|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
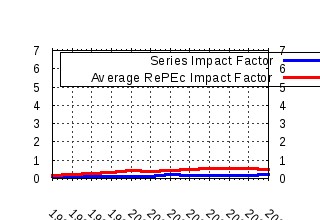
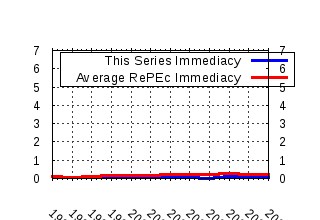
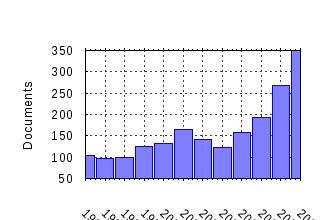
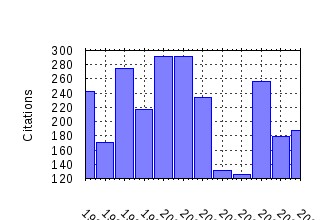
Ecological Economics Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Recent citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:15:y:1995:i:2:p:91-95 Economic growth, carrying capacity, and the environment (1995). (2) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:18:y:1996:i:3:p:243-253 A comparison of stated preference methods for environmental valuation (1996). (3) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:39:y:2001:i:3:p:449-462 Why farmers continue to use pesticides despite environmental, health and sustainability costs (2001). (4) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:23:y:1997:i:3:p:251-264 Spatial landscape indices in a hedonic framework: an ecological economics analysis using GIS (1997). (5) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:18:y:1996:i:3:p:197-206 Economic benefits of rare and endangered species: summary and meta-analysis (1996). (6) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:15:y:1995:i:2:p:89-90 Economic growth, carrying capacity, and the environment (1995). (7) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:25:y:1998:i:2:p:195-208 Economic growth, trade and energy: implications for the environmental Kuznets curve (1998). (8) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:31:y:1999:i:3:p:409-423 The environmental Kuznets curve: does one size fit all? (1999). (9) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:19:y:1996:i:2:p:169-184 Discounting and distributional considerations in the context of global warming (1996). (10) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:8:y:1993:i:2:p:103-108 Capital theory and the measurement of sustainable development: an indicator of weak sustainability (1993). (11) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:25:y:1998:i:2:p:147-160 Income, inequality, and pollution: a reassessment of the environmental Kuznets Curve (1998). (12) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:25:y:1998:i:2:p:209-220 The determinants of atmospheric SO2 concentrations: reconsidering the environmental Kuznets curve (1998). (13) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:43:y:2002:i:2-3:p:105-126 Technological change in economic models of environmental policy: a survey (2002). (14) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:32:y:2000:i:1:p:137-152 Environmental value transfer: state of the art and future prospects (2000). (15) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:19:y:1996:i:1:p:67-90 The damage costs of climate change towards a dynamic representation (1996). (16) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:6:y:1992:i:1:p:7-34 Towards an ecological economics of sustainability (1992). (17) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:54:y:2005:i:2-3:p:164-174 A tale of two market failures: Technology and environmental policy (2005). (18) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:12:y:1995:i:3:p:191-208 Preferences, information and biodiversity preservation (1995). (19) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:49:y:2004:i:4:p:431-455 Environmental Kuznets Curve Hypothesis: A Survey (2004). (20) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:25:y:1998:i:2:p:161-175 Economic growth and emissions: reconsidering the empirical basis of environmental Kuznets curves (1998). (21) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:26:y:1998:i:1:p:31-41 Can capital markets create incentives for pollution control? (1998). (22) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:32:y:2000:i:3:p:431-443 The Environmental Kuznets Curve, environmental protection policy and income distribution (2000). (23) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:37:y:2001:i:2:p:257-270 The economic value of wetland services: a meta-analysis (2001). (24) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:25:y:1998:i:3:p:249-264 The human development index: a critical review (1998). (25) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:28:y:1999:i:2:p:267-277 A dynamic approach to the Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis (1999). (26) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:32:y:2000:i:2:p:269-286 A test of policy labels in environmental choice modelling studies (2000). (27) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:33:y:2000:i:1:p:77-91 A simple bioeconomic model of a marine reserve (2000). (28) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:40:y:2002:i:3:p:337-349 Environmental amenities and agricultural land values: a hedonic model using geographic information systems data (2002). (29) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:52:y:2005:i:1:p:111-125 Climate and happiness (2005). (30) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:54:y:2005:i:2-3:p:277-292 The impact of technological change on climate protection and welfare: Insights from the model MIND (2005). (31) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:12:y:1995:i:2:p:161-179 Elicitation and truncation effects in contingent valuation studies (1995). (32) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:45:y:2003:i:3:p:409-426 Valuing indigenous cattle breeds in Kenya: an empirical comparison of stated and revealed preference value estimates (2003). (33) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:32:y:2000:i:3:p:395-412 A future for carbon taxes (2000). (34) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:35:y:2000:i:3:p:311-322 Beyond Homo economicus: evidence from experimental economics (2000). (35) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:28:y:1999:i:1:p:55-73 Measuring sustainability: A time series of alternative indicators for Scotland (1999). (36) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:39:y:2001:i:1:p:85-99 Economic growth and atmospheric pollution in Spain: discussing the environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis (2001). (37) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:2:y:1990:i:1:p:1-6 Toward some operational principles of sustainable development (1990). (38) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:27:y:1998:i:1:p:29-41 Alternative approaches for incorporating respondent uncertainty when estimating willingness to pay: the case of the Mexican spotted owl (1998). (39) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:42:y:2002:i:1-2:p:201-220 Explaining changes in global sulfur emissions: an econometric decomposition approach (2002). (40) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:47:y:2003:i:1:p:95-103 Valuing wetland attributes: an application of choice experiments (2003). (41) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:48:y:2004:i:1:p:71-81 Trade, the pollution haven hypothesis and the environmental Kuznets curve: examining the linkages (2004). (42) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:11:y:1994:i:3:p:169-178 Inequality as a cause of environmental degradation (1994). (43) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:24:y:1998:i:1:p:1-14 Undesirable facilities and property values: a summary of empirical studies (1998). (44) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:32:y:2000:i:1:p:63-74 Comparison of contingent valuation and conjoint analysis in ecosystem management (2000). (45) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:39:y:2001:i:2:p:203-222 Economic valuation of biodiversity: sense or nonsense? (2001). (46) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:52:y:2005:i:3:p:305-313 How trade politics affect invasive species control (2005). (47) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:60:y:2007:i:3:p:509-516 Environmental degradation and happiness (2007). (48) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:20:y:1997:i:3:p:199-207 The effect of distance on willingness to pay values: a case study of wetlands and salmon in California (1997). (49) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:36:y:2001:i:3:p:487-498 Inspections, pollution prices, and environmental performance: evidence from China (2001). (50) RePEc:eee:ecolec:v:41:y:2002:i:1:p:69-83 Intergenerational equity and sustainability (2002). Recent citations received in: | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 Recent citations received in: 2007 (1) RePEc:ags:arerjl:44696 Carving Out Policy Space for Sustainability in Biofuel Production (2007). Agricultural and Resource Economics Review (2) RePEc:aub:uhewps:2007_10 The biophysical perspective of a middle income economy: Material Flows in Mexico (2007). Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Departament d'Economia i Història Econòmica, Unitat d'Història Econòmica / UHE Working papers (3) RePEc:bol:bodewp:617 Assessing visitor satisfaction with tourism rejuvenation policies: the case of Rimini, Italy (2007). Dipartimento Scienze Economiche, Universita' di Bologna / Working Papers (4) RePEc:drm:wpaper:2007-20 Maximizing minimal rights for sustainability: a viability approach (2007). University of Paris West - Nanterre la Défense, EconomiX / EconomiX Working Papers (5) RePEc:ecl:wisagr:519 Spatial Externalities in Agriculture: Empirical Analysis, Statistical Identification, and Policy Implications (2007). University of Wisconsin, Agricultural and Applied Economics / Staff Paper Series (6) RePEc:fem:femwpa:2007.20 Endogenous Business Cycles and the Economic Response to Exogenous Shocks (2007). Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei / Working Papers (7) RePEc:fem:femwpa:2007.76 Estimating Tourist Externalities on Residents: A Choice Modeling Approach to the Case of Rimini (2007). Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei / Working Papers (8) RePEc:fem:femwpa:2007.84 Environmental and Pro-Social Norms: Evidence from 30 Countries (2007). Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei / Working Papers (9) RePEc:grt:wpegrt:2007-18 Wealth, Well-being and Value(s): A Proposition of Structuring Concepts for a (real) Transdisciplinary Dialogue within Ecological Economics (2007). Groupe de Recherche en Economie Théorique et Appliquée / Cahiers du GREThA (10) RePEc:ide:wpaper:7393 Innovation Markets in the Policy Appraisal of Climate Change Mitigation (2007). Institut d'Ãconomie Industrielle (IDEI), Toulouse / IDEI Working Papers (11) RePEc:kap:enreec:v:38:y:2007:i:3:p:285-310 Environmental policy and growth when inputs are differentiated in pollution intensity (2007). Environmental & Resource Economics (12) RePEc:kap:jproda:v:28:y:2007:i:1:p:57-69 Eco-efficiency analysis of consumer durables using absolute shadow prices (2007). Journal of Productivity Analysis (13) RePEc:ler:wpaper:07.04.225 Economic growth and Climate change in a decentralized Economy: A Theoretical and Empirical Approach (2007). LERNA, University of Toulouse / Working Papers (14) RePEc:ler:wpaper:07.12.233 Innovation markets in the policy appraisal of climate change mitigation (2007). LERNA, University of Toulouse / Working Papers (15) RePEc:lue:wpaper:63 The Monetary Value of Cultural Goods: A Contingent Valuation Study of the Municipal Supply of Cultural Goods in Lueneburg, Germany (2007). University of Lüneburg, Institute of Economics / Working Paper Series in Economics (16) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:13616 Technology, International Trade, and Pollution from U.S. Manufacturing (2007). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (17) RePEc:pid:journl:v:46:y:2007:i:4:p:337-350 Climate Change and Economic Development: A Pragmatic Approach (2007). The Pakistan Development Review (18) RePEc:pra:mprapa:10103 A viability theory approach to a two-stage optimal control problem (2007). University Library of Munich, Germany / MPRA Paper (19) RePEc:pra:mprapa:3705 Can the Poor Participate in Payments for Environmental Services?: Lessons from the Silvopastoral Project in Nicaragua (2007). University Library of Munich, Germany / MPRA Paper (20) RePEc:pra:mprapa:4794 Poor Household Participation in Payments for Environmental Services: Lessons from the Silvopastoral Project in QuindÃo, Colombia (2007). University Library of Munich, Germany / MPRA Paper (21) RePEc:pra:mprapa:5343 ???????? ???????? ? ?????????? ?????? ?????? ????? ? ?????? (2007). University Library of Munich, Germany / MPRA Paper (22) RePEc:qut:dpaper:220 Environmental and Pro-Social Norms: Evidence from 30 Countries (2007). School of Economics and Finance, Queensland University of Technology / School of Economics and Finance Discussion Papers and Working Papers Series (23) RePEc:rff:dpaper:dp-07-40 Technology, International Trade, and Pollution from U.S. Manufacturing (2007). Resources For the Future / Discussion Papers (24) RePEc:rff:dpaper:dp-07-50 Policies to Reduce Emissions from Deforestation and Degradation (REDD) in Tropical Forests: An Examination of the Issues Facing the Incorporation of REDD into Market-Based Climate Policies (2007). Resources For the Future / Discussion Papers (25) RePEc:sgc:wpaper:151 SPECIES DIVERSITY AND HUMAN WELL-BEING: A SPATIAL ECONOMETRIC APPROACH (2007). Research unit Sustainability and Global Change, Hamburg University / Working Papers (26) RePEc:shr:wpaper:07-13 Corruption, Inequality, and Environmental Regulation (2007). Departement d'Economique de la Faculte d'administration àl'Universite de Sherbrooke / Cahiers de recherche (27) RePEc:wbk:wbrwps:4117 Forest cover change in space and time : combining the von Thunen and forest transition theories (2007). The World Bank / Policy Research Working Paper Series (28) RePEc:zbw:zewdip:6802 Climate Policy and Ancillary Benefits: A Survey and Integration into the Modelling of International Negotiations on Climate Change (2007). ZEW - Zentrum für Europäische Wirtschaftsforschung / Center for European Economic Research / ZEW Discussion Papers Recent citations received in: 2006 (1) RePEc:ags:aaea06:21221 Context Similarity and the Validity of Benefits Transfer: Is the Common Wisdom Correct? (2006). American Agricultural Economics Association (New Name 2008: Agricultural and Applied Economics Association) / 2006 Annual meeting, July 23-26, Long Be (2) RePEc:aub:uhewps:2006_04 Income growth and atmospheric pollution in Spain: an Input-Output approach (2006). Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Departament d'Economia i Història Econòmica, Unitat d'Història Econòmica / UHE Working papers (3) RePEc:dgr:unumer:2006038 Economics and Transitions: Lessons from Economic Sub-disciplines (2006). United Nations University, Maastricht Economic and social Research and training centre on Innovation and Technology / UNU-MERIT Working Paper Series (4) RePEc:fem:femwpa:2006.121 A Bayesian Approach to the Estimation of Environmental Kuznets Curves for CO2 Emissions (2006). Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei / Working Papers (5) RePEc:fem:femwpa:2006.155 Municipal Waste Production, Economic Drivers, and ââ¬ËNewââ¬â¢ Waste Policies: EKC Evidence from Italian Regional and Provincial Panel Data (2006). Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei / Working Papers (6) RePEc:fem:femwpa:2006.22 On the Robustness of Robustness Checks of the Environmental Kuznets Curve (2006). Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei / Working Papers (7) RePEc:hhb:aarbma:2006-005 Business Process Risk Management, Compliance and Internal Control: A Research Agenda (2006). Aarhus School of Business, Department of Business Studies / Management Accounting Research Group Working Papers (8) RePEc:pab:wpaper:06.06 Virtual water and water trade in Andalusia. A study by means of an input-output model (2006). Universidad Pablo de Olavide, Departamento de EconomiÂa / Working Papers (9) RePEc:pra:mprapa:1693 Measuring Environmental Efficiency of Industry: A Case Study of Thermal Power Generation in India (2006). University Library of Munich, Germany / MPRA Paper (10) RePEc:rff:dpaper:dp-06-49 Output and Abatement Effects of Allocation Readjustment in Permit Trade (2006). Resources For the Future / Discussion Papers (11) RePEc:ros:wpaper:60 The Social Costs of Unemployment: Accounting for Unemployment Duration (2006). University of Rostock, Institute of Economics, Germany / Thünen-Series of Applied Economic Theory (12) RePEc:ssb:dispap:476 âThe worth of a wildflowerâ Precautionary perspectives on the environmental risk of GMOs (2006). Research Department of Statistics Norway / Discussion Papers (13) RePEc:wbk:wbrwps:3888 Firmsenvironmental performance : does news matter ? (2006). The World Bank / Policy Research Working Paper Series (14) RePEc:zbw:zewdip:5472 Environmentally oriented energy policy and stock returns : an empirical analysis (2006). ZEW - Zentrum für Europäische Wirtschaftsforschung / Center for European Economic Research / ZEW Discussion Papers Recent citations received in: 2005 (1) RePEc:ags:aaea05:19135 Environmental Restoration of Invaded Ecosystems: How Much Versus How Often? (2005). American Agricultural Economics Association (New Name 2008: Agricultural and Applied Economics Association) / 2005 Annual meeting, July 24-27, Provide (2) RePEc:ags:aaea05:19177 Carbon Sequestration in Agriculture: an Offset Program versus Other Conservation Programs (2005). American Agricultural Economics Association (New Name 2008: Agricultural and Applied Economics Association) / 2005 Annual meeting, July 24-27, Provide (3) RePEc:ags:aaea05:19515 Invasive Species Management through Tariffs: Are Prevention and Protection Synonymous? (2005). American Agricultural Economics Association (New Name 2008: Agricultural and Applied Economics Association) / 2005 Annual meeting, July 24-27, Provide (4) RePEc:anp:en2005:137 DETERMINANTS OF TECHNICAL EFFICIENCY IN AGRICULTURE AND CATTLE RANCHING: A SPATIAL ANALYSIS FOR THE BRAZILIAN AMAZON (2005). ANPEC - Associação Nacional do Centros de Pos-graduação em Economia [Brazilian Association of Graduate Programs in Economics] / Anais do XXXIII Encont (5) RePEc:cen:wpaper:05-03 Assessing Multi-Dimensional Performance: Environmental and Economic Outcomes (2005). Center for Economic Studies, U.S. Census Bureau / Working Papers (6) RePEc:ias:cpaper:05-wp390 Consequences of Co-benefits for the Efficient Design of Carbon Sequestration Programs, The (2005). Center for Agricultural and Rural Development (CARD) at Iowa State University / Center for Agricultural and Rural Development (CARD) Publications (7) RePEc:ias:cpaper:05-wp407 Tariff Escalation and Invasive Species Risk (2005). Center for Agricultural and Rural Development (CARD) at Iowa State University / Center for Agricultural and Rural Development (CARD) Publications (8) RePEc:ias:cpaper:05-wp413 Biosecurity and Infectious Animal Disease (2005). Center for Agricultural and Rural Development (CARD) at Iowa State University / Center for Agricultural and Rural Development (CARD) Publications (9) RePEc:ias:fpaper:05-wp407 Tariff Escalation and Invasive Species Risk (2005). Food and Agricultural Policy Research Institute (FAPRI) at Iowa State University / Food and Agricultural Policy Research Institute (FAPRI) Publication (10) RePEc:inq:inqwps:ecineq2005-13 Reconsidering the Environmental Kuznets Curve hypothesis: the trade off between environment and welfare (2005). (11) RePEc:isu:genres:12269 Consequences of Co-benefits for the Efficient Design of Carbon Sequestration Programs, The (2005). Iowa State University, Department of Economics / Staff General Research Papers (12) RePEc:isu:genres:12442 Tariff Escalation and Invasive Species Damages (2005). Iowa State University, Department of Economics / Staff General Research Papers (13) RePEc:isu:genres:12475 Biosecurity and Infectious Animal Disease (2005). Iowa State University, Department of Economics / Staff General Research Papers (14) RePEc:kof:wpskof:05-112 Sind unsere gesamtwirtschaftlichen Probleme überhaupt lösbar? (2005). Swiss Institute for Business Cycle Research (KOF), Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich (ETH), / Working papers (15) RePEc:lnd:wpaper:200506 On- and off-farm labor decisions by slash-and-burn farmers in Yucatan (Mexico) (2005). University of Cambridge, Department of Land Economics / Environmental Economy and Policy Research Working Papers (16) RePEc:lvl:lagrcr:0505 Can Environmental Regulations be Good for Business? an Assessment of the Porter Hypothesis (2005). (17) RePEc:rff:dpaper:dp-05-24 The Incidence of Pollution Control Policies (2005). Resources For the Future / Discussion Papers (18) RePEc:rff:dpaper:dp-05-33 Technology Prizes for Climate Change Mitigation (2005). Resources For the Future / Discussion Papers (19) RePEc:rpi:rpiwpe:0422 Physical and Monetary Input-Output Analysis: What Makes the Difference? (2005). Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Department of Economics / Rensselaer Working Papers in Economics (20) RePEc:sgc:wpaper:68 A NO CAP BUT TRADE PROPOSAL FOR GREENHOUS GAS EMISSION REDUCTION TARGETS FOR BRAZIL, CHINA AND INDIA (2005). Research unit Sustainability and Global Change, Hamburg University / Working Papers (21) RePEc:uma:periwp:wp_brenner_riddle_boyce A Chinese Sky Trust? Distributional Impacts of Carbon charges and Revenue Recycling in China (2005). Political Economy Research Institute, University of Massachusetts at Amherst / Working Papers (22) RePEc:wai:econwp:05/08 Experimental Designs for Environmental Valuation with Choice-Experiments: A Monte-Carlo Investigation (2005). University of Waikato, Department of Economics / Working Papers in Economics (23) RePEc:wiw:wiwrsa:ersa05p701 Tackling Local Conflicts Caused by Renewable Energy Sources - Lessons Learned from Real-World Case Studies (2005). European Regional Science Association / ERSA conference papers (24) RePEc:wpa:wuwppe:0511005 A Rational Irrational Man (2005). EconWPA / Public Economics Recent citations received in: 2004 (1) RePEc:qld:uqcepa:18 Explaining Agricultural Productivity Levels and Growth: An International Perspective (2004). School of Economics, University of Queensland, Australia / CEPA Working Papers Series (2) RePEc:sgc:wpaper:52 THE IMPACT OF CLIMATE CHANGE ON TOURISM AND RECREATION (2004). Research unit Sustainability and Global Change, Hamburg University / Working Papers Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||