|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
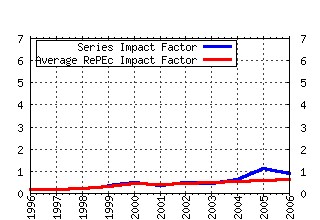
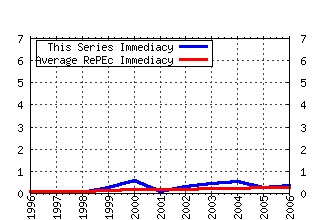
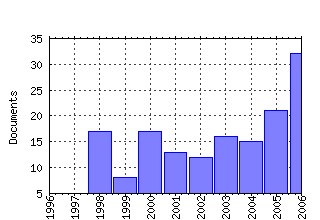
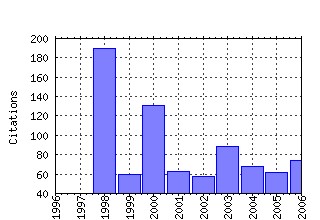
Experimental Economics Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Recent citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:10:y:2007:i:2:p:171-178 z-Tree: Zurich toolbox for ready-made economic experiments (2007). (2) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:1:y:1998:i:1:p:9-41 Quantal Response Equilibria for Extensive Form Games (1998). (3) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:1:y:1998:i:1:p:101-108 Individual and Group Behavior in the Ultimatum Game: Are Groups More âRationalâ Players? (1998). (4) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:1:y:1998:i:2:p:115-131 On the Validity of the Random Lottery Incentive System (1998). (5) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:2:y:2000:i:3:p:227-238 Hot vs. Cold: Sequential Responses and Preference Stability in Experimental Games (2000). (6) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:1:y:1998:i:3:p:207-219 Measuring Motivations for the Reciprocal Responses Observed in a Simple Dilemma Game (1998). (7) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:2:y:1999:i:2:p:107-127 Eliciting Individual Discount Rates (1999). (8) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:6:y:2003:i:1:p:75-90 The Hot Versus Cold Effect in a Simple Bargaining Experiment (2003). (9) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:9:y:2006:i:2:p:79-101 The value of reputation on eBay: A controlled experiment (2006). (10) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:4:y:2001:i:3:p:203-219 Tests of Fairness Models Based on Equity Considerations in a Three-Person Ultimatum Game (2001). (11) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:2:y:1999:i:1:p:5-30 Heterogeneity and the Voluntary Provision of Public Goods (1999). (12) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:3:y:2000:i:3:p:261-280 Dominant Strategy Adoption and Bidders Experience with Pricing Rules (2000). (13) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:7:y:2004:i:2:p:171-188 Cultural Differences in Ultimatum Game Experiments: Evidence from a Meta-Analysis (2004). (14) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:9:y:2006:i:3:p:193-208 Decomposing trust and trustworthiness (2006). (15) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:3:y:2000:i:1:p:55-79 Framing Effects in Public Goods Experiments (2000). (16) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:8:y:2005:i:4:p:347-367 Regular Quantal Response Equilibrium (2005). (17) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:3:y:2000:i:1:p:81-100 Trust, Reciprocity, and Social History: A Re-examination (2000). (18) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:7:y:2004:i:2:p:123-140 Experimental Methods and Elicitation of Values (2004). (19) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:5:y:2002:i:1:p:53-84 Risk Attitudes of Children and Adults: Choices Over Small and Large Probability Gains and Losses (2002). (20) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:4:y:2001:i:3:p:257-269 The Endowment Effect and Repeated Market Trials: Is the Vickrey Auction Demand Revealing? (2001). (21) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:6:y:2003:i:3:p:235-251 Learning to Open Monty Halls Doors (2003). (22) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:8:y:2005:i:1:p:35-54 Heterogeneous Agents in Public Goods Experiments (2005). (23) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:2:y:2000:i:3:p:239-259 Step Returns in Threshold Public Goods: A Meta- and Experimental Analysis (2000). (24) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:7:y:2004:i:2:p:189-205 How Robust is Laboratory Gift Exchange? (2004). (25) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:5:y:2002:i:1:p:5-27 Efficient Contracting and Fair Play in a Simple Principal-Agent Experiment (2002). (26) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:1:y:1998:i:1:p:43-61 Axiomatic Characterization of the Quadratic Scoring Rule (1998). (27) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:8:y:2005:i:1:p:5-20 Learning Direction Theory and the Winnerâs Curse (2005). (28) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:6:y:2003:i:3:p:273-297 Nonparametric Tests of Differences in Medians: Comparison of the WilcoxonâMannâWhitney and Robust Rank-Order Tests (2003). (29) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:1:y:1998:i:2:p:163-183 Bounded Rationality in Individual Decision Making (1998). (30) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:5:y:2002:i:3:p:223-231 House Money Effects in Public Good Experiments (2002). (31) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:7:y:2004:i:2:p:153-169 An Application of the English Clock Market Mechanism to Public Goods Games (2004). (32) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:9:y:2006:i:3:p:265-279 Can second-order punishment deter perverse punishment? (2006). (33) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:3:y:2000:i:3:p:241-260 The False Consensus Effect Disappears if Representative Information and Monetary Incentives Are Given (2000). (34) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:1:y:1998:i:3:p:191-206 Nash as an Organizing Principle in the Voluntary Provision of Public Goods: Experimental Evidence (1998). (35) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:1:y:1998:i:1:p:87-100 A Monte Carlo Analysis of the Fisher Randomization Technique: Reviving Randomization for Experimental Economists (1998). (36) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:5:y:2002:i:1:p:29-38 Price Competition Between Teams (2002). (37) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:6:y:2003:i:2:p:141-158 Reinforcement and Directional Learning in the Ultimatum Game with Responder Competition (2003). (38) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:3:y:2000:i:1:p:5-9 The Impact of Exchange Context on the Activation of Equity in Ultimatum Games (2000). (39) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:3:y:2000:i:3:p:215-240 Control Without Deception: Individual Behaviour in Free-Riding Experiments Revisited (2000). (40) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:3:y:2000:i:1:p:11-29 Learning to Accept in Ultimatum Games: Evidence from an Experimental Design that Generates Low Offers (2000). (41) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:6:y:2003:i:2:p:181-207 Relative versus Absolute Speed of Adjustment in Strategic Environments: Responder Behavior in Ultimatum Games (2003). (42) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:7:y:2004:i:3:p:235-247 Rewards and Sanctions and the Provision of Public Goods in One-Shot Settings (2004). (43) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:8:y:2005:i:2:p:85-106 Subsidy Schemes and Charitable Contributions: A Closer Look (2005). (44) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:4:y:2001:i:1:p:87-105 Price Bubbles in Laboratory Asset Markets with Constant Fundamental Values (2001). (45) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:6:y:2003:i:2:p:159-180 The Right Choice at the Right Time: A Herding Experiment in Endogenous Time (2003). (46) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:4:y:2001:i:3:p:221-228 Testing for the Presence of a Tremble in Economic Experiments (2001). (47) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:6:y:2003:i:2:p:123-140 Explaining Overbidding in First Price Auctions Using Controlled Lotteries (2003). (48) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:6:y:2003:i:1:p:5-25 Order of Play, Forward Induction, and Presentation Effects in Two-Person Games (2003). (49) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:4:y:2001:i:1:p:5-54 Does Repetition Improve Consistency? (2001). (50) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:5:y:2002:i:2:p:133-153 Voluntary Participation and Spite in Public Good Provision Experiments: An International Comparison (2002). Recent citations received in: | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 Recent citations received in: 2006 (1) RePEc:cla:levrem:784828000000000272 An Experimental Test of Advice and Social Learning (2006). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (2) RePEc:dgr:uvatin:20060099 Group Polarization in the Team Dictator Game reconsidered (2006). Tinbergen Institute / Tinbergen Institute Discussion Papers (3) RePEc:hol:holodi:0603 Where are you from? Cultural Differences in Public Good Experiments. (2006). Department of Economics, Royal Holloway University of London / Royal Holloway, University of London: Discussion Papers in Economics (4) RePEc:iim:iimawp:2006-02-06 Risk, Ambiguity - Gains, Losses (2006). Indian Institute of Management Ahmedabad, Research and Publication Department / IIMA Working Papers (5) RePEc:mpg:wpaper:2006_4 Noisy commitments: The impact of information accuracy on efficiency (2006). Max Planck Institute for Reserach on Collective Goods / Working Paper Series of the Max Planck Institute for Reserach on Collective Goods (6) RePEc:mse:wpsorb:bla06063 Group and individual risk preferences : a lottery-choice experiment. (2006). Université Panthéon-Sorbonne (Paris 1) / Cahiers de la Maison des Sciences Economiques (7) RePEc:pra:mprapa:2523 Linfluence de la connaissance du genre du partenaire dans les relations de confiance et de réciprocité: une étude expérimentale (2006). University Library of Munich, Germany / MPRA Paper (8) RePEc:ste:nystbu:06-32 The Dynamics of Seller Reputation: Evidence from eBay (2006). New York University, Leonard N. Stern School of Business, Department of Economics / Working Papers (9) RePEc:trf:wpaper:62 Last Minute Feedback (2006). SFB/TR 15 Governance and the Efficiency of Economic Systems, University of Mannheim / Discussion Papers (10) RePEc:tut:cremwp:200620 Pourquoi évaluer son partenaire lors dâune transaction à la eBay ? une approche expérimentale (2006). Center for Research in Economics and Management (CREM), University of Rennes 1, University of Caen and CNRS / Economics Working Paper Archive (Univers (11) RePEc:upf:upfgen:934 Risk aversion and embedding bias (2006). Department of Economics and Business, Universitat Pompeu Fabra / Economics Working Papers Recent citations received in: 2005 (1) RePEc:aea:aecrev:v:95:y:2005:i:5:p:1731-1737 Bubbles and Experience: An Experiment (2005). American Economic Review (2) RePEc:cla:levrem:666156000000000602 The Origin of the Winnerâs Curse: A Laboratory Study (2005). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (3) RePEc:hhs:hastef:0605 Strategic equivalence and bounded rationality in extensive form games (2005). Stockholm School of Economics / Working Paper Series in Economics and Finance (4) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:8:y:2005:i:4:p:301-323 Modelling the Stochastic Component of Behaviour in Experiments: Some Issues for the Interpretation of Data (2005). Experimental Economics (5) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:8:y:2005:i:4:p:347-367 Regular Quantal Response Equilibrium (2005). Experimental Economics (6) RePEc:zur:iewwpx:261 Heterogeneous social preferences and the dynamics of free riding in public goods (2005). Institute for Empirical Research in Economics - IEW / IEW - Working Papers Recent citations received in: 2004 (1) RePEc:clt:sswopa:1183 Fairness, or just gambling on it? An experimental analysis of the gift exchange game (2004). California Institute of Technology, Division of the Humanities and Social Sciences / Working Papers (2) RePEc:dgr:uvatin:20040100 Gift Exchange in a Multi-worker Firm (2004). Tinbergen Institute / Tinbergen Institute Discussion Papers (3) RePEc:esi:discus:2004-29 Leadership and cooperation in public goods experiments (2004). Max Planck Institute of Economics, Strategic Interaction Group / Discussion Papers on Strategic Interaction (4) RePEc:feb:artefa:0050 Estimating Risk Attitudes in Denmark: A Field Experiment (2004). The Field Experiments Website / Artefactual Field Experiments (5) RePEc:gat:wpaper:0408 Other-Regarding Preferences and Performance Pay â An Experiment on Incentives and Sorting (2004). Groupe d'Analyse et de Théorie Economique (GATE), Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS), Université Lyon 2, Ecole Normale Supérieure / W (6) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1191 Other-Regarding Preferences and Performance Pay â An Experiment on Incentives and Sorting (2004). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (7) RePEc:lau:crdeep:04.15 Verified Trust: Reciprocity, Altruism, and Noise in Trust Games (2004). Université de Lausanne, Ecole des HEC, DEEP / Cahiers de Recherches Economiques du Département d'Econométrie et d'Economie politique (DEEP) (8) RePEc:vcu:wpaper:0401 Rebates, Matches, and Consumer Behavior (2004). VCU School of Business, Department of Economics / Working Papers Recent citations received in: 2003 (1) RePEc:aub:autbar:586.03 Forward induction and the excess capacity puzzle: An experimental investigation (2003). Unitat de Fonaments de l'Anà lisi Econòmica (UAB) and Institut d'Anà lisi Econòmica (CSIC) / UFAE and IAE Working Papers (2) RePEc:cir:cirwor:2003s-69 Redesigning Teams and Incentives in a Merger: An Experiment with Managers and Students (2003). CIRANO / CIRANO Working Papers (3) RePEc:cla:levrem:666156000000000253 Forward induction and the excess capacity puzzle: An experimental investigation (2003). UCLA Department of Economics / Levine's Bibliography (4) RePEc:kap:expeco:v:6:y:2003:i:1:p:53-73 Coordination and Information in Critical Mass Games: An Experimental Study (2003). Experimental Economics (5) RePEc:mcm:mceelp:2003-04 Advance Production Duopolies and Posted Prices or Market-Clearing Prices (2003). McMaster University / McMaster Experimental Economics Laboratory Publications (6) RePEc:upf:upfgen:703 Forward Induction and the Excess Capacity Puzzle: An Experimental Investigation (2003). Department of Economics and Business, Universitat Pompeu Fabra / Economics Working Papers (7) RePEc:usi:wpaper:405 Drift effect and timing without observability: experimental evidence (2003). Department of Economics, University of Siena / Experimental Economics Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||