|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
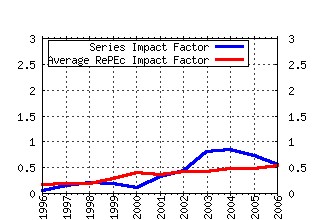
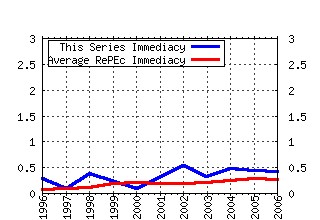
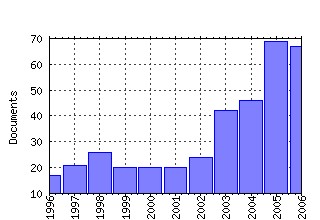
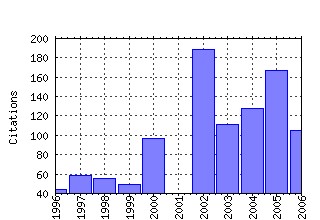
Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Recent citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2000-001 Learning about monetary policy rules (2002). (2) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2000-010 Perfecting the markets knowledge of monetary policy (2000). (3) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2002-023 Is inflation persistence intrinsic in industrial economies? (2003). (4) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2002-007 How well do monetary fundamentals forecast exchange rates? (2002). (5) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2005-030 An analysis of recent studies of the effect of foreign exchange intervention (2005). (6) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:1996-006 Is technical analysis in the foreign exchange market profitable? a genetic programming approach (1997). (7) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:1998-016 Learning and excess volatility (1998). (8) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2000-028 The practice of central bank intervention: looking under the hood (2000). (9) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:1995-013 Why do banks disappear? The determinants of U.S. bank failures and acquisitions (1995). (10) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:1999-001 Foreign direct investment in China: a spatial econometric study (1999). (11) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:1996-007 Monetary aggregation theory and statistical index numbers (1996). (12) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2005-018 Sticky-price models and the natural rate hypothesis (2005). (13) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2003-013 Did the Great Inflation occur despite policymaker commitment to a Taylor rule? (2004). (14) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2004-003 Tobins imperfect asset substitution in optimizing general equilibrium (2004). (15) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2005-035 Comovement: its not a puzzle (2005). (16) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2000-018 The temporal pattern of trading rule returns and central bank intervention: intervention does not generate technical trading rule profits (2000). (17) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:1997-012 How costly is sustained low inflation for the U.S. economy? (1998). (18) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2001-020 What happens when the technology growth trend changes?: transition dynamics, capital growth and the new economy (2001). (19) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2000-030 Determinacy, learnability, and monetary policy inertia (2003). (20) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2001-021 Can Markov switching models predict excess foreign exchange returns? (2006). (21) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:1997-018 Location determinants of new foreign-owned manufacturing plants (1997). (22) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:1999-008 Gender differences in self-employment (2004). (23) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2000-029 NAFTA and the changing pattern of state exports (2002). (24) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2000-002 The domestic adjusted monetary base (2000). (25) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:1999-009 What makes a region entrepreneurial? evidence from Britain (1999). (26) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2000-014 Changing technology trends, transition dynamics and growth accounting (2005). (27) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:1993-002 Explaining bank failures: deposit insurance, regulation, and efficiency (1993). (28) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2004-002 What explains the varying monetary response to technology shocks in G-7 countries? (2005). (29) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2003-021 The empirical failure of the expectations hypothesis of the term structure of bond yields (2005). (30) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:1989-006 On the frequency of large stock returns: putting booms and busts into perspective (1988). (31) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2004-016 Learning and structural change in macroeconomic data (2004). (32) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2004-001 The Great Inflation of the seventies: what really happened? (2004). (33) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:1999-003 The end of moderate inflation in three transition economies? (1999). (34) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2003-029 Size matters: asymmetric exchange rate pass-through at the industry level (2004). (35) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2004-011 Targeting vs. instrument rules for monetary policy (2004). (36) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:1991-004 Learning equilibria (1991). (37) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2003-010 The use of long-run restrictions for the identification of technology shocks (2003). (38) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2003-027 Inflation targeting: why it works and how to make it work better (2003). (39) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:1996-004 A revised measure of the St. Louis adjusted monetary base (1996). (40) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2005-034 International asset allocation under regime switching, skew and kurtosis preferences (2006). (41) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2001-001 Uncovering the risk-return relation in the stock market (2005). (42) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2003-017 A leisurely reading of the life-cycle consumption data (2006). (43) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:1995-006 On learning and the stability of cycles (1995). (44) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2002-014 Nonlinearity and the permanent effects of recessions (2003). (45) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2005-006 Optimal portfolio choice under regime switching, skew and kurtosis preferences (2005). (46) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:1997-003 New evidence on returns to scale and product mix among U.S. commercial banks (1997). (47) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:1997-010 Predictability in international asset returns: a reexamination (1999). (48) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:1995-016 Interbank netting agreement and the distribution of bank default risk (1995). (49) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2005-031 Identifying the effects of U.S. intervention on the levels of exchange rates (2006). (50) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2004-026 The monetary instrument matters (2005). Recent citations received in: | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 Recent citations received in: 2006 (1) RePEc:ces:ceswps:_1766 Japanese Foreign Exchange Intervention and the Yen/Dollar Exchange Rate: A Simultaneous Equations Approach Using Realized Volatility (2006). CESifo GmbH / CESifo Working Paper Series (2) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5614 Simulating Stock Returns Under Switching Regimes - A New Test of Market Efficiency (2006). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (3) RePEc:dul:wpaper:06-03rs Do interactions between political authorities and central banks influence FX interventions? Evidence from Japan (2006). Université libre de Bruxelles, Department of Applied Economics (DULBEA) / Working Papers DULBEA (4) RePEc:ebg:iesewp:d-0620 Estudio de la tasa de cambio dólar euro (2006). IESE Business School / IESE Research Papers (5) RePEc:ecb:ecbwps:20060667 The behaviour of the real exchange rate: evidence from regression quantiles. (2006). European Central Bank / Working Paper Series (6) RePEc:ehu:dfaeii:200508 The Relationship between Risk and Expected Return in Europe. (2006). University of the Basque Country - Department of Foundations of Economic Analysis II / DFAEII Working Papers (7) RePEc:eui:euiwps:eco2006/42 Strategic Wage Bargaining, Labor Market Volatility, and Persistence (2006). European University Institute / Economics Working Papers (8) RePEc:fip:fedfwp:2006-15 Time-varying U.S. inflation dynamics and the New-Keynesian Phillips Curve (2006). Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco / Working Paper Series (9) RePEc:fip:fedlrv:y:2006:i:nov:p:527-542:n:v.88no.6 The transition to electronic communications networks in the secondary treasury market (2006). Review (10) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2003-024 Contemporaneous threshold autoregressive models: estimation, testing and forecasting (2006). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (11) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2004-027 Aggregate idiosyncratic volatility in G7 countries (2006). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (12) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2005-025 Idiosyncratic volatility, economic fundamentals, and foreign exchange rates (2006). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (13) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2006-006 Investigating the intertemporal risk-return relation in international stock markets with the component GARCH model (2006). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (14) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2006-019 Understanding stock return predictability (2006). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (15) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2006-022 Predatory lending laws and the cost of credit (2006). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (16) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2006-036 The relation between time-series and cross-sectional effects of idiosyncratic variance on stock returns in G7 countries (2006). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (17) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2006-053 Regional business cycle phases in Japan (2006). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (18) RePEc:fip:fednsr:262 Price discovery in the foreign currency futures and spot market (2006). Federal Reserve Bank of New York / Staff Reports (19) RePEc:han:dpaper:dp-352 The Obstinate Passion of Foreign Exchange Professionals: Technical Analysis (2006). Universität Hannover, Wirtschaftswissenschaftliche Fakultät / Diskussionspapiere der Wirtschaftswissenschaftlichen Fakultät der Universität Hanno (20) RePEc:kud:epruwp:06-04 Evaluating Foreign Exchange Market Intervention: Self-Selection, Counterfactuals and Average Treatment Effects (2006). Economic Policy Research Unit (EPRU), University of Copenhagen. Department of Economics (formerly Institute of Economics) / EPRU Working Paper Series (21) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:12341 Consumption Over the Life Cycle: The Role of Annuities (2006). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (22) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:12605 Sticky Information in General Equilibrium (2006). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (23) RePEc:pra:mprapa:157 How Law Affects Lending (2006). University Library of Munich, Germany / MPRA Paper (24) RePEc:ste:nystbu:06-16 Institutions and Bank Behavior (2006). New York University, Leonard N. Stern School of Business, Department of Economics / Working Papers (25) RePEc:trf:wpaper:182 Acquisition versus greenfield: The impact of the mode of foreign bank entry on information and bank lending rates (2006). SFB/TR 15 Governance and the Efficiency of Economic Systems, University of Mannheim / Discussion Papers (26) RePEc:uct:uconnp:2006-19 Interbank Markets under Currency Boards (2006). University of Connecticut, Department of Economics / Working papers (27) RePEc:wrk:warwec:769 The Obstinate Passion of Foreign Exchange Professionals : Technical Analysis (2006). University of Warwick, Department of Economics / The Warwick Economics Research Paper Series (TWERPS) (28) RePEc:zbw:bubdp1:5170 How good are dynamic factor models at forecasting output and inflation? A meta-analytic approach (2006). Deutsche Bundesbank, Research Centre / Discussion Paper Series 1: Economic Studies Recent citations received in: 2005 (1) RePEc:boc:bocoec:607 Changes in the Federal Reserveâs Inflation Target: Causes and Consequences (2005). Boston College Department of Economics / Boston College Working Papers in Economics (2) RePEc:ces:ceswps:_1520 The Impact of FX Central Bank Intervention in a Noise Trading Framework (2005). CESifo GmbH / CESifo Working Paper Series (3) RePEc:cfs:cfswop:wp200522 Stock Returns and Expected Business Conditions: Half a Century of Direct Evidence (2005). Center for Financial Studies / CFS Working Paper Series (4) RePEc:cnb:wpaper:2005/07 Foreign Exchange Interventions and Interest Rate Policy in the Czech Republic: Hand in Glove? (2005). Czech National Bank, Research Department / Working Papers (5) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5384 Real Business Cycle Models: Past, Present and Future (2005). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (6) RePEc:dul:wpaper:05-09rs Why do central banks intervene secretly? Preliminary evidence from the Bank of Japan (2005). Université libre de Bruxelles, Department of Applied Economics (DULBEA) / Working Papers DULBEA (7) RePEc:fam:rpseri:rp132 Conditional Asset Allocation under Non-Normality: How Costly is the Mean-Variance Criterion? (2005). International Center for Financial Asset Management and Engineering / FAME Research Paper Series (8) RePEc:fip:fedlrd:y:2005:i:nov:p:3-16:n:v.1no.1 The 2001 recession and the states of the Eighth Federal Reserve District (2005). Regional Economic Development (9) RePEc:fip:fedlrv:y:2005:i:mar:p:93-101:n:v.87no.2,pt.1 The FOMC: preferences, voting, and consensus (2005). Review (10) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2003-028 Idiosyncratic volatility, stock market volatility, and expected stock returns (2005). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (11) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2005-005 Pessimistic beliefs under rational learning: quantitative implications for the equity premium puzzle (2005). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (12) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2005-011 High equity premia and crash fears. Rational foundations (2005). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (13) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2005-053 The 2001 recession and the states of the Eighth Federal Reserve District (2005). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (14) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2005-054 No smoking at the slot machines: the effect of a smoke-free law on Delaware gaming revenues (2005). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (15) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2005-056 Are the dynamic linkages between the macroeconomy and asset prices time-varying? (2005). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (16) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2005-061 Regional disparities in the spatial correlation of state income growth (2005). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (17) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2005-062 Recent developments in monetary macroeconomics and U.S. dollar policy (2005). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (18) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2005-075 Small caps in international equity portfolios: the effects of variance risk (2005). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (19) RePEc:fir:econom:wp2005_15 The Effect of Seasonal Adjustment on the Properties of Business Cycle Regimes (2005). Universita' degli Studi di Firenze, Dipartimento di Statistica G. Parenti / Econometrics Working Papers Archive (20) RePEc:kud:epruwp:05-07 Daily Effects of Foreign Exchange Intervention: Evidence from Official Bank of Canada Data (2005). Economic Policy Research Unit (EPRU), University of Copenhagen. Department of Economics (formerly Institute of Economics) / EPRU Working Paper Series (21) RePEc:mod:depeco:518 Economic Growth Rates and Recession Probabilities:the predictive power of the term spread in Italy (2005). Universita di Modena e Reggio Emilia, Dipartimento di Economia Politica / Dipartimento di Economia Politica (Economics Department) (22) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:11130 Trends in Hours, Balanced Growth, and the Role of Technology in the Business Cycle (2005). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (23) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:11401 Real Business Cycle Models: Past, Present, and Future (2005). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (24) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:11411 The Impact of State Physical Education Requirements on Youth Physical Activity and Overweight (2005). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (25) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:11437 Crafting A Class: The Trade Off Between Merit Scholarships and Enrolling Lower-Income Students (2005). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (26) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:11736 Stock Returns and Expected Business Conditions: Half a Century of Direct Evidence (2005). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (27) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:11824 Downside Risk (2005). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (28) RePEc:roc:rocher:522 Real Business Cycle Models: Past, Present and Future (2005). University of Rochester - Center for Economic Research (RCER) / RCER Working Papers (29) RePEc:upf:upfgen:829 Trends in Hours, Balanced Growth and the Role of Technology in the Business Cycle (2005). Department of Economics and Business, Universitat Pompeu Fabra / Economics Working Papers (30) RePEc:wpa:wuwpfi:0506009 Portfolio Selection with Two-Stage Preferences (2005). EconWPA / Finance (31) RePEc:wpa:wuwpma:0512006 Technology Shocks and UK Business Cycles (2005). EconWPA / Macroeconomics Recent citations received in: 2004 (1) RePEc:cir:cirwor:2004s-16 The Informational Content of Over-the-Counter Currency Options (2004). CIRANO / CIRANO Working Papers (2) RePEc:cmf:wpaper:wp2004_0422 ECONOMIC AND REGULATORY CAPITAL. WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE? (2004). CEMFI / Working Papers (3) RePEc:ecm:nasm04:26 Cointegration and Regime-Switching Risk Premia in the US Term Structure of Interest Rates (2004). Econometric Society / Econometric Society 2004 North American Summer Meetings (4) RePEc:fip:fedfpr:y:2004:i:mar:x:9 Permanent and transitory policy shocks in an empirical macro model with asymmetric information (2004). Proceedings (5) RePEc:fip:fedgfe:2004-05 The effects of the 1986 and 1993 tax reforms on self-employment (2004). Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (U.S.) / Finance and Economics Discussion Series (6) RePEc:fip:fedgfe:2004-57 Quantitative monetary easing and risk in financial asset markets (2004). Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (U.S.) / Finance and Economics Discussion Series (7) RePEc:fip:fedgif:799 The Great Inflation of the 1970s (2004). Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (U.S.) / International Finance Discussion Papers (8) RePEc:fip:fedgif:804 The decline of activist stabilization policy: natural rate misperceptions, learning, and expectations (2004). Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (U.S.) / International Finance Discussion Papers (9) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2003-011 Business cycle phases in U.S. states (2004). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (10) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2004-001 The Great Inflation of the seventies: what really happened? (2004). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (11) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2004-008 Monetary policy neglect and the Great Inflation in Canada, Australia, and New Zealand (2004). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (12) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2004-013 A dynamic factor analysis of the response of U. S. interest rates to news (2004). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (13) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2004-016 Learning and structural change in macroeconomic data (2004). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (14) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2004-030 Non-Markovian regime switching with endogenous states and time-varying state strengths (2004). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (15) RePEc:hhs:rbnkwp:0174 State Dependent Pricing and Exchange Rate Pass-Through (2004). Sveriges Riksbank (Central Bank of Sweden) / Working Paper Series (16) RePEc:ide:wpaper:2173 The New Keynesian Model with Imperfect Information and Learning (2004). Institut d'Économie Industrielle (IDEI), Toulouse / IDEI Working Papers (17) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1134 What a Difference a Y Makes: Female and Male Nascent Entrepreneurs in Germany (2004). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (18) RePEc:sce:scecf4:144 The Decline of Activist Stabilization Policy: Natural Rate Misperceptions, Learning, and Expectations (2004). Society for Computational Economics / Computing in Economics and Finance 2004 (19) RePEc:sce:scecf4:146 Permanent and Transitory Policy Shocks in an Empirical Macro Model with Asymmetric Information (2004). Society for Computational Economics / Computing in Economics and Finance 2004 (20) RePEc:sce:scecf4:176 Does Central Bank Transparency Matter for Economic Stability (2004). Society for Computational Economics / Computing in Economics and Finance 2004 (21) RePEc:sce:scecf4:53 Cointegration and Regime-Switching Risk Premia in the U.S. Term Structure of Interest Rates (2004). Society for Computational Economics / Computing in Economics and Finance 2004 (22) RePEc:wpa:wuwpif:0409002 A Dynamic Model of Endogenous Exchange Rate Pass-Through (2004). EconWPA / International Finance Recent citations received in: 2003 (1) RePEc:bon:bonedp:bgse21_2003 Monetary Policy in Europe: Evidence from Time-Varying Taylor Rules (2003). University of Bonn, Germany / Bonn Econ Discussion Papers (2) RePEc:cfs:cfswop:wp200341 Permanent and Transitory Policy Shocks in an Empirical Macro Model with Asymmetric Information (2003). Center for Financial Studies / CFS Working Paper Series (3) RePEc:fip:fedkrw:rwp03-09 Permanent and transitory policy shocks in an empirical macro model with asymmetric information (2003). Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City / Research Working Paper (4) RePEc:fip:fedlrv:y:2003:i:mar:p:47-61:n:v.85no.2 Identifying business cycle turning points in real time (2003). Review (5) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2002-008 On the out-of-sample predictability of stock market returns (2003). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (6) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2002-025 Business cycle detrending of macroeconomic data via a latent business cycle index (2003). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (7) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2003-027 Inflation targeting: why it works and how to make it work better (2003). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (8) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2003-033 Testing the expectations hypothesis: some new evidence for Japan (2003). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (9) RePEc:imf:imfwpa:03/208 The Term Structure of Interest Rates and Monetary Policy During A Zero-Interest-Rate Period (2003). International Monetary Fund / IMF Working Papers (10) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:9927 Uncovering the Risk-Return Relation in the Stock Market (2003). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (11) RePEc:ore:uoecwp:2003-29 Comment on Imperfect Knowledge, Inflation Expectations and Monetary Policy by Athanasios Orphanides and John C. Williams (2003). University of Oregon Economics Department / University of Oregon Economics Department Working Papers (12) RePEc:sce:scecf3:92 Alternative Sources of the Lag Dynamics of Inflation (2003). Society for Computational Economics / Computing in Economics and Finance 2003 (13) RePEc:uwo:uwowop:20036 What Was Lost with IS-LM (2003). University of Western Ontario, Department of Economics / UWO Department of Economics Working Papers (14) RePEc:uwo:uwowop:20037 Monetary Policy without Money: Hamlet without the Ghost (2003). University of Western Ontario, Department of Economics / UWO Department of Economics Working Papers Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||