|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
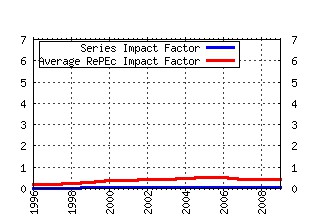
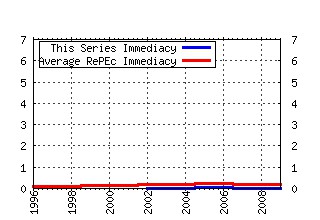
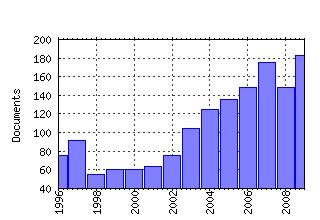
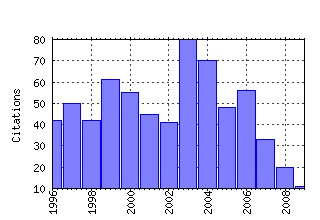
Health Policy Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Recent citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:47:y:1999:i:2:p:97-123 The contingent valuation method in health care (1999). (2) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:54:y:2000:i:2:p:87-123 Review of the literature on reference pricing (2000). (3) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:24:y:1993:i:3:p:227-238 The trade-off between severity of illness and treatment effect in cost-value analysis of health care (1993). (4) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:65:y:2003:i:1:p:21-35 Needs for further improvement: risk adjustment in the German health insurance system (2003). (5) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:63:y:2003:i:1:p:17-36 The economic impact of malaria in Africa: a critical review of the evidence (2003). (6) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:40:y:1997:i:3:p:237-255 Household income and health care expenditures in Mexico (1997). (7) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:65:y:2003:i:1:p:63-74 Risk adjustment in Switzerland (2003). (8) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:37:y:1996:i:1:p:53-72 EuroQol: the current state of play (1996). (9) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:75:y:2006:i:2:p:178-186 Life expectancy and health care expenditures: A new calculation for Germany using the costs of dying (2006). (10) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:17:y:1991:i:1:p:1-23 Economic evaluation in health care: Is there a role for cost-benefit analysis? (1991). (11) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:67:y:2004:i:2:p:149-165 Incentives and pharmaceutical reimbursement reforms in Spain (2004). (12) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:60:y:2002:i:3:p:235-254 Free choice of sickness funds in regulated competition: evidence from Germany and The Netherlands (2002). (13) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:52:y:2000:i:1:p:53-70 On hypothetical bias and calibration in cost-benefit studies (2000). (14) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:65:y:2003:i:1:p:75-98 Risk adjustment and risk selection on the sickness fund insurance market in five European countries (2003). (15) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:51:y:2000:i:1:p:19-30 A qualitative study of the extent to which health gain matters when choosing between groups of patients (2000). (16) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:60:y:2002:i:2:p:133-150 Reforming Chinas urban health insurance system (2002). (17) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:69:y:2004:i:1:p:55-72 Technical efficiency in the use of health care resources: a comparison of OECD countries (2004). (18) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:49:y:1999:i:1-2:p:63-74 Public views on health care rationing: a group discussion study (1999). (19) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:68:y:2004:i:2:p:197-209 The impact of urban health insurance reform on hospital charges: a case study from two cities in China (2004). (20) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:60:y:2002:i:3:p:201-218 Policy relevant determinants of health: an international perspective (2002). (21) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:42:y:1997:i:3:p:223-237 Willingness to pay for health insurance in a developing economy. A pilot study of the informal sector of Ghana using contingent valuation (1997). (22) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:57:y:2001:i:2:p:141-153 Scope and scale insensitivities in a contingent valuation study of risk reductions (2001). (23) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:51:y:2000:i:2:p:109-131 An update on Spains health care system: is it time for managed competition? (2000). (24) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:77:y:2006:i:3:p:268-278 Comparing hospital cost efficiency between Norway and Finland (2006). (25) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:34:y:1995:i:2:p:135-143 Value for money? A contingent valuation study of the optimal size of the Swedish health care budget (1995). (26) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:90:y:2009:i:2-3:p:140-148 Economic incentives in general practice: The impact of pay-for-participation and pay-for-compliance programs on diabetes care (2009). (27) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:44:y:1998:i:3:p:233-252 Primary health care meets the market in China and Vietnam (1998). (28) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:55:y:2001:i:1:p:51-69 Health-related quality of life by disease and socio-economic group in the general population in Sweden (2001). (29) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:57:y:2001:i:1:p:1-13 Health economics in low income countries: adapting to the reality of the unofficial economy (2001). (30) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:72:y:2005:i:2:p:201-215 Tackling excessive waiting times for elective surgery: a comparative analysis of policies in 12 OECD countries (2005). (31) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:65:y:2003:i:1:p:49-62 Risk adjusted premium subsidies and risk sharing: key elements of the competitive sickness fund market in the Netherlands (2003). (32) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:40:y:1997:i:1:p:1-12 Patients willingness to pay for autologous blood donation (1997). (33) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:60:y:2002:i:3:p:255-273 A typology for provider payment systems in health care (2002). (34) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:58:y:2001:i:1:p:1-14 The relationship between per capita income and diffusion of medical technologies (2001). (35) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:76:y:2006:i:3:p:320-333 The Norwegian hospital reform of 2002: Central government takes over ownership of public hospitals (2006). (36) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:31:y:1995:i:3:p:183-195 Evaluating the effects of GP remuneration: problems and prospects (1995). (37) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:47:y:1999:i:3:p:207-223 Public spending on health care: how are different criteria related? (1999). (38) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:71:y:2005:i:2:p:213-222 Tobacco consumption patterns and its health implications in India (2005). (39) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:83:y:2007:i:2-3:p:332-342 Care for a break? An investigation of informal caregivers attitudes toward respite care using Q-methodology (2007). (40) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:20:y:1992:i:3:p:309-320 Economic evaluation of lipid lowering -- A feasibility test of the contingent valuation approach (1992). (41) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:38:y:1996:i:3:p:189-203 Modelling valuations for health states: the effect of duration (1996). (42) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:65:y:2003:i:2:p:167-179 The availability of drugs: what does it mean in Ugandan primary care (2003). (43) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:67:y:2004:i:1:p:57-74 The impact of ageing on hospital care and long-term care--the example of Germany (2004). (44) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:70:y:2004:i:2:p:217-228 Willingness to pay for public health care: a comparison of two approaches (2004). (45) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:35:y:1996:i:3:p:205-216 An epidemiological approach towards measuring the trade-off between equity and efficiency in health policy (1996). (46) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:46:y:1998:i:1:p:21-41 The new pharmaceutical policy in Italy (1998). (47) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:38:y:1996:i:3:p:155-171 Is community financing necessary and feasible for rural China? (1996). (48) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:68:y:2004:i:1:p:47-54 The effect of generic competition on the price of brand-name drugs (2004). (49) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:65:y:2003:i:1:p:5-19 Belgium: risk adjustment and financial responsibility in a centralised system (2003). (50) RePEc:eee:hepoli:v:66:y:2003:i:1:p:73-93 Service production and contract choice in primary physician services (2003). Recent citations received in: | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 Recent citations received in: 2009 (1) RePEc:bol:bodewp:660 Incentives In Primary Care and Their Impact on Potentially Avoidable Hospital Admissions (2009). Working Papers (2) RePEc:wly:hlthec:v:18:y:2009:i:s2:p:s7-s23 Chinas health system and its reform: a review of recent studies (2009). Health Economics Recent citations received in: 2008 (1) RePEc:zbw:udewwd:167 Die Aufhebung des Fremd- und Mehrbesitzverbotes im deutschen Apothekenwesen vor dem Hintergrund internationaler Erfahrungen im Vereinigten Königreich und in Norwegen (2008). Diskussionsbeiträge Recent citations received in: 2007 (1) RePEc:her:chewps:2007/12 The provision of informal care in terminal illness: An analysis of carers needs using a discrete choice experiment (2007). Working Papers (2) RePEc:pra:mprapa:3354 The advantages and disadvantages of needs-based resource allocation in integrated health systems and market systems of health care provider reimbursement (2007). MPRA Paper (3) RePEc:pra:mprapa:6093 Hospital Choice: Survey Evidence From Istanbul (2007). MPRA Paper Recent citations received in: 2006 (1) RePEc:hhs:bergec:2006_002 Centralized or decentralized? A case study of Norwegian hospital reform (2006). Working Papers in Economics (2) RePEc:lug:wpaper:0607 Small area variations and welfare loss in the use of antibiotics in the community (2006). Quaderni della facoltà di Scienze economiche dell'Università di Lugano (3) RePEc:ner:leuven:urn:hdl:123456789/119264 Acceptable costs and risk adjustment: Policy choices and ethical trade-offs. (2006). Open Access publications from Katholieke Universiteit Leuven (4) RePEc:zbw:grewdp:092006 Demographischer Wandel, medizinischer Fortschritt und Ausgaben für Gesundheitsleistungen: eine theoretische Analyse (2006). Wirtschaftswissenschaftliche Diskussionspapiere (5) RePEc:zbw:grewdp:102006 Gesundheitsausgaben für Ãberlebende und Verstorbene im demographischen Wandel: der Einfluss des medizinischen Fortschritts (2006). Wirtschaftswissenschaftliche Diskussionspapiere Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||