|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
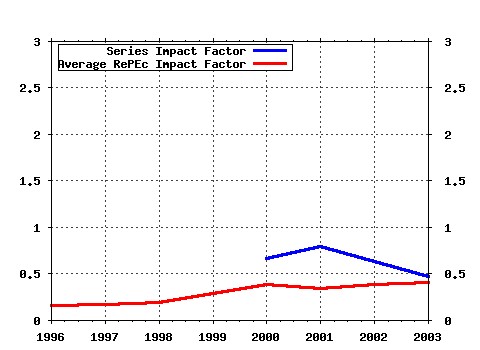
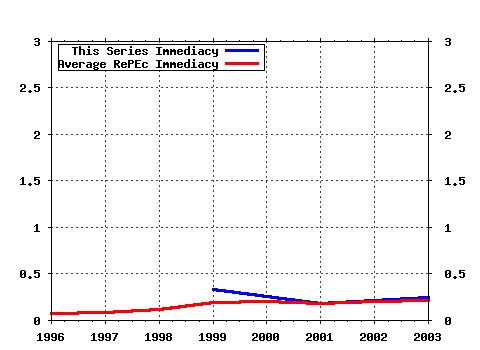
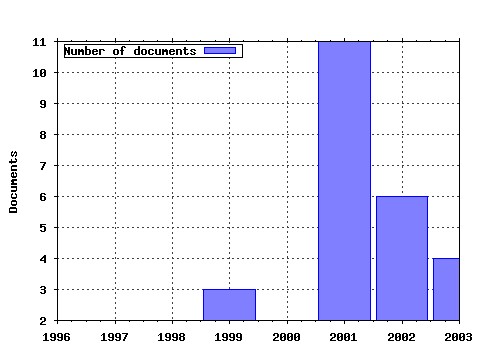
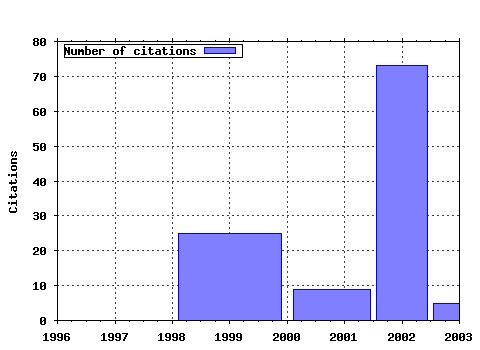
Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Latest citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:pri:cheawb:262 Economic status and health in childhood: the origins of the gradient (2002). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (2) RePEc:pri:cheawb:279 Mortality, education, income and inequality among American cohorts (1999). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (3) RePEc:pri:cheawb:249 EXPERIMENTAL ANALYSIS OF NEIGHBORHOOD EFFECTS ON YOUTH (2004). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (4) RePEc:pri:cheawb:248 YOUTH CRIMINAL BEHAVIOR IN THE MOVING TO OPPORTUNITY EXPERIMENT (2004). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (5) RePEc:pri:cheawb:256 Orphans in Africa: Parental Death, Poverty and School Enrollment (2004). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (6) RePEc:pri:cheawb:280 Inequalities in income and inequalities in health (1999). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (7) RePEc:pri:cheawb:275 Relative deprivation, inequality, and mortality (2001). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (8) RePEc:pri:cheawb:245 Health in an age of globalization (2004). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (9) RePEc:pri:cheawb:255 Health Inequality, Education and Medical Innovation (2003). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (10) RePEc:pri:cheawb:235 The Determinants of Mortality (2005). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (11) RePEc:pri:cheawb:236 Health and wealth among the poor: India and South Africa compared (2005). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (12) RePEc:pri:cheawb:230 Child mortality, income and adult height (2007). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (13) RePEc:pri:cheawb:26 Global patterns of income and health: facts, interpretations, and policies (2006). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (14) RePEc:pri:cheawb:263 Mortality, inequality and race in American cities and states (2002). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (15) RePEc:pri:cheawb:231 Global patterns of income and health: facts, interpretations, and policies (2006). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (16) RePEc:pri:cheawb:27 Stature and status: Height, ability, and labor market outcomes (2006). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (17) RePEc:pri:cheawb:250 Booms, Busts, and Babiesâ Health (2004). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (18) RePEc:pri:cheawb:278 Work, Welfare, and Child Maltreatment (1999). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (19) RePEc:pri:cheawb:272 The Relationship Between Education and Adult Mortality in the U. S. (2001). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (20) RePEc:pri:cheawb:242 Child Health and Economic Crisis in Peru (2004). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (21) RePEc:pri:cheawb:268 Does Money Protect Health Status?
Evidence from South African Pensions (2001). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (22) RePEc:pri:cheawb:239 Cognitive Development Among Young Children in Ecuador:
The Roles of Wealth, Health and Parenting (2005). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (23) RePEc:pri:cheawb:265 Relative Deprivation, Poor Health Habits and Mortality (2001). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (24) RePEc:pri:cheawb:252 Medical Compliance and Income-Health Gradients (2004). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (25) RePEc:pri:cheawb:261 Consumption, health, gender and poverty (2002). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (26) RePEc:pri:cheawb:240 The impact of parental death on school enrollment and achievement: Longitudinal evidence from South Africa (2005). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (27) RePEc:pri:cheawb:266 Efficacy and cost-effectiveness of environmental management for malaria control (2001). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (28) RePEc:pri:cheawb:254 The Reach of The South African Child Support Grant: Evidence from KwaZulu-Natal (2003). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (29) RePEc:pri:cheawb:264 Welfare Reforms, Family Resources, and Child Maltreatment (2001). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers (30) RePEc:pri:cheawb:234 Health and wellbeing in Udaipur and South Africa (2006). Princeton University, Woodrow Wilson School of Public and International Affairs, Center for Health and Wellbeing. / Working Papers Latest citations received in: | 2003 | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 Latest citations received in: 2003 (1) RePEc:erm:papers:0317 Health Status and Socio-Economic Inequalities : A Review of the French Litterature (2003). ERMES, University Paris 2 / Working Papers ERMES Latest citations received in: 2002 Latest citations received in: 2001 (1) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:8556 Changes in the Age Distribution of Mortality Over the 20th Century (2001). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (2) RePEc:wop:jopovw:217 Welfare Reform and Child Well-being (2001). Northwestern University/University of Chicago Joint Center for Poverty Research / JCPR Working Papers Latest citations received in: 2000 Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |