|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
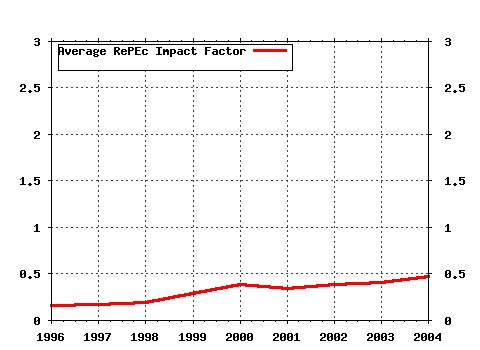
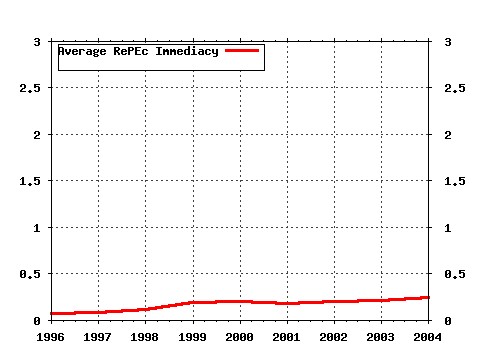
Society for Computational Economics / Computing in Economics and Finance 2005 Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Latest citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:sce:scecf5:478 Monetary Policy under Uncertainty in Micro-Founded Macroeconometric Models (2005). (2) RePEc:sce:scecf5:323 Do Actions Speak Louder Than Words?The Response of Asset Prices to Monetary Policy Actions and Statements (2005). (3) RePEc:sce:scecf5:108 Monetary Policy with Model Uncertainty: Distribution Forecast Targeting (2005). (4) RePEc:sce:scecf5:474 Term Structure Estimation with Survey Data on Interest Rate Forecasts (2005). (5) RePEc:sce:scecf5:128 Expansionary Fiscal Shocks and the Trade Deficit (2005). (6) RePEc:sce:scecf5:60 How the Bundesbank really conducted monetary policy (2005). (7) RePEc:sce:scecf5:183 A QUANTITATIVE COMPARISON OF STICKY-PRICE AND STICKY-INFORMATION MODELS OF PRICE SETTING (2005). (8) RePEc:sce:scecf5:321 A Limited Information Approach to the Simultaneous Estimation of Wage and Price Dynamics (2005). (9) RePEc:sce:scecf5:80 Monetary Policy under Adaptive Learning (2005). (10) RePEc:sce:scecf5:87 Persistence and Nominal Inertia in a Generalized Taylor Economy: How Longer Contracts Dominate Shorter Contracts (2005). (11) RePEc:sce:scecf5:304 Accounting for Changes in the Homeownership Rate (2005). (12) RePEc:sce:scecf5:141 Approximate Aggregation (2005). (13) RePEc:sce:scecf5:388 The Design of Monetary and Fiscal Policy: A Global Perspective (2005). (14) RePEc:sce:scecf5:457 Gains from International Monetary Policy Coordination: Does It Pay to Be Different? (2005). (15) RePEc:sce:scecf5:400 Robust Monetary Policy with Imperfect Knowledge (2005). (16) RePEc:sce:scecf5:452 Optimal Interest Rate Rules, Asset Prices and Credit Frictions (2005). (17) RePEc:sce:scecf5:431 DSGE Models in a Data-Rich Environment (2005). (18) RePEc:sce:scecf5:102 Non-Ricardian Households and Fiscal Policy in an Estimated DSGE Model of the Euro Area (2005). (19) RePEc:sce:scecf5:37 Commercial Mortgage Backed Securities: How Much Subordination is Enough? (2005). (20) RePEc:sce:scecf5:98 Measuring the Effects of Employment Protection on Job Flows: Evidence from Seasonal Cycles (2005). (21) RePEc:sce:scecf5:252 Trend and Cycles: A New Approach and Explanations of Some Old Puzzles (2005). (22) RePEc:sce:scecf5:107 U.K. Monetary Regimes and Macroeconomic Stylised Facts (2005). (23) RePEc:sce:scecf5:169 Welfare Effects of Tax Policy in Open Economies: Stabilization and Cooperation (2005). (24) RePEc:sce:scecf5:370 Price setting in General Equilibrium: Alternative Specifications (2005). (25) RePEc:sce:scecf5:427 Simple Pricing Rules, the Phillips Curve and the Microfoundations of Inflation Persistence (2005). (26) RePEc:sce:scecf5:123 Aging, pension reform, and capital flows: A multi-country simulation model (2005). (27) RePEc:sce:scecf5:202 Estimating the Stochastic Discount Factor without a Utility Function (2005). (28) RePEc:sce:scecf5:405 On the Benefits of Exchange Rate Flexibility under Endogenous Tradedness of Goods (2005). (29) RePEc:sce:scecf5:186 Spurious regression under broken trend stationarity (2005). (30) RePEc:sce:scecf5:134 Time Consistent Policy in Markov Switching Models (2005). (31) RePEc:sce:scecf5:459 Measuring Inflation Persistence: A Structural Time Series Approach (2005). (32) RePEc:sce:scecf5:258 Common Trends and Common Cycles in Latin America: A 2-step vs an Iterative Approach (2005). (33) RePEc:sce:scecf5:191 Vacancy Persistence (2005). (34) RePEc:sce:scecf5:293 The Fed and the Stock Market (2005). (35) RePEc:sce:scecf5:298 A Two Sector Small Open Economy Model. Which Inflation to Target? (2005). (36) RePEc:sce:scecf5:140 Extreme Value Theory and Fat Tails in Equity Markets (2005). (37) RePEc:sce:scecf5:33 Model Uncertainty and Endogenous Volatility (2005). (38) RePEc:sce:scecf5:275 On the Effects of Redistribution on Growth and Entrepreneurial Risk-Taking (2005). (39) RePEc:sce:scecf5:127 Bias in Federal Reserve Inflation Forecasts: Is the Federal Reserve Irrational or Just Cautious? (2005). (40) RePEc:sce:scecf5:205 The Scarring Effect of Recessions (2005). (41) RePEc:sce:scecf5:412 A Computational Approach to Proving Uniqueness in Dynamic Games (2005). (42) RePEc:sce:scecf5:147 Optimal Nonlinear Policy: Signal Extraction with a Non-Normal Prior (2005). (43) RePEc:sce:scecf5:351 Agency Conflicts, Investment, and Asset Pricing (2005). (44) RePEc:sce:scecf5:49 Climate Change and Extreme Events: an Assessment of Economic Implications (2005). (45) RePEc:sce:scecf5:25 The Optimal Inflation Buffer with a Zero Bound on Nominal Interest Rates (2005). (46) RePEc:sce:scecf5:138 Central Bank Estimates of the Unemployment Natural Rate (2005). (47) RePEc:sce:scecf5:215 Using Copulas to Construct Bivariate Foreign Exchange Distributions with an Application to the Sterling Exchange Rate Index (2005). (48) RePEc:sce:scecf5:62 Monetary and Fiscal Interactions without Commitment and the Value of Monetary Conservatism (2005). (49) RePEc:sce:scecf5:277 Social Networks in Labor Markets: The Effects of Symmetry, Randomness and Exclusion on Output and Inequality (2005). (50) RePEc:sce:scecf5:46 Measuring the NAIRU with Reduced Uncertainty: A Multiple Indicator-Common Component Approach (2005). Latest citations received in: | 2004 | 2003 | 2002 | 2001 Latest citations received in: 2004 Latest citations received in: 2003 Latest citations received in: 2002 Latest citations received in: 2001 Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |