|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
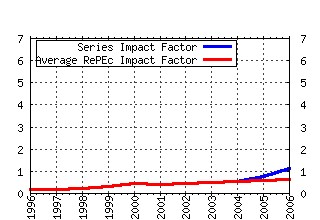
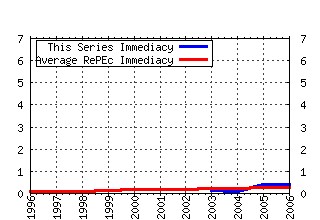
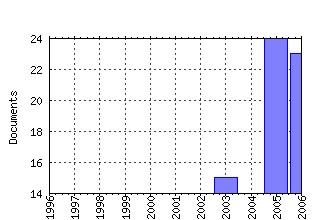
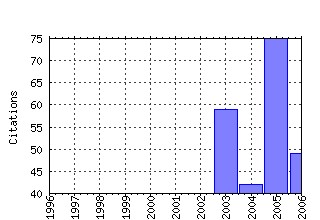
Journal of Economic Inequality Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Recent citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:3:y:2005:i:2:p:109-124 Redistribution and labour supply (2005). (2) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:1:y:2003:i:1:p:25-49 The Measurement of Multidimensional Poverty (2003). (3) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:4:y:2006:i:1:p:77-106 Microsimulation as a tool for evaluating redistribution policies (2006). (4) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:2:y:2004:i:1:p:3-10 Wage Decompositions with Selectivity-Corrected Wage Equations: A Methodological Note (2004). (5) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:1:y:2003:i:1:p:51-65 Multidimensional Deprivation: Contrasting Social Welfare and Counting Approaches (2003). (6) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:3:y:2005:i:3:p:221-241 Racial conflict and the malignancy of identity (2005). (7) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:5:y:2007:i:1:p:97-114 Tracing out the effects of demographic changes on the income distribution (2007). (8) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:4:y:2006:i:1:p:107-122 Inequality and happiness: Insights from Latin America (2006). (9) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:1:y:2003:i:1:p:67-99 For Richer or for Poorer? Evidence from Indonesia, South Africa, Spain, and Venezuela (2003). (10) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:2:y:2004:i:2:p:89-103 Restricted Lorenz dominance of economic inequality in one and many dimensions (2004). (11) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:2:y:2004:i:1:p:11-30 Ranking Income Distributions According to Equality of Opportunity (2004). (12) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:1:y:2003:i:1:p:5-24 Generalized Gini Indices of Equality of Opportunity (2003). (13) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:5:y:2007:i:1:p:1-19 An Extension of a Measure of Polarization, with an application to the income distribution of five OECD countries (2007). (14) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:4:y:2006:i:3:p:375-383 The Luxembourg Wealth Study â A cross-country comparable database for household wealth research (2006). (15) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:2:y:2004:i:2:p:61-87 Lorenz non-consistent welfare and inequality measurement (2004). (16) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:2:y:2004:i:3:p:193-218 Inequality and welfare evaluation of heterogeneous income distributions (2004). (17) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:4:y:2006:i:1:p:57-76 Income distribution in discrete hours behavioural microsimulation models: An illustration (2006). (18) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:5:y:2007:i:2:p:179-197 Removing the anonymity axiom in assessing pro-poor growth (2007). (19) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:3:y:2005:i:3:p:281-302 Community and anti-poverty targeting (2005). (20) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:4:y:2006:i:3:p:303-323 Comparing poverty and deprivation dynamics: Issues of reliability and validity (2006). (21) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:2:y:2005:i:2:p:89-103 Restricted Lorenz dominance of economic inequality in one and many dimensions (2005). (22) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:2:y:2004:i:3:p:219-228 The measurement of structural and exchange income mobility (2004). (23) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:1:y:2003:i:3:p:191-219 Distribution-Free Inference for Welfare Indices under Complete and Incomplete Information (2003). (24) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:1:y:2003:i:2:p:107-127 Income Satisfaction Inequality and its Causes (2003). (25) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:3:y:2005:i:1:p:21-42 The difference between wages and wage potentials: Earnings disadvantages of immigrants in Germany (2005). (26) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:1:y:2003:i:2:p:129-146 A Family of Correlation Coefficients Based on the Extended Gini Index (2003). (27) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:4:y:2006:i:1:p:1-32 A polarization of inequality? The distribution of national Gini coefficients 1970â1996 (2006). (28) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:3:y:2005:i:3:p:243-262 Social isolation and inequality (2005). (29) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:5:y:2007:i:1:p:53-72 Does persistence of social exclusion exist in Spain? (2007). (30) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:2:y:2005:i:2:p:105-116 Ranking opportunity sets in the space of functionings (2005). (31) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:3:y:2005:i:3:p:193-219 Social capital and the reproduction of economic inequality in polarized societies (2005). (32) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:4:y:2006:i:3:p:325-345 The measurement of transient poverty: Theory and application to Pakistan (2006). (33) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:2:y:2004:i:3:p:171-191 Poverty dynamics corrected for measurement error (2004). (34) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:4:y:2006:i:1:p:33-55 Survey nonresponse and the distribution of income (2006). (35) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:1:y:2003:i:2:p:147-179 Additively Decomposable Segregation Indexes. The Case of Gender Segregation by Occupations and Human Capital Levels in Spain (2003). (36) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:1:y:2003:i:3:p:281-284 DAD, an Innovative Tool for Income Distribution Analysis (2003). (37) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:5:y:2007:i:1:p:115-122 Region-specific versus country-specific poverty lines in analysis of poverty (2007). (38) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:3:y:2005:i:2:p:145-168 Gender segregation and the wage gap in Portugal: an analysis at the establishment level (2005). (39) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:2:y:2004:i:2:p:105-116 (). (40) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:4:y:2006:i:3:p:253-277 The effect on inequality of changing one or two incomes (2006). (41) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:5:y:2007:i:2:p:149-158 The comparative statics of differential rents in two-sided matching markets (2007). (42) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:4:y:2006:i:2:p:181-207 Measuring the impact of prices on inequality: With applications to Thailand and Korea (2006). (43) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:1:y:2003:i:2:p:181-187 A New Poverty Decomposition (2003). (44) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:4:y:2006:i:3:p:397-399 Generational income mobility in North America and Europe (2006). (45) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:3:y:2005:i:1:p:65-79 Why measure inequality? (2005). (46) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:5:y:2007:i:1:p:21-37 Robust stochastic dominance: A semi-parametric approach (2007). (47) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:3:y:2005:i:3:p:187-191 Social groups and economic inequality (2005). (48) RePEc:kap:jecinq:v:6:y:2008:i:2:p:117-148 Beyond OaxacaâBlinder: Accounting for differences in household income distributions (2008). Recent citations received in: | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 Recent citations received in: 2006 (1) RePEc:eso:journl:v:37:y:2006:i:1:p:91-1190 Trends in Economic Vulnerability in the Republic of Ireland (2006). The Economic and Social Review (2) RePEc:inq:inqwps:ecineq2006-35 Chronic and Transient Poverty: Measurement and Estimation, with Evidence from China (2006). ECINEQ, Society for the Study of Economic Inequality / Working Papers (3) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2078 Chronic and Transient Poverty: Measurement and Estimation, with Evidence from China (2006). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (4) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2468 Designing Optimal Taxes with a Microeconometric Model of Household Labour Supply (2006). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (5) RePEc:lvl:lacicr:0611 Chronic and Transient Poverty: Measurement and Estimation, with Evidence from China (2006). (6) RePEc:pse:psecon:2006-32 Strategic weight within couples: a microsimulation approach (2006). PSE (Ecole normale supérieure) / PSE Working Papers (7) RePEc:ssb:dispap:475 Designing Optimal Taxes with a Microeconometric Model of Household Labour Supply (2006). Research Department of Statistics Norway / Discussion Papers (8) RePEc:wbk:wbrwps:4069 Partially awakened giants : uneven growth in China and India (2006). The World Bank / Policy Research Working Paper Series (9) RePEc:wpc:wplist:wp20_06 Designing Optimal Taxes with a Microeconometric Model of Household Labour Supply (2006). CHILD - Centre for Household, Income, Labour and Demographic economics - ITALY / CHILD Working Papers Recent citations received in: 2005 (1) RePEc:hpe:wpaper:y:2005:i:14 MODELLING TAX DECENTRALISATION AND REGIONAL GROWTH (2005). Instituto de Estudios Fiscales / Working Papers (2) RePEc:hpe:wpaper:y:2005:i:17 OPTIMAL PROVISION OF PUBLIC INPUTS IN A SECOND BEST SCENARIO (*) (2005). Instituto de Estudios Fiscales / Working Papers (3) RePEc:hpe:wpaper:y:2005:i:22 ESTIMACIÃN DE LOS RENDIMIENTOS Y LA DEPRECIACIÃN DEL CAPITAL HUMANO PARA LAS REGIONES DEL SUR DE ESPAÃA (2005). Instituto de Estudios Fiscales / Working Papers (4) RePEc:hpe:wpaper:y:2005:i:25 ANÃLISIS DE LOS FACTORES DETERMINANTES DE LAS DESIGUALDADES INTERNACIONALES EN LAS EMISIONES DE CO2 PER CÃPITA APLICANDO EL ENFOQUE DISTRIBUTIVO: UNA METODOLOGÃA DE DESCOMPOSICIÃN POR FACTORES DE (2005). Instituto de Estudios Fiscales / Working Papers (5) RePEc:hpe:wpaper:y:2005:i:26 PLANIFICACIÃN FISCAL CON EL IMPUESTO DUAL SOBRE LA RENTA (2005). Instituto de Estudios Fiscales / Working Papers (6) RePEc:hpe:wpaper:y:2005:i:27 EL COSTE RECAUDATORIO DE LAS REDUCCIONES POR APORTACIONES A PLANES DE PENSIONES Y LAS DEDUCCIONES POR INVERSIÃN EN VIVIENDA EN EL IRPF 2002 (2005). Instituto de Estudios Fiscales / Working Papers (7) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1761 Work and Family: Marriage, Children, Child Gender and the Work Hours and Earnings of West German Men (2005). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (8) RePEc:max:cprwps:70 Ranking Inequality: Applications of Multivariate Subset Selection (2005). Center for Policy Research, Maxwell School, Syracuse University / Center for Policy Research Working Papers (9) RePEc:siu:wpaper:12-2005 Non-market Leadership Experience and Labor Market Success: Evidence From Military Rank (2005). Singapore Management University, School of Economics / Working Papers (10) RePEc:wpa:wuwpdc:0512006 Shocks, Livestock Asset Dynamics, and Social Capital in Ethiopia (2005). EconWPA / Development and Comp Systems Recent citations received in: 2004 (1) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1362 Wage Differentials in the 1990s in Israel: Endowments, Discrimination, and Selectivity (2004). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers Recent citations received in: 2003 (1) RePEc:cte:werepe:we033612 GENDER SEGREGATION: FROM BIRTH TO OCCUPATION (2003). Universidad Carlos III, Departamento de Economía / Economics Working Papers (2) RePEc:diw:diwwpp:dp364 The Measurement of Social Exclusion (2003). DIW Berlin, German Institute for Economic Research / Discussion Papers of DIW Berlin Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||