|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
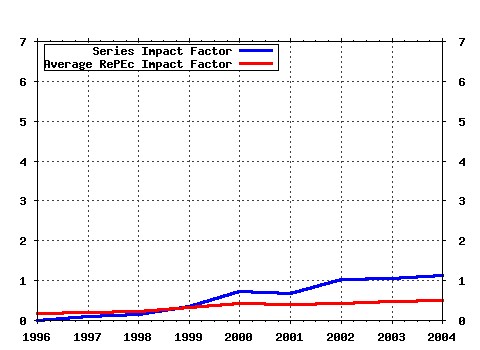
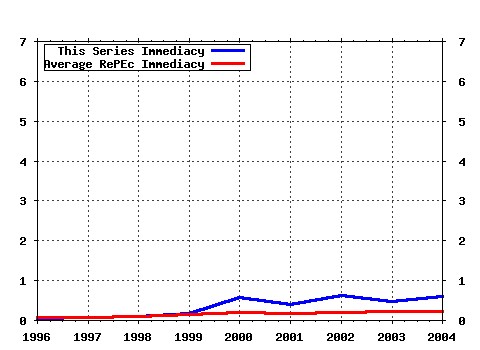
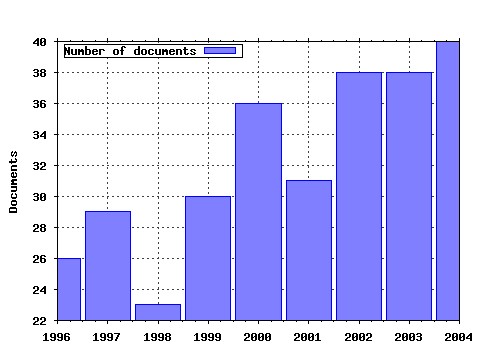
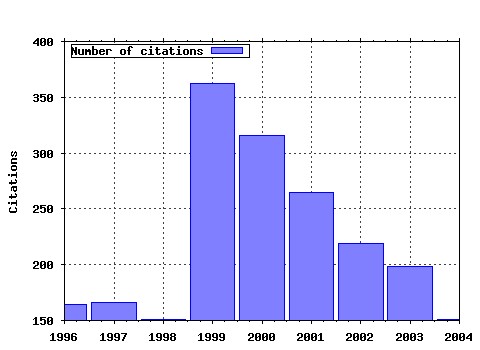
Labour Economics Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Latest citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:4:y:1997:i:4:p:341-372 Job satisfaction and gender: Why are women so happy at work? (1997). (2) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:7:y:2000:i:5:p:471-505 Self-employment in OECD countries (2000). (3) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:6:y:1999:i:2:p:253-275 The measurement and structure of household wealth (1999). (4) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:9:y:2002:i:1:p:63-91 Temporary jobs, employment protection and labor market performance (2002). (5) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:8:y:2001:i:2:p:131-159 Employment protection (2001). (6) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:3:y:1996:i:1:p:65-80 Tax progression is good for employment in popular models of trade union behaviour (1996). (7) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:6:y:1999:i:1:p:95-118 Desired and actual labour supply of unmarried men and women in the Netherlands (1999). (8) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:6:y:1999:i:1:p:1-20 Product markets and labour markets1 (1999). (9) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:9:y:2002:i:5:p:601-630 Gross worker and job flows in a transition economy: an analysis of Estonia (2002). (10) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:1:y:1994:i:2:p:187-201 Personal contacts and earnings : It is who you know! (1994). (11) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:6:y:1999:i:2:p:179-202 The dynamic effects of health on the labor force transitions of older workers (1999). (12) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:7:y:2000:i:5:p:629-663 Business start-ups by the unemployed -- an econometric analysis based on firm data (2000). (13) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:8:y:2001:i:2:p:223-242 What really matters in a job? Hedonic measurement using quit data (2001). (14) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:10:y:2003:i:5:p:499-530 The costs of hiring and separations (2003). (15) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:6:y:1999:i:4:p:453-470 A review of estimates of the schooling/earnings relationship, with tests for publication bias (1999). (16) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:7:y:2000:i:5:p:575-601 Business start-ups or disguised unemployment? Evidence on the character of self-employment from transition economies (2000). (17) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:7:y:2000:i:2:p:153-180 Spell durations with long unemployment insurance periods (2000). (18) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:7:y:2000:i:4:p:409-426 An examination of cross-country differences in the gender gap in labor force participation rates (2000). (19) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:1:y:1993:i:1:p:85-113 Efficient contracts are on the labour demand curve : Theory and facts (1993). (20) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:6:y:1999:i:3:p:435-452 Optimal tax progressivity in imperfect labour markets (1999). (21) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:1:y:1994:i:3-4:p:303-326 A model of labor demand with linear adjustment costs (1994). (22) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:3:y:1996:i:3:p:337-356 The gender wage gap in Russia: Some empirical evidence (1996). (23) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:10:y:2003:i:2:p:105-131 The real thin theory: monopsony in modern labour markets (2003). (24) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:8:y:2001:i:1:p:103-129 Widening differences in Italian regional unemployment (2001). (25) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:11:y:2004:i:3:p:355-371 Does education reduce wage inequality? Quantile regression evidence from 16 countries (2004). (26) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:4:y:1997:i:4:p:373-418 Social security and the labor supply of older married couples (1997). (27) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:9:y:2002:i:1:p:1-16 Estimates of the economic return to schooling for 28 countries (2002). (28) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:5:y:1998:i:1:p:1-24 War of the models: Which labour market institutions for the 21st century?1 (1998). (29) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:5:y:1998:i:3:p:313-329 Sample selection rules and the intergenerational correlation of earnings (1998). (30) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:6:y:1999:i:4:p:581-593 Education and wages in the Czech and Slovak Republics during transition (1999). (31) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:12:y:2005:i:2:p:269-280 Incentives and selection in cyclical absenteeism (2005). (32) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:2:y:1995:i:3:p:275-297 Formal and informal sector employment in urban areas of Bolivia (1995). (33) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:7:y:2000:i:5:p:545-574 Effects of the United States tax system on transitions into self-employment (2000). (34) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:5:y:1998:i:4:p:425-448 Measuring wage effects of plant size (1998). (35) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:7:y:2000:i:1:p:1-19 Returns to firm-provided training: evidence from French worker-firm matched data1 (2000). (36) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:8:y:2001:i:1:p:15-41 Estimating wage losses of displaced workers in Germany (2001). (37) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:3:y:1996:i:3:p:255-278 Matching across space: Evidence on mobility in the Czech Republic (1996). (38) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:3:y:1996:i:3:p:233-254 Regional mismatch and the transition to a market economy (1996). (39) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:8:y:2001:i:3:p:313-333 Externalities in the matching of workers and firms in ritain (2001). (40) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:8:y:2001:i:2:p:291-308 The intensification of work in Europe (2001). (41) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:10:y:2003:i:2:p:185-203 Synchronous leisure, jointness and household labor supply (2003). (42) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:8:y:2001:i:2:p:181-202 The incentive for working hard: explaining hours worked differences in the US and Germany (2001). (43) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:7:y:2000:i:1:p:79-93 Is tax progression really good for employment? A model with endogenous hours of work (2000). (44) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:11:y:2004:i:4:p:487-506 Evaluating the effectiveness of private education across countries: a comparison of methods (2004). (45) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:5:y:1998:i:3:p:295-312 Were communists good human capitalists? The case of the Czech Republic (1998). (46) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:2:y:1995:i:1:p:67-76 The wage effects of overschooling revisited (1995). (47) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:9:y:2002:i:6:p:717-735 The search for success: do the unemployed find stable employment? (2002). (48) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:10:y:2003:i:2:p:205-214 Dispersion in the economic return to schooling (2003). (49) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:10:y:2003:i:4:p:399-406 Why labour market experiments? (2003). (50) RePEc:eee:labeco:v:8:y:2001:i:4:p:419-442 Three observations on wages and measured cognitive ability (2001). Latest citations received in: | 2004 | 2003 | 2002 | 2001 Latest citations received in: 2004 (1) RePEc:aea:aecrev:v:94:y:2004:i:2:p:212-216 The Structure of Wages and Internal Mobility (2004). American Economic Review (2) RePEc:anp:en2004:135 ENTREPRENEURSHIP AND LIQUIDITY CONSTRAINTS IN DEPRIVED AREAS: EVIDENCE FROM THE SLUMS OF RIO DE JANEIRO (2004). ANPEC - Associação Nacional do Centros de Pos-graduação em Economia [Brazilian Association of Graduate Programs in Economics] / Anais do XXXII Encontr (3) RePEc:ctl:louvir:2004025 Low-Skilled Unemployment, Capital-Skill Complementarity and Embodied Technical Progress (2004). Université catholique de Louvain, Institut de Recherches Economiques et Sociales (IRES) / Université catholique de Louvain, Institut de Recherches Eco (4) RePEc:ctl:louvir:2004031 The impact of technological and organizatioanl changes on labor flows. Evidence on French establishments (2004). Université catholique de Louvain, Institut de Recherches Economiques et Sociales (IRES) / Université catholique de Louvain, Institut de Recherches Eco (5) RePEc:ctl:louvir:2004032 Tax Progression in Imperfect Labour Markets : A Survey (2004). Université catholique de Louvain, Institut de Recherches Economiques et Sociales (IRES) / Université catholique de Louvain, Institut de Recherches Eco (6) RePEc:ctl:louvir:2004035 Impact of Selective Reductions in Labor Taxation (2004). Université catholique de Louvain, Institut de Recherches Economiques et Sociales (IRES) / Université catholique de Louvain, Institut de Recherches Eco (7) RePEc:deg:conpap:c009_028 Risky Human Capital Investment, Income Distribution, and Macroeconomic Dynamics (2004). Dynamics, Economic Growth, and International Trade (DEGIT) / Conference Papers (8) RePEc:del:abcdef:2004-25 The impact of technological and organizational changes on labor flows. Evidence on French establishments. (2004). DELTA (Ecole normale supérieure) / DELTA Working Papers (9) RePEc:dgr:umamet:2004028 Hourly wages and working time in the Dutch market sector 1962-1995 (2004). Maastricht : METEOR, Maastricht Research School of Economics of Technology and Organization / Research Memoranda (10) RePEc:dia:wpaper:dt200409 Which Human Capital Matters for Rich and Poors Wages?Evidence from Matched Worker-Firm Data from Tunisia (2004). DIAL (Développement, Institutions & Analyses de Long terme) / Working Papers (11) RePEc:dlw:wpaper:04-01 A Quantile Regression Analysis of Wages in Panama. (2004). University of Delaware, Department of Economics / Working Papers (12) RePEc:ebl:ecbull:v:10:y:2004:i:8:p:1-8 Education as advertisement (2004). Economics Bulletin (13) RePEc:erm:papers:0406 On the Optimality of Search Matching Equilibrium when workers are risk adverse (2004). ERMES, University Paris 2 / Working Papers ERMES (14) RePEc:ese:iserwp:2004-18 Minimum Wages Enhancing Trainers Incentives (2004). Institute for Social and Economic Research / ISER working papers (15) RePEc:iab:iabfob:200405 Mehr Beschäftigung durch längere Arbeitszeiten? : ein Beitrag zu der Diskussion um eine generelle Erhöhung der Arbeitszeit (2004). Institut für Arbeitsmarkt und Berufsforschung (IAB), Nürnberg [Institute for Employment Research, Nuremberg, Germany] / IAB-Forschungsbericht (16) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1204 Wage Differentials and International Trade in Italy Using Individual Micro Data 1991-1996 (2004). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (17) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1265 High Performance Workplace Practices and Job Satisfaction: Evidence from Europe (2004). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (18) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1276 Wage Determination under Communism and in Transition: Evidence from Central Europe (2004). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (19) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1336 Diploma No Problem: Can Private Schools Be of Lower Quality than Public Schools? (2004). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (20) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1348 In the Right Place at the Wrong Time: The Role of Firms and Luck in Young Workersâ Careers (2004). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (21) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1364 Labor Market Institutions and the Employment-Productivity Trade-Off: A Wage Posting Approach (2004). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (22) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1382 Firm-Level Social Returns to Education (2004). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (23) RePEc:mil:wpdepa:2004-25 Technology, MNEs activity and Italian skill upgrading (2004). Department of Economics University of Milan Italy / Departemental Working Papers (24) RePEc:wdi:papers:2004-717 Wage Determination Under Communism and In Transition: Evidence from Central Europe (2004). William Davidson Institute at the University of Michigan Stephen M. Ross Business School / William Davidson Institute Working Papers Series Latest citations received in: 2003 (1) RePEc:ces:ceswps:_918 The Rise and Fall of Swedish Unemployment (2003). CESifo GmbH / CESifo Working Paper Series (2) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:3722 Search Intensity, Cost of Living and Local Labour Markets in Britain (2003). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (3) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:3905 Household Labour Supply and Welfare Participation in Sweden (2003). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (4) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:3993 Does Education Raise Productivity or Just Reflect It? (2003). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (5) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:4058 Efficiency Wages and Unemployment in Cities: The Case of High Relocation Costs (2003). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (6) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:4153 Efficiency Wages, Urban Unemployment and Housing Consumption (2003). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (7) RePEc:diw:diwwpp:dp368 Nobody to Play with? : The Implications of Leisure Coordination (2003). DIW Berlin, German Institute for Economic Research / Discussion Papers of DIW Berlin (8) RePEc:ese:iserwp:2003-19 Nobody to Play With? The Implications of Leisure Co-Ordination (2003). Institute for Social and Economic Research / ISER working papers (9) RePEc:hhs:iuiwop:0606 Efficiency Wages, Urban Unemployment and Housing Consumption (2003). The Research Institute of Industrial Economics / IUI Working Paper Series (10) RePEc:hhs:iuiwop:0607 Search Activities, Cost of Living and Local Labor Markets (2003). The Research Institute of Industrial Economics / IUI Working Paper Series (11) RePEc:hhs:uunewp:2003_013 The Rise and Fall of Swedish Unemployment (2003). Uppsala University, Department of Economics / Working Paper Series (12) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp769 Household Labor Supply and Welfare Participation in Sweden (2003). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (13) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp793 Foreign Direct Investment, Labour Market Regulation and Self-Interested Governments (2003). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (14) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp850 Nobody to Play With? The Implications of Leisure Coordination (2003). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (15) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp963 Compensating Wage Differentials for Schooling Risk in Denmark (2003). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (16) RePEc:may:mayecw:n1271003 Compensating Wage Differentials for Schooling Risk in Denmark (2003). Department of Economics, National University of Ireland - Maynooth / Economics Department Working Paper Series (17) RePEc:taf:applec:v:35:y:2003:i:18:p:1911-1914 Quits, layoffs, and job destruction (2003). Applied Economics (18) RePEc:upf:upfgen:714 Nonparametric Bounds on The Returns to Language Skills (2003). Department of Economics and Business, Universitat Pompeu Fabra / Economics Working Papers Latest citations received in: 2002 (1) RePEc:aea:jecper:v:16:y:2002:i:3:p:153-170 The Central Role of Entrepreneurs in Transition Economies (2002). Journal of Economic Perspectives (2) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:3531 So Many Rocket Scientists, so Few Marketing Clerks: Occupational Mobility in Times of Rapid Technological Change (2002). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (3) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:3614 Unemployment Compensation Finance and Aggregate Employment Fluctuations (2002). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (4) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:3663 The Reallocation of Workers and Jobs in Russian Industry: New Evidence on Measures and Determinants (2002). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (5) RePEc:dnb:wormem:712 On Wage Formation, Wage Development and Unemployment Flexibility: a Comparison between European Countries and the United States (2002). Netherlands Central Bank, Research Department / WO Research Memoranda (discontinued) (6) RePEc:ecj:econjl:v:112:y:2002:i:480:p:f214-f244 The Perverse Effects of Partial Labour Market Reform: fixed--Term Contracts in France (2002). Economic Journal (7) RePEc:hwe:certdp:0208 Job Reallocation and Productivity Growth under Alternative Economic Systems and Policies: Evidence from the Soviet Transition (2002). Centre for Economic Reform and Transformation, Heriot Watt University / CERT Discussion Papers (8) RePEc:hwe:certdp:0210 The Incidence and Cost of Job Loss in a Transition Economy: Displaced Workers in Estonia, 1989-1999 (2002). Centre for Economic Reform and Transformation, Heriot Watt University / CERT Discussion Papers (9) RePEc:irs:iriswp:2002-04 Returns to education and experience in self-employment: Evidence from Germany (2002). IRISS at CEPS/INSTEAD / IRISS Working Paper Series (10) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp564 The Reallocation of Workers and Jobs in Russian Industry: New Evidence on Measures and Determinants (2002). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (11) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp644 Job Reallocation and Productivity Growth Under Alternative Economic Systems and Policies: Evidence from the Soviet Transition (2002). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (12) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp657 Employment Consequences of Restrictive Permanent Contracts: Evidence from Spanish Labor Market Reforms (2002). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (13) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp675 Gross Job Flows in Ukraine: Size, Ownership and Trade Effects (2002). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (14) RePEc:jku:econwp:2002_06 Job search methods, intensity and success in Britain in the 1990s (2002). Department of Economics, Johannes Kepler University Linz, Austria / Economics working papers (15) RePEc:kud:kuieca:2002_03 Returning Long-Term Sick-Listed to Work - The effects of education in a competing risk model with time varying covariates and unobserved heterogeneity (2002). University of Copenhagen. Institute of Economics. Centre for Applied Microeconometrics / CAM Working Papers (16) RePEc:lic:licosd:12002 Do Schumpeterian Waves of Creative Destruction Lead to Higher Productivity? Panel Data Evidence from Poland (2002). LICOS - Centre for Institutions and Economic Performance, K.U.Leuven / LICOS Discussion Papers (17) RePEc:lic:licosd:12602 Gross Job Flows in Ukraine: Size, Ownership and Trade Effects (2002). LICOS - Centre for Institutions and Economic Performance, K.U.Leuven / LICOS Discussion Papers (18) RePEc:mcm:deptwp:2002-14 Asset Accumulation and Short Term Employment (2002). McMaster University / Department of Economics Working Papers (19) RePEc:upf:upfgen:651 Employment Consequences of Restrictive Permanent Contracts: Evidence from Spanish Labor Market Reforms (2002). Department of Economics and Business, Universitat Pompeu Fabra / Economics Working Papers (20) RePEc:upj:weupjo:02-83 The Reallocation of Workers and Jobs in Russian Industry: New Evidence on Measures and Determinants (2002). W.E. Upjohn Institute for Employment Research / Staff Working Papers (21) RePEc:upj:weupjo:02-88 Job Reallocation and Productivity Growth Under Alternative Economic Systems and Policies: Evidence from the Soviet Transition (2002). W.E. Upjohn Institute for Employment Research / Staff Working Papers (22) RePEc:wdi:papers:2002-490 The Reallocation of Workers and Jobs in Russian Industry: New Evidence on Measures and Determinants (2002). William Davidson Institute at the University of Michigan Stephen M. Ross Business School / William Davidson Institute Working Papers Series (23) RePEc:wdi:papers:2002-514 Job Reallocation and Productivity Growth under Alternative Economic Systems and Policies: Evidence from the Soviet Transition (2002). William Davidson Institute at the University of Michigan Stephen M. Ross Business School / William Davidson Institute Working Papers Series (24) RePEc:wdi:papers:2002-521 Gross Job Flows in Ukraine: Size, Ownership and Trade Effects (2002). William Davidson Institute at the University of Michigan Stephen M. Ross Business School / William Davidson Institute Working Papers Series Latest citations received in: 2001 (1) RePEc:ces:ceswps:_414 Beyond National Institutions: Labor Taxes and Regional Unemployment in Italy (2001). CESifo GmbH / CESifo Working Paper Series (2) RePEc:ces:ceswps:_582 Redundancy Pay and Collective Dismissals (2001). CESifo GmbH / CESifo Working Paper Series (3) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:2806 Improving Nurse Retention in the National Health Service in England: The Impact of Job Satisfaction on Intentions to Quit (2001). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (4) RePEc:cte:wsrepe:ws013824 INNOVATION AND JOB CREATION AND DESTRUCTION: EVIDENCE FROM SPAIN (2001). Universidad Carlos III, Departamento de Estadística y Econometría / Statistics and Econometrics Working Papers (5) RePEc:diw:diwwpp:dp255 Life Course Risks, Mobility Regimes, and Mobility Consequences : A Comparison of Sweden, Germany and the U.S. (2001). DIW Berlin, German Institute for Economic Research / Discussion Papers of DIW Berlin (6) RePEc:hhs:sunrpe:2001_0012 On the Determinants of Labour Market Institutions: Rent Seeking vs. Social Insurance (2001). Stockholm University, Department of Economics / Research Papers in Economics (7) RePEc:ivi:wpasad:2001-25 INNOVATION AND JOB CREATION AND DESTRUCTION: EVIDENCE FROM SPAIN (2001). Instituto Valenciano de Investigaciones Económicas, S.A. (Ivie) / Working Papers. Serie AD (8) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp335 Disaggregate Matching Functions (2001). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (9) RePEc:lan:wpaper:000034 The school-to-work transition, skill preferences and matching (2001). Lancaster University Management School, Economics Department / Working Papers (10) RePEc:man:sespap:0113 The Determinants of Work Effort: Evidence from the Employment in Britain Survey (2001). School of Economics, The University of Manchester / The School of Economics Discussion Paper Series (11) RePEc:ukc:ukcedp:0109 Job Insecurity and Wage Outcomes in Britain (2001). Department of Economics, University of Kent / Studies in Economics (12) RePEc:wpc:wplist:wp02_01 JOINT DECISIONS ON HOUSEHOLD MEMBERSHIP AND HUMAN CAPITAL ACCUMULATION OF YOUTHS The role of expected earnings and local markets (2001). CHILD - Centre for Household, Income, Labour and Demographic economics - ITALY / CHILD Working Papers Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |