|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
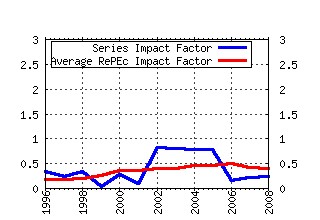
Universite de Montreal, Departement de sciences economiques / Cahiers de recherche Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Recent citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:mtl:montde:8633 Testing for a Unit Root in Time Series Regression (1986). (2) RePEc:mtl:montde:9613 Stochastic Volatility. (1996). (3) RePEc:mtl:montde:2002-18 Testing for a Unit Root in Panels with Dynamic Factors (2002). (4) RePEc:mtl:montde:9552 Estimating and Testing Linear Models with Multiple Structural Changes. (1995). (5) RePEc:mtl:montde:2003-12 Identification, Weak Instruments and Statistical Inference in Econometrics (2003). (6) RePEc:mtl:montde:2000-05 International Business Cycles: What Are the Facts? (2000). (7) RePEc:mtl:montde:2001-02 Ranking Sets of Objects (2001). (8) RePEc:mtl:montde:9607 Rank Regressions, Wage Distributions and the Gender Gap. (1996). (9) RePEc:mtl:montde:2001-29 An Eigenfunction Approach for Volatility Modeling. (2001). (10) RePEc:mtl:montde:2006-15 Population Ethics (2006). (11) RePEc:mtl:montde:9811 Simulation-Based Finite-Sample Normality Tests in Linear Regressions (1998). (12) RePEc:mtl:montde:9408 Periodic Autoregressive Conditional Heteroskedasticity. (1994). (13) RePEc:mtl:montde:9427 Useful Modifications to Some Unit Root Tests with Dependent Errors and Their Local Asymptotic Properties. (1994). (14) RePEc:mtl:montde:9536 Market Time and Asset Price Movements: Theory and Estimation. (1995). (15) RePEc:mtl:montde:2001-05 Religion and Economic Growth: Was Weber Right? (2001). (16) RePEc:mtl:montde:2003-23 Methods to Estimate Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium Models (2003). (17) RePEc:mtl:montde:2005-16 The Transmission of Monetary Policy in a Multi-Sector Economy (2005). (18) RePEc:mtl:montde:9614 The Exchange Rate in a Dynamic-Optimizing Current Account Model with Nominal Rigidities: a Quantitative Investigation. (1996). (19) RePEc:mtl:montde:2004-01 Deprivation and Social Exclusion (2004). (20) RePEc:mtl:montde:2000-06 International Transmission of the Business Cycle in a Multi-Sector Model. (2000). (21) RePEc:mtl:montde:9232 Consumption, Real Exchange Rates and the Structure of International Asset Markets. (1992). (22) RePEc:mtl:montde:2002-07 Does the Barro-Gordon Model Explain the Behavior of US Inflation? a Reexamination of the Empirical Evidence (2002). (23) RePEc:mtl:montde:9128 Duopoly and Quality Standards. (1991). (24) RePEc:mtl:montde:8424 Self-Insurance, Self-Protection and Increased Risk Aversion (1984). (25) RePEc:mtl:montde:9516 Testing for Homogeneity in Demand Systems when the Regressors Are Non-Stationary. (1995). (26) RePEc:mtl:montde:2002-05 Nonparametric Instrumental Regression (2002). (27) RePEc:mtl:montde:9028 On the Economic and Econometrics of Seasonality. (1990). (28) RePEc:mtl:montde:8612 A Study Towards a Dynamic Theory of Seasonality for Economic Time Series (1986). (29) RePEc:mtl:montde:9505 Are the Effects of Monetary Policy Asymmetric? (1995). (30) RePEc:mtl:montde:8749 The Great Crash, the Oil Prices and the Unit Root Hypothesis. (1987). (31) RePEc:mtl:montde:2005-08 Consistent House Allocation (2005). (32) RePEc:mtl:montde:9103 Structural Adjustment and Growth in a Highy Indebted Market Economy: Brazil. (1991). (33) RePEc:mtl:montde:2001-08 Simulation-Based Finite-Sample Tests for Heteroskedasticity and ARCH Effects. (2001). (34) RePEc:mtl:montde:2004-06 Interpersonal Comparisons of Well-Being (2004). (35) RePEc:mtl:montde:2002-21 Correcting the Errors : A Note on Volatility Forecast Evaluation Based on High-Frequency Data and Realized Volatilities (2002). (36) RePEc:mtl:montde:2001-07 A Prudent Central Banker (2001). (37) RePEc:mtl:montde:2002-03 Arrows Theorem in Spatial Environments (2002). (38) RePEc:mtl:montde:2002-08 Habit Formation and the Persistence of Monetary Shocks (2002). (39) RePEc:mtl:montde:2003-24 Nonlinear Monetary Policy Rules: Some New Evidence for the U.S. (2003). (40) RePEc:mtl:montde:9119 Testing Causality Between Two Vectors in Multivariate Arma Models. (1991). (41) RePEc:mtl:montde:9807 Computation and Analysis of Multiple Structural-Change Models (1998). (42) RePEc:mtl:montde:2003-09 Exact Skewness-Kurtosis Tests for Multivariate Normality and Goodness-of-fit in Multivariate Regressions with Application to Asset Pricing Models (2003). (43) RePEc:mtl:montde:2003-21 Explaining the Transition Between Exchange Rate Regimes (2003). (44) RePEc:mtl:montde:2006-02 The Dynamic (In)efficiency of Monetary Policy by Committee (2006). (45) RePEc:mtl:montde:9428 An Analysis of the Real Interest rate Under Regime Shifts. (1994). (46) RePEc:mtl:montde:9539 Some Impossibility Theorems in Econometrics with Applications to Instrumental Variables, Dynamic Models and Cointegration. (1995). (47) RePEc:mtl:montde:2000-07 Optimal Licensing Contracts and the Value of a Patent. (2000). (48) RePEc:mtl:montde:8127 Rank Tests for Serial Dependence (1981). (49) RePEc:mtl:montde:9557 Environmental Protection Producer Insolvency and Lender Liability (1995). (50) RePEc:mtl:montde:8129 Recursive Stability Analysis of Linear Regression Relationships (1981). Recent citations received in: | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 Recent citations received in: 2008 (1) RePEc:ube:dpvwib:dp0902 Priorities in the Location of Multiple Public Facilities (2008). Universitat Bern, Volkswirtschaftliches Institut / Diskussionsschriften Recent citations received in: 2007 Recent citations received in: 2006 (1) RePEc:ces:ceswps:_1697 Optimal Central Bank Design: Benchmarks for the ECB (2006). CESifo GmbH / CESifo Working Paper Series (2) RePEc:ces:ifofor:v:7:y:2006:i:4:p:35-41 Unfinished business? The ECB reform ahead of euro area enlargement (2006). CESifo Forum (3) RePEc:ess:wpaper:id:707 Premature Mortality and Poverty Measurement (2006). esocialsciences.com / Working Papers (4) RePEc:imf:imfwpa:06/281 Central Bank Boards Around the World: Why Does Membership Size Differ? (2006). International Monetary Fund / IMF Working Papers (5) RePEc:mtl:montde:2006-03 Consistent Relations (2006). Universite de Montreal, Departement de sciences economiques / Cahiers de recherche (6) RePEc:mtl:montde:2006-06 Solidarity in Choosing a Location on a Cycle (2006). Universite de Montreal, Departement de sciences economiques / Cahiers de recherche (7) RePEc:spr:revint:v:1:y:2006:i:3:p:207-235 Optimal central bank design: Benchmarks for the ECB (2006). The Review of International Organizations Recent citations received in: 2005 (1) RePEc:cir:cirwor:2005s-02 Monte Carlo tests with nuisance parameters: a general approach to finite-sample inference and non-standard asymptotics (2005). CIRANO / CIRANO Working Papers (2) RePEc:mtl:montde:2005-03 Monte Carlo Tests with Nuisance Parameters: A General Approach to Finite-Sample Inference and Nonstandard Asymptotics (2005). Universite de Montreal, Departement de sciences economiques / Cahiers de recherche (3) RePEc:mtl:montde:2005-13 Rational Choice on Arbitrary Domains: A Comprehensive Treatment (2005). Universite de Montreal, Departement de sciences economiques / Cahiers de recherche (4) RePEc:mtn:ancoec:si7 The properties of the extended Gini measures of variability and inequality (2005). Metron - International Journal of Statistics (5) RePEc:wpa:wuwpem:0503016 Causation Delays and Causal Neutralization up to Three Steps Ahead: The Money-Output Relationship Revisited (2005). EconWPA / Econometrics (6) RePEc:wpa:wuwpge:0510013 Intergenerational anonymity as an alternative to the discounted- sum criterion in the calculus of optimal growth I: Consensual optimality (2005). EconWPA / GE, Growth, Math methods (7) RePEc:wpa:wuwpge:0511007 Intergenerational anonymity as an alternative to the discounted- sum criterion in the calculus of optimal growth II: Pareto optimality and some economic interpretations (2005). EconWPA / GE, Growth, Math methods Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||