|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
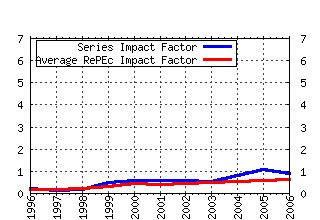
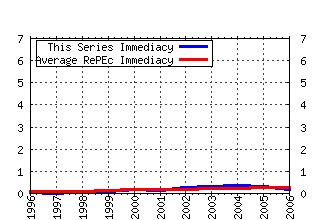
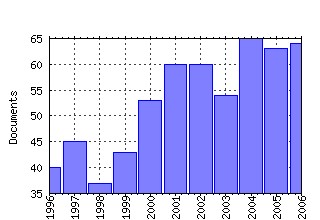
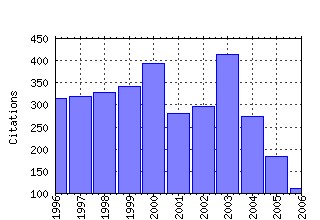
Journal of Health Economics Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Recent citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:16:y:1997:i:1:p:93-112 Income-related inequalities in health: some international comparisons (1997). (2) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:15:y:1996:i:1:p:67-85 New evidence on the relationship between income and health (1996). (3) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:23:y:2004:i:3:p:565-587 An economic analysis of adult obesity: results from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (2004). (4) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:18:y:1999:i:2:p:173-193 Health problems as determinants of retirement: Are self-rated measures endogenous? (1999). (5) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:24:y:2005:i:2:p:365-389 The lasting impact of childhood health and circumstance (2005). (6) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:22:y:2003:i:2:p:151-185 The price of innovation: new estimates of drug development costs (2003). (7) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:20:y:2001:i:4:p:461-494 Estimating log models: to transform or not to transform? (2001). (8) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:22:y:2003:i:1:p:61-87 Inequalities in self-reported health: validation of a new approach to measurement (2003). (9) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:22:y:2003:i:5:p:713-730 Exploring the health-wealth nexus (2003). (10) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:19:y:2000:i:5:p:553-583 Equity in the delivery of health care in Europe and the US (2000). (11) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:17:y:1998:i:4:p:427-474 The demand for cocaine by young adults: a rational addiction approach (1998). (12) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:10:y:1991:i:1:p:43-64 The effects of excise taxes and regulations on cigarette smoking (1991). (13) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:17:y:1998:i:5:p:537-555 Creaming, skimping and dumping: provider competition on the intensive and extensive margins1 (1998). (14) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:19:y:2000:i:6:p:855-876 The demand for private health care in the UK (2000). (15) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:9:y:1990:i:4:p:375-396 Optimal payment systems for health services (1990). (16) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:21:y:2002:i:4:p:601-625 The structure of demand for health care: latent class versus two-part models (2002). (17) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:14:y:1995:i:2:p:123-148 The demand for alcohol: The differential response to price (1995). (18) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:22:y:2003:i:3:p:477-504 Maternal employment and overweight children (2003). (19) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:17:y:1998:i:3:p:247-281 Much ado about two: reconsidering retransformation and the two-part model in health econometrics (1998). (20) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:10:y:1991:i:2:p:107-142 Cost of innovation in the pharmaceutical industry (1991). (21) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:17:y:1998:i:1:p:1-19 Contracting for health services when patient demand does not reflect quality (1998). (22) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:21:y:2002:i:4:p:643-658 The reliability of self-assessed health status (2002). (23) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:16:y:1997:i:1:p:33-64 Accounting for future costs in medical cost-effectiveness analysis (1997). (24) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:13:y:1994:i:2:p:213-230 The hazard of starting smoking: Estimates from a split population duration model (1994). (25) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:19:y:2000:i:3:p:403-420 Adaptation and scale of reference bias in self-assessments of quality of life (2000). (26) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:16:y:1997:i:1:p:1-31 Economic foundations of cost-effectiveness analysis (1997). (27) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:18:y:1999:i:1:p:1-29 An economic theory of cigarette addiction (1999). (28) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:15:y:1996:i:3:p:333-357 Quality of health care, survival and health outcomes in Ghana (1996). (29) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:5:y:1986:i:1:p:1-30 Measurement of health state utilities for economic appraisal : A review (1986). (30) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:20:y:2001:i:3:p:423-440 Modeling the effects of health on economic growth (2001). (31) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:1:y:1982:i:2:p:121-145 The potential for using excise taxes to reduce smoking (1982). (32) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:13:y:1994:i:3:p:255-280 Measuring hospital efficiency with frontier cost functions (1994). (33) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:16:y:1997:i:2:p:207-229 Is health care really a luxury? (1997). (34) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:11:y:1992:i:2:p:173-181 The determinants and effects of health expenditure in developed countries (1992). (35) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:15:y:1996:i:4:p:435-454 Alcohol policies and highway vehicle fatalities (1996). (36) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:15:y:1996:i:2:p:209-231 Valuing health states: A comparison of methods (1996). (37) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:14:y:1995:i:5:p:583-603 Economic conditions and alcohol problems (1995). (38) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:22:y:2003:i:4:p:637-658 Good times make you sick (2003). (39) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:12:y:1993:i:4:p:431-457 Equity and equality in health and health care (1993). (40) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:12:y:1993:i:4:p:459-467 On the decision rules of cost-effectiveness analysis (1993). (41) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:11:y:1992:i:3:p:217-233 The effects of market structure and bargaining position on hospital prices (1992). (42) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:16:y:1997:i:5:p:543-562 Adverse selection and the purchase of Medigap insurance by the elderly (1997). (43) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:17:y:1998:i:1:p:53-68 Alcohol use and wages: New results from the national household survey on drug abuse (1998). (44) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:18:y:1999:i:3:p:263-290 Equity in the finance of health care: some further international comparisons1 (1999). (45) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:25:y:2006:i:4:p:621-649 Ill health and retirement in Britain: A panel data-based analysis (2006). (46) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:5:y:1986:i:3:p:195-233 The demand for health : Some new empirical evidence (1986). (47) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:7:y:1988:i:3:p:259-284 Competition among hospitals (1988). (48) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:23:y:2004:i:5:p:965-995 Socio-economic status, health and lifestyle (2004). (49) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:21:y:2002:i:2:p:271-292 The estimation of a preference-based measure of health from the SF-36 (2002). (50) RePEc:eee:jhecon:v:6:y:1987:i:2:p:109-127 Aggregate health care expenditures and national income : Is health care a luxury good? (1987). Recent citations received in: | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 Recent citations received in: 2006 (1) RePEc:ant:wpaper:2006027 Correcting the Concentration Index (2006). University of Antwerp, Faculty of Applied Economics / Working Papers (2) RePEc:ant:wpaper:2006029 Beyond the Health Concentration Index: An Atkinson Alternative for the Measurement of the Socioeconomic Inequality of Health (2006). University of Antwerp, Faculty of Applied Economics / Working Papers (3) RePEc:dgr:uvatin:20060033 Does Reporting Heterogeneity bias the Measurement of Health Disparities? (2006). Tinbergen Institute / Tinbergen Institute Discussion Papers (4) RePEc:dgr:uvatin:20060108 The Effect of Growth and Inequality in Incomes on Health Inequality: Theory and Empirical Evidence from the European Panel (2006). Tinbergen Institute / Tinbergen Institute Discussion Papers (5) RePEc:fip:fedhwp:wp-06-21 Mortality, mass-layoffs, and career outcomes: an analysis using administrative data (2006). Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago / Working Paper Series (6) RePEc:her:chewps:2006/14 Men?s preferences for treatment of early stage prostate cancer: Results from a discrete choice experiment, CHERE Working Paper 2006/14 (2006). CHERE, University of Technology, Sydney / Working Papers (7) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2006n24 Designing Choice Experiments with Many Attributes: An Application to Setting Priorities for Orthopaedic Waiting Lists (2006). Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research, The University of Melbourne / Melbourne Institute Working Paper Series (8) RePEc:kap:decono:v:154:y:2006:i:4:p:491-516 Drug Demand â Initiation, Continuation and Quitting (2006). De Economist (9) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:12504 The Effect of State Community Rating Regulations on Premiums and Coverage in the Individual Health Insurance Market (2006). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (10) RePEc:pra:mprapa:1800 Interaction of job disamenities, job satisfaction, and sickness absences: Evidence from a representative sample of Finnish workers (2006). University Library of Munich, Germany / MPRA Paper (11) RePEc:wly:hlthec:v:15:y:2006:i:12:p:1257-1259 The productivity of health care (2006). Health Economics Recent citations received in: 2005 (1) RePEc:aea:aecrev:v:95:y:2005:i:2:p:258-262 The 1918 Influenza Pandemic and Subsequent Health Outcomes: An Analysis of SIPP Data (2005). American Economic Review (2) RePEc:aea:aecrev:v:95:y:2005:i:2:p:267-272 Heavy Alcohol Use and the Commission of Nuisance Crime: Evidence from Underage Drunk Driving Laws (2005). American Economic Review (3) RePEc:auu:dpaper:496 Socio-Economic Status, Health Shocks, Life Satisfaction and Mortality: Evidence from an Increasing Mixed Proportional Hazard Model (2005). Centre for Economic Policy Research, RSSS, ANU / Discussion Papers (4) RePEc:hai:wpaper:200504 Business Cycles, Migration and Health (2005). University of Hawaii at Manoa, Department of Economics / Working Papers (5) RePEc:hai:wpaper:200513 Business Cycles, Migration and Health (2005). University of Hawaii at Manoa, Department of Economics / Working Papers (6) RePEc:hhs:osloec:2005_035 Earnings persistence across generations: Transmission through health? (2005). Oslo University, Department of Economics / Memorandum (7) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2005n19 The Productivity of Doctors in Australia: The Flat of the Curve and Beyond? (2005). Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research, The University of Melbourne / Melbourne Institute Working Paper Series (8) RePEc:ifs:cemmap:20/05 The effects of taxes and bans on passive smoking (2005). Centre for Microdata Methods and Practice, Institute for Fiscal Studies / CeMMAP working papers (9) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1488 Socio-Economic Status, Health Shocks, Life Satisfaction and Mortality: Evidence from an Increasing Mixed Proportional Hazard Model (2005). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (10) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1832 The Impact of Parental Income and Education on the Health of their Children (2005). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (11) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1864 From the Cradle to the Labor Market? The Effect of Birth Weight on Adult Outcomes (2005). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (12) RePEc:mcm:sedapp:144 The Health Behaviors of Immigrants and Native-born People in Canada (2005). McMaster University / Social and Economic Dimensions of an Aging Population Research Papers (13) RePEc:mhe:cherps:2005-11 Translational research in the area of inequalities in health related to obesity in Australia (2005). Monash University, Centre for Health Economics / Centre for Health Economics Research Papers (14) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:11109 Estimating the Impact of Medical Innovation: A Case Study of HIV Antiretroviral Treatments (2005). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (15) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:11395 Price and the Health Plan Choices of Retirees (2005). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (16) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:11567 Biology as Destiny? Short and Long-Run Determinants of Intergenerational Transmission of Birth Weight (2005). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (17) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:11677 Health Risk, Income, and Employment-Based Health Insurance (2005). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (18) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:11707 The Effects of Cardiac Specialty Hospitals on the Cost and Quality of Medical Care (2005). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (19) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:11796 From the Cradle to the Labor Market? The Effect of Birth Weight on Adult Outcomes (2005). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (20) RePEc:rwi:dpaper:0033 The Effect of Poverty on the Health of Newborn Children â Evidence from Germany (2005). Rheinisch-Westfälisches Institut für Wirtschaftsforschung / RWI Discussion Papers (21) RePEc:wpa:wuwpla:0505018 Unraveling the SES-Health Connection (2005). EconWPA / Labor and Demography Recent citations received in: 2004 (1) RePEc:cep:sticas:088 Social Mobility, Life Chances, and the Early Years (2004). Centre for Analysis of Social Exclusion, LSE / CASE Papers (2) RePEc:cns:cnscwp:200416 Mortality, Lifestyle and Socio-Economic Status (2004). Centre for North South Economic Research, University of Cagliari and Sassari, Sardinia / Working Paper CRENoS (3) RePEc:diw:diwwpp:dp452 Life Expectancy and Health Care Expenditures : A New Calculation for Germany Using the Costs of Dying (2004). DIW Berlin, German Institute for Economic Research / Discussion Papers of DIW Berlin (4) RePEc:gen:geneem:2004.03 A robust approach for skewed and heavy-tailed outcomes in the analysis of health care expenditures (2004). Département d'Econométrie, Université de Genève / Cahiers du Département d'Econométrie (5) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1346 The Evolution of Income-Related Health Inequalities in Switzerland over Time (2004). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (6) RePEc:jae:japmet:v:19:y:2004:i:4:p:473-503 The dynamics of health in the British Household Panel Survey (2004). Journal of Applied Econometrics (7) RePEc:mcm:qseprr:390 Exploring the Use of a Nonparametrically Generated Instrumental Variable in the Estimation of a Linear Parametric Equation (2004). McMaster University / Quantitative Studies in Economics and Population Research Reports (8) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:10691 Maternal Employment and Adolescent Development (2004). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (9) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:10948 Individual Behaviors and Substance Use: The Role of Price (2004). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (10) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:11007 Macroeconomic Conditions, Health and Mortality (2004). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (11) RePEc:pri:indrel:8 Cut to the Bone Hospital Takeovers and Nurse Employment Contracts (2004). Princeton University, Department of Economics, Industrial Relations Section. / Working Papers (12) RePEc:pri:indrel:864 Cut to the Bone? Hospital Takeovers and Nurse Employment Contracts (2004). Princeton University, Department of Economics, Industrial Relations Section. / Working Papers (13) RePEc:taf:applec:v:36:y:2004:i:19:p:2151-2159 Cigarettes and addiction information: simulating the demand effects of the tobacco industrys conspiracy of silence (2004). Applied Economics (14) RePEc:ube:dpvwib:dp0414 The evolution of income-related health inequalities in Switzerland over time (2004). Universitat Bern, Volkswirtschaftliches Institut / Diskussionsschriften (15) RePEc:uca:ucapdv:38 Rational Addiction to Cinema? A Dynamic Panel Analysis of European Countries. (2004). Department of Public Policy and Public Choice - POLIS / P.O.L.I.S. department's Working Papers (16) RePEc:van:wpaper:0314 The Normative Approach to the Measurement of Multidimensional Inequality (2004). Department of Economics, Vanderbilt University / Working Papers (17) RePEc:ver:wpaper:12 Behavioral Differences Between Public and Private Not-For-Profit Hospitals in the Italian National Health Service (2004). Università di Verona, Dipartimento di Scienze economiche / Working Papers (18) RePEc:wil:wileco:194 Do Maternal Investments in Human Capital Affect Childrens Academic Achievement? (2004). Department of Economics, Williams College / Department of Economics Working Papers (19) RePEc:wiw:wiwrsa:ersa04p230 Can income inequality contribute to understand inequalities in health? An empirical approach based on the European Community Household Panel (2004). European Regional Science Association / ERSA conference papers (20) RePEc:wly:hlthec:v:13:y:2004:i:7:p:609-628 Explaining the differences in income-related health inequalities across European countries (2004). Health Economics (21) RePEc:wpa:wuwphe:0411004 Early Childbirth, Health Inputs and Child Mortality: Recent Evidence from Bangladesh (2004). EconWPA / HEW (22) RePEc:wpa:wuwpla:0402004 Understanding the Effects of Sibling Composition on Child (2004). EconWPA / Labor and Demography Recent citations received in: 2003 (1) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:4088 Measuring Heterogeneity in the Returns to Education in Norway Using Educational Reforms (2003). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (2) RePEc:fip:fedhep:y:2003:i:qiii:p:30-48:n:v.27no.3 Economic perspectives on childhood obesity (2003). Economic Perspectives (3) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp815 Measuring Heterogeneity in the Returns to Education in Norway Using Educational Reforms (2003). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (4) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp931 Time, Money, Peers, and Parents: Some Data and Theories on Teenage Behavior (2003). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (5) RePEc:mcm:qseprr:387 Socioeconomic Influence on the Health of Older People: Estimates Based on Two Longitudinal Surveys (2003). McMaster University / Quantitative Studies in Economics and Population Research Reports (6) RePEc:mcm:sedapp:112 Socioeconomic Influence on the Health of Older People: Estimates Based on Two Longitudinal Surveys (2003). McMaster University / Social and Economic Dimensions of an Aging Population Research Papers (7) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:10035 Health and Wealth Accumulation: Evidence from Nineteenth-Century America (2003). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (8) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:10038 Market Size in Innovation: Theory and Evidence From the Pharmaceutical Industry (2003). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (9) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:10092 Health Insurance Coverage and the Macroeconomy (2003). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (10) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:10122 The Timing of Births: Is the Health of Infants Counter-Cyclical? (2003). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (11) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:9615 Productivity in Pharmaceutical Biotechnology R&D: The Role of Experience and Alliances (2003). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (12) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:9769 The Effect of Welfare Reform on Prenatal Care and Birth Weight (2003). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (13) RePEc:rif:dpaper:878 A Note on Impact of Hours Worked in Mortality in the OECD. (2003). The Research Institute of the Finnish Economy / Discussion Papers (14) RePEc:upf:upfgen:676 A Consistency Test of the Time Trade-Off (2003). Department of Economics and Business, Universitat Pompeu Fabra / Economics Working Papers (15) RePEc:upf:upfgen:711 Measurement and Explanation of Socioeconomic Inequality in Health with Longitudinal Data (2003). Department of Economics and Business, Universitat Pompeu Fabra / Economics Working Papers (16) RePEc:upf:upfses:676 A Consistency Test of the Time Trade-Off (2003). Department of Economics and Business, Universitat Pompeu Fabra / Working Papers, Research Center on Health and Economics (17) RePEc:upf:upfses:711 Measurement and Explanation of Socioeconomic Inequality in Health with Longitudinal Data (2003). Department of Economics and Business, Universitat Pompeu Fabra / Working Papers, Research Center on Health and Economics (18) RePEc:wly:hlthec:v:12:y:2003:i:10:p:873-877 The value of life: individual preferences and social choice. A comment to Magnus Johannesson (2003). Health Economics Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||