Econ Discussion Papers (6) RePEc:bro:econwp:2005-01 Information Transmission in Coalitional Voting Games (2005). Brown University, Department of Economics / Working Papers (7) RePEc:bro:econwp:2005-02 An Axiomatization of the Inner Core Using Appropriate Reduced Games (2005). Brown University, Department of Economics / Working Papers (8) RePEc:cdx:dpaper:2005-08 Enlargement and the Balance of Power: an Experimental Study (2005). The Centre for Decision Research and Experimental Economics, School of Economics, University of Nottingham / Discussion Papers (9) RePEc:ces:ceswps:_1583 Minorities and Storable Votes (2005). CESifo GmbH / CESifo Working Paper Series (10) RePEc:cla:levarc:618897000000000876 A Dual Self Model of Impulse Control (2005). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Working Paper Archive (11) RePEc:cla:levarc:784828000000000034 Willpower and the Optimal Control of Visceral Urges (2005). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Working Paper Archive (12) RePEc:cla:levrem:122247000000000914 The Swing Voters Curse in the Laboratory (2005). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (13) RePEc:cla:levrem:172782000000000073 The Brain as a Hierarchical Organization (2005). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (14) RePEc:cla:levrem:784828000000000205 The Brain as a Hierarchical Organization (2005). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (15) RePEc:cla:levrem:784828000000000476 Modeling the Psychology of Consumer and Firm Behavior with Behavioral Economics (2005). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (16) RePEc:cla:levrem:784828000000000539 Discussion of BEHAVIORAL ECONOMICS (2005). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (17) RePEc:cla:levrem:784828000000000609 Learning in Games with Unstable Equilibria (2005). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (18) RePEc:clu:wpaper:0506-02 Minorities and storable votes (2005). Columbia University, Department of Economics / Discussion Papers (19) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5278 Minorities and Storable Votes (2005). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (20) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5291 Efficiency, Equity and Timing in Voting Mechanisms (2005). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (21) RePEc:cte:werepe:we055726 INFORMATION TRANSMISSION IN COALITIONAL VOTING GAMES (2005). Universidad Carlos III, Departamento de Economía / Economics Working Papers (22) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005036 Networks of Manufacturers and Retailers (2005). Université catholique de Louvain, Département des Sciences Economiques / Université catholique de Louvain, Département des Sciences Economiques Workin (23) RePEc:cwl:cwldpp:1479r Coordination Failure in Repeated Games with Almost-Public Monitoring (2005). Cowles Foundation, Yale University / Cowles Foundation Discussion Papers (24) RePEc:cwl:cwldpp:1503 Aggregation of Expert Opinions (2005). Cowles Foundation, Yale University / Cowles Foundation Discussion Papers (25) RePEc:dgr:kubcen:2005117 Learning to be prepared (2005). Tilburg University, Center for Economic Research / Discussion Paper (26) RePEc:dgr:kubcen:200553 An axiomatization of minimal curb sets (2005). Tilburg University, Center for Economic Research / Discussion Paper (27) RePEc:dgr:kubcen:200584 Stable networks and convex payoffs (2005). Tilburg University, Center for Economic Research / Discussion Paper (28) RePEc:dgr:kubcen:200594 The cutting power of preparation (2005). Tilburg University, Center for Economic Research / Discussion Paper (29) RePEc:dgr:umamet:2005018 The Coordinate-Wise Core for Multiple-Type Housing Markets is Second-Best Incentive Compatible (2005). Maastricht : METEOR, Maastricht Research School of Economics of Technology and Organization / Research Memoranda (30) RePEc:dgr:umamet:2005053 A Reason for Sophisticated Investors not to seize Arbitrage Opportunities in Markets without Frictions (2005). Maastricht : METEOR, Maastricht Research School of Economics of Technology and Organization / Research Memoranda (31) RePEc:ecl:prirpe:03-13-2006 The Swing Voters Curse in the Laboratory (2005). Princeton University, Research Program in Political Economy / Papers (32) RePEc:edn:esedps:135 Learning in Games with Unstable Equilibria (2005). Edinburgh School of Economics, University of Edinburgh / ESE Discussion Papers (33) RePEc:emo:wp2003:0507 Temptation and Self-Control: Some Evidence from the Consumer Expenditure Survey (2005). Department of Economics, Emory University (Atlanta) / Emory Economics (34) RePEc:gue:guelph:2005-7 Competitive Burnout: Theory and Experimental Evidence (2005). University of Guelph, Department of Economics / Working Papers (35) RePEc:hhs:hastef:0583 The cutting power of preparation (2005). Stockholm School of Economics / Working Paper Series in Economics and Finance (36) RePEc:hhs:hastef:0589 An axiomatization of minimal curb sets (2005). Stockholm School of Economics / Working Paper Series in Economics and Finance (37) RePEc:hhs:hastef:0590 Learning to be prepared (2005). Stockholm School of Economics / Working Paper Series in Economics and Finance (38) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1890 Affect as a Source of Motivation in the Workplace: A New Model of Labor Supply, and New Field Evidence on Income Targeting and the Goal Gradient (2005). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (39) RePEc:lsu:lsuwpp:2005-13 Stable Networks and Convex Payoffs (2005). Department of Economics, Louisiana State University / Departmental Working Papers (40) RePEc:pen:papers:05-014 Coordination Failure in Repeated Games with Almost-Public Monitoring (2005). Penn Institute for Economic Research, Department of Economics, University of Pennsylvania / PIER Working Paper Archive (41) RePEc:pen:papers:05-016 Aggregation of Expert Opinions (2005). Penn Institute for Economic Research, Department of Economics, University of Pennsylvania / PIER Working Paper Archive (42) RePEc:wpa:wuwpex:0507001 Enlargement and the Balance of Power: An Experimental Study (2005). EconWPA / Experimental (43) RePEc:wpa:wuwpex:0511006 Auctions with Anticipated Regret (2005). EconWPA / Experimental (44) RePEc:wpa:wuwpga:0503010 Dynamic Behavior in Minimum Effort Coordination Games - Some Theory of Group Size and Inter-Group Competition as Coordination Devices (2005). EconWPA / Game Theory and Information (45) RePEc:wpa:wuwpmi:0407005 Rationalizing Boundedly Rational Choice: Sequential Rationalizability and Rational Shortlist Methods. (2005). EconWPA / Microeconomics (46) RePEc:wpa:wuwpmi:0510014 Efficient Egalitarian Equivalent Allocations over a Single Good (2005). EconWPA / Microeconomics (47) RePEc:xrs:sfbmaa:05-02 A Network Experiment in Continuous Time: (2005). Sonderforschungsbereich 504, University of Mannheim / Sonderforschungsbereich 504 Publications Recent citations received in: 2004 (1) RePEc:aea:aecrev:v:94:y:2004:i:3:p:484-498 Distinguishing Informational Cascades from Herd Behavior in the Laboratory (2004). American Economic Review (2) RePEc:aea:aecrev:v:94:y:2004:i:4:p:857-869 Inequality Aversion, Efficiency, and Maximin Preferences in Simple Distribution Experiments (2004). American Economic Review (3) RePEc:aub:autbar:634.04 An Ordinal Shapley Value for Economic Environments (Revised Version) (2004). Unitat de Fonaments de l'Anà lisi Econòmica (UAB) and Institut d'Anà lisi Econòmica (CSIC) / UFAE and IAE Working Papers (4) RePEc:boc:bocoec:620 Pairwise Kidney Exchange (2004). Boston College Department of Economics / Boston College Working Papers in Economics (5) RePEc:bri:cmpowp:04/108 Efficient Contracts for Digital Content (2004). Department of Economics, University of Bristol, UK / The Centre for Market and Public Organisation (6) RePEc:cej:primer:v:2:y:2004:i:1:p:189-212 Gradual Nash bargaining with endogenous agenda. A path-dependent model (2004). Colombian Economic Journal (7) RePEc:cla:levrem:122247000000000153 Self-Correcting Information Cascades (2004). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (8) RePEc:cla:levrem:122247000000000236 Stated Beliefs and Play in Normal Form Games (2004). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (9) RePEc:cla:levrem:122247000000000350 Pairwise Kidney Exchange (2004). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (10) RePEc:cla:levrem:122247000000000750 Incentive Compatibility in Multi-unit Auctions (2004). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (11) RePEc:cla:uclatw:121473000000000021 Multidimensional Private Value Auctions (2004). UCLA Department of Economics / Theory workshop papers (12) RePEc:dgr:kubcen:2004111 Enemies and friends in hedonic games : individual deviations, stability and manipulation (2004). Tilburg University, Center for Economic Research / Discussion Paper (13) RePEc:dgr:kubcen:2004114 Symmetric convex games and stable structures (2004). Tilburg University, Center for Economic Research / Discussion Paper (14) RePEc:dgr:kubcen:20045 Simple priorities and core stability in hedonic games (2004). Tilburg University, Center for Economic Research / Discussion Paper (15) RePEc:dgr:kubcen:200453 Obligation rules for minimum cost spanning tree situations and their monotonicity properties (2004). Tilburg University, Center for Economic Research / Discussion Paper (16) RePEc:dgr:kubcen:200457 On representative social capital (2004). Tilburg University, Center for Economic Research / Discussion Paper (17) RePEc:dgr:umamet:2004018 The minimal dominant set is a non-empty core-extension (2004). Maastricht : METEOR, Maastricht Research School of Economics of Technology and Organization / Research Memoranda (18) RePEc:dgr:uvatin:20040100 Gift Exchange in a Multi-worker Firm (2004). Tinbergen Institute / Tinbergen Institute Discussion Papers (19) RePEc:ebl:ecbull:v:3:y:2004:i:45:p:1-11 Matching Markets: the Particular Case of Couples (2004). Economics Bulletin (20) RePEc:ecm:feam04:472 A Unified Approach to Information, Knowledge, and Stability (2004). Econometric Society / Econometric Society 2004 Far Eastern Meetings (21) RePEc:ecm:nasm04:135 Simple Priorities and Core Stability in Hedonic Games (2004). Econometric Society / Econometric Society 2004 North American Summer Meetings (22) RePEc:esa:iesawp:0407 How do subjects assess the Social Trade-off invilved in the Prisoners Dilemma? (2004). Institute for Social Syudies of Andalusia - Higher Council for Scientific Research / IESA Working Papers Series (23) RePEc:esi:discus:2004-01 Age and the development of trust and reciprocity (2004). Max Planck Institute of Economics, Strategic Interaction Group / Discussion Papers on Strategic Interaction (24) RePEc:esi:discus:2004-36 Express Yourself: The Price of Fairness in a Simple Distribution Game (2004). Max Planck Institute of Economics, Strategic Interaction Group / Discussion Papers on Strategic Interaction (25) RePEc:feb:artefa:0039 The Hidden Costs and Returns of Incentives - Trust and Trustworthiness among CEOs (2004). The Field Experiments Website / Artefactual Field Experiments (26) RePEc:fem:femwpa:2004.51 Simple Priorities and Core Stability in Hedonic Games (2004). Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei / Working Papers (27) RePEc:fem:femwpa:2004.97 Defining Rules in Cost Spanning Tree Problems Through the Canonical Form (2004). Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei / Working Papers (28) RePEc:has:discpr:0421 The minimal dominant set is a non-empty core-extension (2004). Institute of Economics, Hungarian Academy of Sciences / IEHAS Discussion Papers (29) RePEc:hhs:aareco:2004_016 Can Information Backfire? - Experimental Evidence from the Ultimatum Game (2004). Aarhus School of Business, Department of Economics / Working Papers (30) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1145 On Representative Social Capital (2004). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (31) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1203 Distrust - The Hidden Cost of Control (2004). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (32) RePEc:kyo:wpaper:582 Trade with Heterogeneous Multiple Priors (2004). Kyoto University, Institute of Economic Research / Working Papers (33) RePEc:lau:crdeep:04.15 Verified Trust: Reciprocity, Altruism, and Noise in Trust Games (2004). Université de Lausanne, Ecole des HEC, DEEP / Cahiers de Recherches Economiques du Département d'Econométrie et d'Economie politique (DEEP) (34) RePEc:mdl:mdlpap:0412 Who is Post-Walrasian Man? (2004). Middlebury College, Department of Economics / Middlebury College Working Paper Series (35) RePEc:mpg:wpaper:2004_14 Optimal Income Taxation, Public-Goods Provision and Public-Sector Pricing: A Contribution to the Foundations of Public Economics (2004). Max Planck Institute for Reserach on Collective Goods / Working Paper Series of the Max Planck Institute for Reserach on Collective Goods (36) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:10698 Pairwise Kidney Exchange (2004). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (37) RePEc:trf:wpaper:11 Fairness and the Optimal Allocation of Ownership Rights (2004). SFB/TR 15 Governance and the Efficiency of Economic Systems, University of Mannheim / Discussion Papers (38) RePEc:ubc:pmicro:robson-04-02-12-12-44-46 Reinterpreting Mixed Strategy Equilibria: A Unification of the Classical and Bayesian Views (2004). Microeconomics.ca Website / Micro Theory Working Papers (39) RePEc:uca:ucapdv:41 Transfers and Altruistic Punishments in Third Party Punishment Game Experiments. (2004). Department of Public Policy and Public Choice - POLIS / P.O.L.I.S. department's Working Papers (40) RePEc:upf:upfgen:788 Global Nash Convergence of Foster and Youngs Regret Testing (2004). Department of Economics and Business, Universitat Pompeu Fabra / Economics Working Papers (41) RePEc:wpa:wuwpex:0406001 A Tractable Model of Reciprocity and Fairness (2004). EconWPA / Experimental (42) RePEc:wpa:wuwpga:0402004 Defining rules in cost spanning tree problems through the canonical form (2004). EconWPA / Game Theory and Information (43) RePEc:wpa:wuwpga:0403001 Realizing efficient outcomes in cost spanning problems (2004). EconWPA / Game Theory and Information (44) RePEc:wpa:wuwpga:0405001 Additivity in cost spanning tree problems (2004). EconWPA / Game Theory and Information (45) RePEc:xrs:sfbmaa:04-42 Optimal Income Taxation, Public-Goods Provision (2004). Sonderforschungsbereich 504, University of Mannheim / Sonderforschungsbereich 504 Publications Recent citations received in: 2003 (1) RePEc:ads:wpaper:0032 Rejecting Small Gambles Under Expected Utility (2003). Institute for Advanced Study, School of Social Science / Economics Working Papers (2) RePEc:att:wimass:200320 Evolution in games with randomly disturbed payoffs (2003). Wisconsin Madison - Social Systems / Working papers (3) RePEc:bep:theadv:v:3:y:2003:i:1:p:1073-1073 Rationalization and Incomplete Information (2003). Advances in Theoretical Economics (4) RePEc:bol:bodewp:495 Dynamic R&D with Spillovers: Competition vs Cooperation (2003). Dipartimento Scienze Economiche, Università di Bologna / Working Papers (5) RePEc:bon:bonedp:bgse6_2003 Splitting Leagues (2003). University of Bonn, Germany / Bonn Econ Discussion Papers (6) RePEc:cir:cirwor:2003s-32 Testing Equilibrium Behaviour At First-Price, Sealed-Bid Auctions With Discrete Bid Increments (2003). CIRANO / CIRANO Working Papers (7) RePEc:cla:levarc:666156000000000374 A Theory of Stability in Many-to-many Matching Markets (2003). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Working Paper Archive (8) RePEc:cla:uclatw:505798000000000042 Excess Payoff Dynamics, Potential Dynamics, and Stable Games (2003). UCLA Department of Economics / Theory workshop papers (9) RePEc:clt:sswopa:1185 A Theory of Stability in Many-to-Many Matching Markets (2003). California Institute of Technology, Division of the Humanities and Social Sciences / Working Papers (10) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:3784 Delay in Contests (2003). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (11) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:3884 Are we Better Off if our Politicians Have More Information? (2003). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (12) RePEc:cwl:cwldpp:1423 Multidimensional Private Value Auctions (2003). Cowles Foundation, Yale University / Cowles Foundation Discussion Papers (13) RePEc:dgr:uvatin:20030041 Hybrid R&D (2003). Tinbergen Institute / Tinbergen Institute Discussion Papers (14) RePEc:esx:essedp:563 Learning in Networks: a survey (2003). University of Essex, Department of Economics / Economics Discussion Papers (15) RePEc:esx:essedp:564 Hybrid R&D (2003). University of Essex, Department of Economics / Economics Discussion Papers (16) RePEc:got:cegedp:21 Easy Targets and the Timing of Conflict (2003). Center for Globalization and Europeanization of the Economy, University of Goettingen (Germany). / CeGE Discussion Papers (17) RePEc:hal:wpaper:hal-00242993_v1 Geometry, Correlated Equilibria and Zero-Sum Games (2003). HAL / Working Papers (18) RePEc:hhs:osloec:2003_005 The semantics of preference-based belief operators. (2003). Oslo University, Department of Economics / Memorandum (19) RePEc:huj:dispap:dp318 Dissolving a Common Value Partnership in a Repeated queto Game (2003). Center for Rationality and Interactive Decision Theory, Hebrew University, Jerusalem / Discussion Paper Series (20) RePEc:nwu:cmsems:1372 Foundations of Dominant Strategy Mechanisms (2003). Northwestern University, Center for Mathematical Studies in Economics and Management Science / Discussion Papers (21) RePEc:nwu:cmsems:1373 No-Regret with Bounded Computational Capacity (2003). Northwestern University, Center for Mathematical Studies in Economics and Management Science / Discussion Papers (22) RePEc:pen:papers:03-027 Core Convergence with Asymmetric Information (2003). Penn Institute for Economic Research, Department of Economics, University of Pennsylvania / PIER Working Paper Archive (23) RePEc:pur:prukra:1162 A Comment on âDavid and Goliath: An Analysis on Asymmetric Mixed-Strategy Games and Experimental Evidenceâ. (2003). Purdue University, Department of Economics / Purdue University Economics Working Papers (24) RePEc:wpa:wuwpga:0306002 Bargaining with commitments (2003). EconWPA / Game Theory and Information (25) RePEc:wpa:wuwpga:0311001 Stable Outcomes For Contract Choice Problems (2003). EconWPA / Game Theory and Information Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||