|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
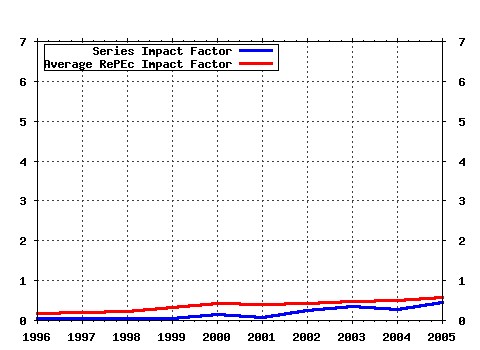
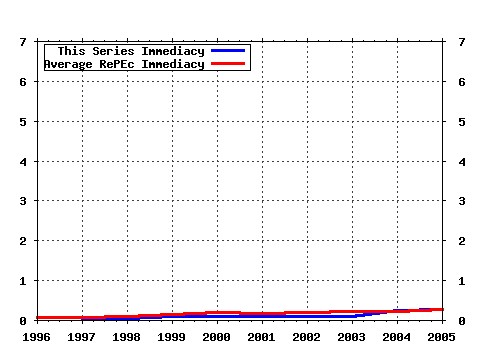
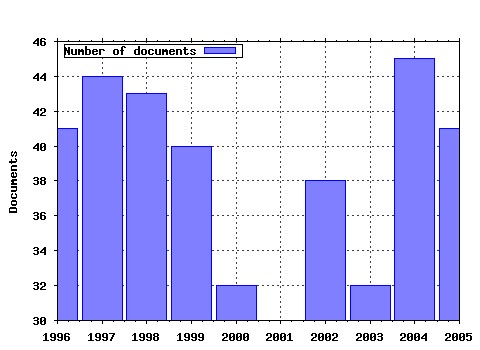
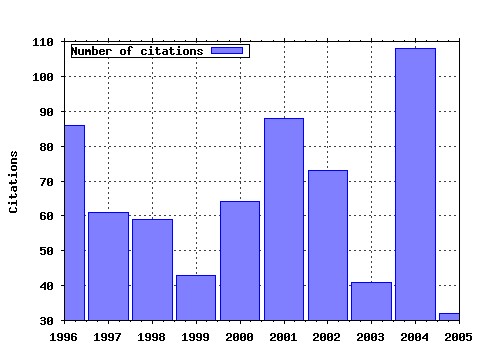
Journal of Macroeconomics Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Latest citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:1:y:1979:i:1:p:79-82 Another possible source of wage stickiness (1979). (2) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:26:y:2004:i:2:p:183-209 Optimal fiscal and monetary policy under imperfect competition (2004). (3) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:18:y:1996:i:4:p:605-619 Why are the effects of money-supply shocks asymmetric? Convex aggregate supply or pushing on a string? (1996). (4) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:18:y:1996:i:1:p:171-176 The black market exchange rate and demand for money in Iran (1996). (5) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:16:y:1994:i:2:p:271-279 Is government capital productive? Evidence from a panel of seven countries (1994). (6) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:24:y:2002:i:4:p:435-468 The state of macroeconomic forecasting (2002). (7) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:12:y:1990:i:2:p:167-195 The macroeconomic impact of the baby boom generation (1990). (8) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:26:y:2004:i:3:p:409-430 Are real interest rates really nonstationary? New evidence from tests with good size and power (2004). (9) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:23:y:2001:i:2:p:241-260 Some Panel Cointegration Models of International R&D Spillovers (2001). (10) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:19:y:1997:i:4:p:781-802 Breaking Trend Functions in Real Exchange Rates: Evidence from Seventeen OECD Countries (1997). (11) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:17:y:1995:i:1:p:1-30 Public and private investment: Are there causal linkages? (1995). (12) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:20:y:1998:i:1:p:81-105 Growth, Welfare, and Trade in an Integrated Model of Human-Capital Accumulation and Research (1998). (13) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:26:y:2004:i:2:p:357-376 Mark-up fluctuations and fiscal policy stabilization in a monetary union (2004). (14) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:26:y:2004:i:2:p:319-347 Monetary and fiscal interactions in open economies (2004). (15) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:23:y:2001:i:4:p:601-614 New Evidence on Real Exchange Rate Stationarity and Purchasing Power Parity in Less Developed Countries (2001). (16) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:15:y:1993:i:1:p:109-122 Tests of long-run Purchasing Power Parity using alternative methodologies (1993). (17) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:24:y:2002:i:4:p:507-531 Forecasting with a real-time data set for macroeconomists (2002). (18) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:26:y:2004:i:1:p:131-145 Are incomes converging among OECD countries? Time series evidence with two structural breaks (2004). (19) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:22:y:2000:i:2:p:189-206 Research, Development and Human Capital Accumulation (2000). (20) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:22:y:2000:i:2:p:271-284 A Re-Examination of Purchasing Power Parity in Japan and Taiwan (2000). (21) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:20:y:1998:i:2:p:325-339 The Transmission of Interest Rate Changes and the Role of Bank Balance Sheets: A VAR-Analysis for the Netherlands (1998). (22) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:28:y:2006:i:1:p:51-85 Constant gain learning and business cycles (2006). (23) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:18:y:1996:i:4:p:621-637 Sources of business-cycle volatility: An exploratory study on a sample of OECD countries (1996). (24) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:13:y:1991:i:2:p:291-298 Further evidence on the asymmetric behavior of unemployment rates over the business cycle (1991). (25) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:17:y:1995:i:4:p:683-702 Inflation and the asymmetric effects of money on output fluctuations (1995). (26) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:23:y:2001:i:2:p:213-239 The Sources of Macroeconomic Fluctuations in Developing Countries: Brazil and Korea (2001). (27) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:16:y:1994:i:3:p:403-422 Purchasing power parity in high-inflation countries: further evidence (1994). (28) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:24:y:2002:i:2:p:267-286 Total factor productivity and the convergence hypothesis (2002). (29) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:17:y:1995:i:3:p:421-446 A simple economy with human capital: Transitional dynamics, technology shocks, and fiscal policies (1995). (30) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:17:y:1995:i:3:p:387-404 The liquidity effect: Identifying short-run interest rate dynamics using long-run restrictions (1995). (31) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:16:y:1994:i:4:p:613-627 Liquidity and business investment: Evidence from dutch panel data (1994). (32) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:18:y:1996:i:3:p:403-428 Do federal deficits affect interest rates? Evidence from three econometric methods (1996). (33) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:23:y:2001:i:1:p:31-44 Population Aging and Economic Growth (2001). (34) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:22:y:2000:i:1:p:1-28 Macroeconomic Modeling with Asymmetric Vector Autoregressions (2000). (35) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:16:y:1994:i:1:p:1-36 Sources of macroeconomic fluctuations in small open economies (1994). (36) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:26:y:2004:i:4:p:597-621 Economic growth, skill-biased technical change and wage inequality: A model and estimations for the US and Europe (2004). (37) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:23:y:2001:i:3:p:477-487 Mean Reversion of Inflation Rates: Evidence from 13 OECD Countries (2001). (38) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:12:y:1990:i:3:p:341-362 Exchange rate volatility and U.S. multilateral trade flows (1990). (39) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:12:y:1990:i:2:p:197-219 Fiscal policy and current account performance: International evidence on the twin deficits (1990). (40) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:18:y:1996:i:1:p:1-26 Oil price volatility and the macroeconomy (1996). (41) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:15:y:1993:i:1:p:175-182 Money in the utility function: Functional equivalence to a shopping-time model (1993). (42) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:24:y:2002:i:1:p:17-39 Is private consumption growth higher (lower) during periods of fiscal contractions (expansions)? (2002). (43) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:18:y:1996:i:1:p:27-47 Aggregate economic fluctuations in endogenous growth models (1996). (44) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:26:y:2004:i:2:p:257-280 Fiscal and monetary policy interactions: Empirical evidence and optimal policy using a structural New-Keynesian model (2004). (45) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:15:y:1993:i:1:p:25-45 Purchasing power parity in the major EMS countries: The role of price and exchange rate adjustment (1993). (46) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:23:y:2001:i:4:p:565-576 Exchange Rate Uncertainty and Firm Profitability (2001). (47) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:25:y:2003:i:1:p:87-107 Efficiency and distribution effects of a revenue-neutral income tax reform (2003). (48) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:23:y:2001:i:3:p:323-347 The Ex Ante Credibility of Disinflation Policy and the Cost of Reducing Inflation (2001). (49) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:14:y:1992:i:4:p:745-754 A note on the sustainability of primary budget deficits (1992). (50) RePEc:eee:jmacro:v:16:y:1994:i:2:p:221-241 Entry barriers and price movements between major and emerging stock markets (1994). Latest citations received in: | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 | 2002 Latest citations received in: 2005 (1) RePEc:dnb:dnbwpp:049 Subjective Expectations and New Keynesian Phillips Curves in Europe (2005). Netherlands Central Bank, Research Department / DNB Working Papers (2) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2001-017 The dynamic relationship between permanent and transitory components of U.S. business cycles (2005). Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis / Working Papers (3) RePEc:hum:wpaper:sfb649dp2005-061 How much of the Macroeconomic Variation in Eastern Europe is Attributable to External Shocks? (2005). Sonderforschungsbereich 649, Humboldt University, Berlin, Germany / SFB 649 Discussion Papers (4) RePEc:iea:carech:0503 Closing International Real Business Cycle Models with Restricted Financial Markets (2005). HEC Montréal, Institut d'économie appliquée / Cahiers de recherche (5) RePEc:kud:kuiedp:0529 The Balassa-Samuelson Effect and the Wage, Price and Unemployment Dynamics in Spain (2005). University of Copenhagen. Department of Economics (formerly Institute of Economics) / Discussion Papers (6) RePEc:lvl:lacicr:0506 Closing International Real Business Cycle Models with Restricted Financial Markets (2005). (7) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:60 Infrastructure Investment and Maintenance Expenditure: Optimal Allocation Rules in a Growing Economy (2005). The School of Economic Studies, The Univeristy of Manchester / Centre for Growth and Business Cycle Research Discussion Paper Series (8) RePEc:nzb:nzbdps:2005/07 Discretionary Policy, Potential Output Uncertainty, and Optimal Learning (2005). Reserve Bank of New Zealand / Reserve Bank of New Zealand Discussion Paper Series (9) RePEc:wai:econwp:05/07 A New Framework for Yield Curve, Output and Inflation Relationships (2005). University of Waikato, Department of Economics / Working Papers in Economics (10) RePEc:wdi:papers:2005-802 Implications of ERM2 for Polandâs Monetary Policy (2005). William Davidson Institute at the University of Michigan Stephen M. Ross Business School / William Davidson Institute Working Papers Series (11) RePEc:wpa:wuwpma:0503022 Monetary Policy Adjustments on the Final Passage towards the Euro (2005). EconWPA / Macroeconomics Latest citations received in: 2004 (1) RePEc:cty:dpaper:0410 Optimal taxation with imperfect competition and increasing returns to specialization (2004). Department of Economics, City University, London / City University Economics Discussion Papers (2) RePEc:ecm:ausm04:280 Fractional Output Convergence, with an Application to Nine Developed Countries (2004). Econometric Society / Econometric Society 2004 Australasian Meetings (3) RePEc:esi:egpdis:2004-03 Technological and Organizational Changes as Determinants of the Skill Bias: Evidence from a Panel of Italian Firms (2004). Max Planck Institute of Economics, Group for Entrepreneurship, Growth and Public Policy / Discussion Papers on Entrepreneurship, Growth and Public Pol (4) RePEc:fip:fedcwp:0408 Friedman meets Hosios: efficiency in search models of money (2004). Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland / Working Paper (5) RePEc:hhs:bofrdp:2004_020 Monetary consequences of alternative fiscal policy rules (2004). Bank of Finland / Research Discussion Papers (6) RePEc:imf:imfwpa:04/63 Balance Sheets, Exchange Rate Policy, and Welfare (2004). International Monetary Fund / IMF Working Papers (7) RePEc:kap:ecopln:v:31:y:2004:i:2:p:117-135 Growth and Welfare Effects of Tax Cuts: The Case of a Productive Public Input with Technological Risk (2004). Economics of Planning (8) RePEc:mmf:mmfc04:50 A Generalized Theory of Monetary and Macroeconomics (2004). Money Macro and Finance Research Group / Money Macro and Finance (MMF) Research Group Conference 2004 (9) RePEc:mmf:mmfc04:84 Non-cooperative Monetary and Fiscal Policy: The Value of Leadership (2004). Money Macro and Finance Research Group / Money Macro and Finance (MMF) Research Group Conference 2004 (10) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:10724 Optimal Operational Monetary Policy in the Christiano-Eichenbaum-Evans Model of the U.S. Business Cycle (2004). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (11) RePEc:tud:ddpiec:138 Education, Research, and Economic Growth (2004). Institut für Volkswirtschaftslehre (Department of Economics), Technische Universität Darmstadt (Darmstadt University of Technology) / Darmstadt Disc Latest citations received in: 2003 (1) RePEc:bri:uobdis:03/555 Measuring trend output: how useful are the Great Ratios? (2003). Department of Economics, University of Bristol, UK / Bristol Economics Discussion Papers (2) RePEc:fce:doctra:0304 Ranking Fiscal Policy Rules: the Golden Rule of Public Finance vs. the Stability and Growth Pact (2003). Observatoire Francais des Conjonctures Economiques (OFCE) / Documents de Travail de l'OFCE (3) RePEc:ihs:ihsesp:140 Estimating the Impact of the Balassa-Samuelson Effect in Transition Economies (2003). Institute for Advanced Studies / Economics Series Latest citations received in: 2002 (1) RePEc:dnb:mebser:2002-18 Central bank bashing: The case of the European Central Bank (2002). Netherlands Central Bank, Monetary and Economic Policy Department / MEB Series (discontinued) (2) RePEc:eeg:euroeg:16 The Euro-Dollar exchange rate: Is it fundamental'DONE' (2002). European Economy Group / European Economy Group Working Papers (3) RePEc:uct:uconnp:2002-33 Total Factor Productivity, Human Capital and Outward Orientation: Differences by Stage of Ddevelopment and Geographic Regions (2002). University of Connecticut, Department of Economics / Working papers (4) RePEc:wpa:wuwpma:0209001 Central bank bashing: The case of the European Central Bank (2002). EconWPA / Macroeconomics Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |