|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
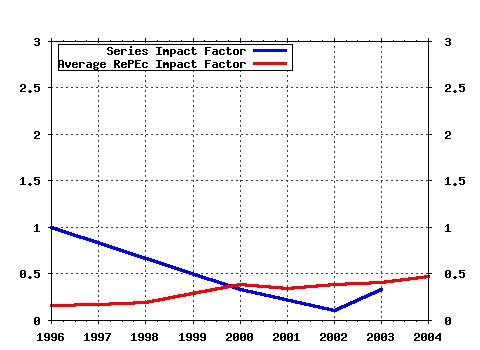
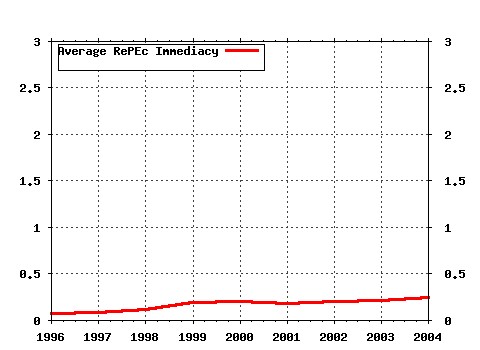
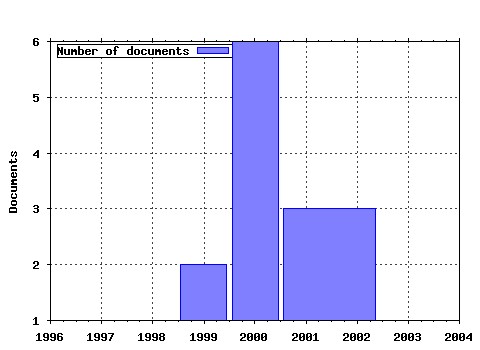
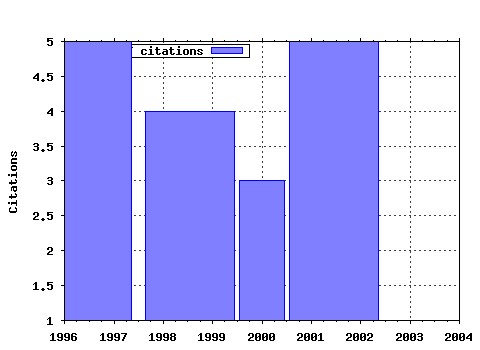
Political Economy Research Institute, University of Massachusetts at Amherst / Published Studies Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Latest citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:uma:perips:ps1 Inequality as a Cause of Environmental Degradation (1994). (2) RePEc:uma:perips:ps14 Ecological Distribution, Agricultural Trade Liberalization, and In Situ
Genetic Diversity (1996). (3) RePEc:uma:perips:ps4 Creating International Credit Rules and the Multilateral Agreement on
Investment: What are the Alternatives? (1999). (4) RePEc:uma:perips:ps13 From Natural Resources to Natural Assets (2001). (5) RePEc:uma:perips:ps6 Structural Contradictions of the Global Neoliberal Regime (2000). (6) RePEc:uma:perips:ps7 Trading State-Led Prosperity for Market Led Stagnation: From the
Golden Age to Global Neoliberalism (2000). (7) RePEc:uma:perips:ps11 To Honor and Obey: Efficiency, Inequality and Patriarchal Property Rights (2001). (8) RePEc:uma:perips:ps9 Koreas Neoliberal Restructuring: Miracle or Disaster? (2001). (9) RePEc:uma:perips:ps17 Economic Analysis of the Florida Minimum Wage Proposal (2004). Latest citations received in: | 2004 | 2003 | 2002 | 2001 Latest citations received in: 2004 Latest citations received in: 2003 Latest citations received in: 2002 Latest citations received in: 2001 Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |