|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
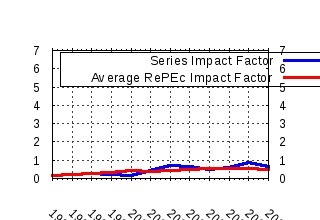
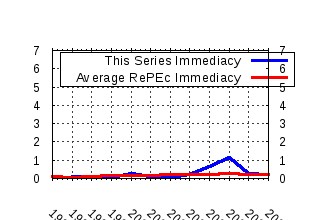
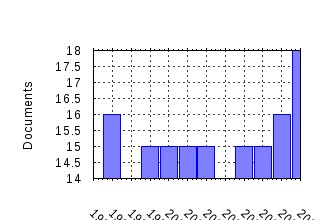
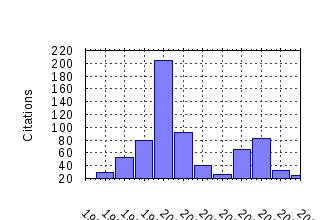
Economics and Politics Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Recent citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:12:y:2000:i:1:p:1-31 The Institutional Environment for Economic Growth (2000). (2) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:12:y:2000:i:1:p:69-81 Causality and Feedback Between Institutional Measures and Economic Growth (2000). (3) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:17:y:2005:i::p:37-75 PROPOSAL FOR A NEW MEASURE OF CORRUPTION, ILLUSTRATED WITH ITALIAN DATA (2005). (4) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:10:y:1998:i:1:p:63-83 Political Control of Administrative Spending: The Case of Local Governments in Norway (1998). (5) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:16:y:2004:i:1:p:1-27 Political Institutions and Policy Volatility (2004). (6) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:11:y:1999:i:3:p:225-253 Aid, Taxation and Development in Sub-Saharan Africa (1999). (7) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:13:y:2001:i:2:p:201-220 The Political Economy of the IRS (2001). (8) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:11:y:1999:i:3:p:275-297 Aid, Growth and Democracy (1999). (9) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:17:y:2005:i::p:177-213 WHICH VARIABLES EXPLAIN DECISIONS ON IMF CREDIT? AN EXTREME BOUNDS ANALYSIS (2005). (10) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:12:y:2000:i:2:p:155-182 Corruption, Income Distribution, and Growth (2000). (11) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:13:y:2001:i:2:p:129-157 Do Crises Induce Reform? Simple Empirical Tests of Conventional Wisdom (2001). (12) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:9:y:1997:i:3:p:205-205 Introduction (1997). (13) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:12:y:2000:i:3:p:225-245 Ethnicity, Politics and Economic Performance (2000). (14) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:11:y:1999:i:2:p:171-199 Does Distributional Skewness Lead to Redistribution? Evidence from the United States (1999). (15) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:14:y:2002:i:3:p:225-257 Democracy and the Variability of Economic Performance (2002). (16) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:13:y:2001:i:3:p:237-256 Political Determinants of Intergovernmental Grants: Evidence From Argentina (2001). (17) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:11:y:1999:i:2:p:109-144 Do Gatt Rules Help Governments Make Domestic Commitments? (1999). (18) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:18:y:2006:i:2:p:103-120 SOCIAL COHESION, INSTITUTIONS, AND GROWTH (2006). (19) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:16:y:2004:i:1:p:53-76 The Influence of IMF Programs on the Re-election of Debtor Governments (2004). (20) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:17:y:2005:i::p:1-35 ACCOUNTABILITY AND CORRUPTION: POLITICAL INSTITUTIONS MATTER (2005). (21) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:16:y:2004:i::p:321-345 VOTING TRANSPARENCY, CONFLICTING INTERESTS, AND THE APPOINTMENT OF CENTRAL BANKERS (2004). (22) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:12:y:2000:i:3:p:275-295 Delays of Inflation Stabilizations (2000). (23) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:13:y:2001:i:3:p:311-342 Electoral Rules, Political Systems, and Institutional Quality (2001). (24) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:10:y:1998:i:2:p:127-142 Foreign Aid and International Support as a Gift Exchange (1998). (25) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:18:y:2006:i:3:p:339-365 PROMISES MADE, PROMISES BROKEN: A MODEL OF IMF PROGRAM IMPLEMENTATION (2006). (26) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:10:y:1998:i:1:p:1-17 Rationalizing the Political Business Cycle: A Workhorse Model (1998). (27) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:15:y:2003:i:2:p:135-162 Restraining the Genuine Homo Economicus: Why the Economy Cannot Be Divorced from Its Governance (2003). (28) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:17:y:2005:i::p:151-176 ELECTIONS AND EXCHANGE RATE POLICY CYCLES (2005). (29) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:12:y:2000:i:2:p:109-135 Repeated Elections with Asymmetric Information (2000). (30) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:13:y:2001:i:3:p:281-309 The ratification of ILO conventions: A hazard rate analysis (2001). (31) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:9:y:1997:i:1:p:27-54 Politically Motivated Fiscal Deficits: Policy Issues in Closed and Open Economies (1997). (32) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:14:y:2002:p:41-63 Private Investment and Political Institutions (2002). (33) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:19:y:2007:i:2:p:191-218 CONTRACT ENFORCEMENT AND INTERNATIONAL TRADE (2007). (34) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:16:y:2004:i:2:p:117-146 Adjustments in Different Government Systems (2004). (35) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:17:y:2005:i::p:265-296 ECONOMIC VOTING AND ELECTORAL BEHAVIOR: HOW DO INDIVIDUAL, LOCAL, AND NATIONAL FACTORS AFFECT THE PARTISAN CHOICE? (2005). (36) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:19:y:2007:i:3:p:317-344 THE QUALITY OF INSTITUTIONS AND FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT (2007). (37) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:17:y:2005:i::p:129-150 FISCAL CONSTRAINTS, COLLECTION COSTS, AND TRADE POLICIES (2005). (38) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:13:y:2001:i:3:p:257-279 Campaign Contributions and Agricultural Subsidies (2001). (39) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:21:y:2009:i:1:p:42-92 INSTABILITY AND THE INCENTIVES FOR CORRUPTION (2009). (40) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:14:y:2002:i:1:p:19-40 Strategic Political Participation and Redistribution (2002). (41) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:10:y:1998:i:2:p:161-183 To Shock or Not to Shock? Economics and Political Economy of Large-Scale Reforms (1998). (42) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:19:y:2007:i:1:p:1-33 PUBLIC FINANCE AND INDIVIDUAL PREFERENCES OVER GLOBALIZATION STRATEGIES (2007). (43) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:11:y:1999:i:1:p:33-50 Estimating Presidential Elections: The Importance of State Fixed Effects and the Role of National Versus Local Information (1999). (44) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:14:y:2002:i:2:p:99-131 Factor or Industry Cleavages in Trade Policy? An Empirical Analysis of the Stolper-Samuelson Theorem (2002). (45) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:13:y:2001:i:2:p:159-184 Political Competition in Weak States (2001). (46) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:15:y:2003:i:3:p:225-246 Educational Policy: Egalitarian or Elitist? (2003). (47) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:13:y:2001:i:1:p:31-47 Cooption and Repression in the Soviet Union (2001). (48) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:16:y:2004:i::p:233-251 DID TIME INCONSISTENCY CONTRIBUTE TO THE GREAT INFLATION? EVIDENCE FROM THE FOMC TRANSCRIPTS (2004). (49) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:11:y:1999:i:2:p:145-169 Russias Tax Crisis: Explaining Falling Revenues in a Transitional Economy (1999). (50) RePEc:bla:ecopol:v:13:y:2001:i:2:p:113-128 Strategic Trade, Competitive Industries and Agricultural Trade Disputes (2001). Recent citations received in: | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 Recent citations received in: 2007 (1) RePEc:hal:cesptp:hal-00270483_v1 Inequalities and growth: Are there good and bad inequalities? (2007). HAL / Université Paris1 Panthéon-Sorbonne, Post-Print (2) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp3183 Do Interest Groups Affect Immigration? (2007). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (3) RePEc:wbk:wbrwps:4113 Location decisions of foreign banks and competitive advantage (2007). The World Bank / Policy Research Working Paper Series (4) RePEc:wly:jintdv:v:19:y:2007:i:6:p:735-753 Trade facilitation, regulatory quality and export performance (2007). Journal of International Development Recent citations received in: 2006 (1) RePEc:cgd:wpaper:85 The Economics of Young Democracies: Policies and Performance (2006). Center for Global Development / Working Papers (2) RePEc:imf:imfwpa:06/210 Growth and Reforms in Latin America: A Survey of Facts and Arguments (2006). International Monetary Fund / IMF Working Papers (3) RePEc:kap:pubcho:v:128:y:2006:i:3:p:383-405 Everyone likes a winner: An empirical test of the effect of electoral closeness on turnout in a context of expressive voting (2006). Public Choice (4) RePEc:pra:mprapa:553 The Economics of Young Democracies: Policies and Performance (2006). University Library of Munich, Germany / MPRA Paper Recent citations received in: 2005 (1) RePEc:ags:aaea05:19544 Reelection Incentives and Political Corruption: Evidence from Brazilian Audit Reports (2005). American Agricultural Economics Association (New Name 2008: Agricultural and Applied Economics Association) / 2005 Annual meeting, July 24-27, Provide (2) RePEc:cam:camdae:0540 Growth, Governance and Corruption in the Presence of Threshold Effects: Theory and Evidence (2005). Faculty of Economics (formerly DAE), University of Cambridge / Cambridge Working Papers in Economics (3) RePEc:cem:jaecon:v:8:y:2005:n:2:p:203-225 Sustaining fixed rates: The political economy of currency pegs in Latin America (2005). Journal of Applied Economics (4) RePEc:ces:ceswps:_1502 Costly Revenue-Raising and the Case for Favoring Import-Competing Industries (2005). CESifo GmbH / CESifo Working Paper Series (5) RePEc:csl:devewp:202 Prolonged Use and Conditionality Failure: Investigating the IMF Responsibility (2005). Centro Studi Luca d'Agliano, University of Milano / Development Working Papers (6) RePEc:csl:devewp:206 IMF Concern for Reputation and Conditional Lending Failure: Theory and Empirics (2005). Centro Studi Luca d'Agliano, University of Milano / Development Working Papers (7) RePEc:fgv:epgewp:597 Special Interests and Political Business Cycles (2005). Graduate School of Economics, Getulio Vargas Foundation (Brazil) / Economics Working Papers (Ensaios Economicos da EPGE) (8) RePEc:idc:wpaper:idec05-5 Short-run and Long-run Effects of Corruption on Economic Growth: Evidence from State-Level Cross-Section Data for the United States (2005). International and Development Economics / International and Development Economics Working Papers (9) RePEc:kof:wpskof:05-118 Independent Actor or Agent? An Empirical Analysis of the impact of US interests on IMF Conditions (2005). Swiss Institute for Business Cycle Research (KOF), Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich (ETH), / Working papers (10) RePEc:pra:mprapa:17772 The Shadowing Role of Redistributive Institutions in the Relationship Between Income Inequality and Redistribution (2005). University Library of Munich, Germany / MPRA Paper (11) RePEc:pra:mprapa:17773 The Role of Efficiency of Redistributive Institutions on Redistribution: An Empirical Assessment (2005). University Library of Munich, Germany / MPRA Paper (12) RePEc:pra:mprapa:8219 Measuring Governance Using Cross-Country Perceptions Data (2005). University Library of Munich, Germany / MPRA Paper (13) RePEc:taf:regstd:v:39:y:2005:i:5:p:603-617 Public capital and total factor productivity: New evidence from the Italian regions, 1970--98 (2005). Regional Studies (14) RePEc:tky:fseres:2005cf348 Short-run and Long-run Effects of Corruption on Economic Growth: Evidence from State-Level Cross-Section Data for the United States (2005). CIRJE, Faculty of Economics, University of Tokyo / CIRJE F-Series (15) RePEc:usi:wpaper:447 IMF concern for reputation and conditional lending failure: theory and empirics (2005). Department of Economics, University of Siena / Experimental Economics (16) RePEc:wpa:wuwpit:0510016 Political and Public Finance Motives for Tariffs (2005). EconWPA / International Trade (17) RePEc:zbw:gdec05:3484 IMF and Economic Growth: The Effects of Programs, Loans, and Compliance with Conditionality (2005). Verein für Socialpolitik, Research Committee Development Economics / Proceedings of the German Development Economics Conference, Kiel 2005 Recent citations received in: 2004 (1) RePEc:bpj:buspol:v:6:y:2004:i:1:n:2 The Political Economy of Trans-Pacific Business Linkages (2004). Business and Politics (2) RePEc:cam:camdae:0438 Core Indicators for Determinants and Performance of Electricity Sector in Developing Countriesââ¬â¢ (2004). Faculty of Economics (formerly DAE), University of Cambridge / Cambridge Working Papers in Economics (3) RePEc:cam:camdae:0439 ââ¬ËElectricity Sector Reform in Developing Countries: A Survey of Empirical Evidence on Determinants and Performanceââ¬â¢ (2004). Faculty of Economics (formerly DAE), University of Cambridge / Cambridge Working Papers in Economics (4) RePEc:cie:wpaper:0408 When Are Stabilizations Delayed? Alesina-Drazen Revisited (2004). Centro de Investigacion Economica, ITAM / Working Papers (5) RePEc:cty:dpaper:0401 Regulatory Effectiveness: The impact of regulation and regulatory governance arrangements on electricity industry outcomes: a review paper (2004). Department of Economics, City University, London / City University Economics Discussion Papers (6) RePEc:ieb:wpaper:505578art150 Yardstick competition and the political costs of raising taxes: An empirical analysis of Spanish municipalities (2004). Institut d'Economia de Barcelona (IEB) / Working Papers (7) RePEc:por:fepwps:138 Political models of budget deficits: a literature review (2004). Universidade do Porto, Faculdade de Economia do Porto / FEP Working Papers (8) RePEc:wdi:papers:2004-712 Votes and Vetoes: The Political Determinants of Commercial Openness (2004). William Davidson Institute at the University of Michigan Stephen M. Ross Business School / William Davidson Institute Working Papers Series (9) RePEc:wpa:wuwpif:0310004 Independent Actor or Agent? An Empirical Analysis of the impact of US interests on IMF Conditions (2004). EconWPA / International Finance (10) RePEc:wpa:wuwpif:0404004 IMF and Economic Growth: The Effects of Programs, Loans, and Compliance with Conditionality (2004). EconWPA / International Finance Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||