|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
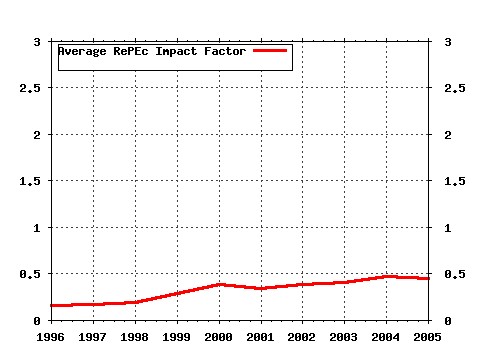
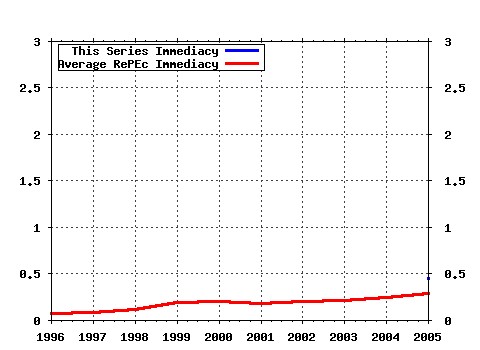
PSE (Ecole normale supérieure) / PSE Working Papers Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Latest citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:pse:psecon:2006-24 Income and happiness: Evidence, explanations and economic implications (2006). (2) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-18 New technologies, workplace organisation and the age structure of the workforce: Firm-level evidence. (2005). (3) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-02 Microsimulation as a tool for evaluating redistribution policies. (2005). (4) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-27 Counseling the unemployed: does it lower unemployment duration and recurrence? (2005). (5) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-22 Tax-benefit revealed social preferences. (2005). (6) RePEc:pse:psecon:2006-07 Welfare state retrenchment: The partisan effect revisited. (2006). (7) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-24 A dynamic equilibrium model of imperfectly integrated financial markets. (2005). (8) RePEc:pse:psecon:2006-03 Effort and comparison income: Survey and experimental evidence. (2006). (9) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-30 The public pay gap in Britain: Small differences that (dont?) matter. (2005). (10) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-23 International equity holdings and stock returns correlations: Does Diversification Matter At All for Portfolio Choice? (2005). (11) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-13 Discrete choice models of labour supply, behavioural microsimulation and the Spanish tax reform. (2005). (12) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-31 On-the-job search, productivity shocks, and the individual earnings process. (2005). (13) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-43 Deliver us from evil: religion as insurance. (2005). (14) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-04 Sharing resources within the household: a multi-country microsimulation analysis of the determinants of intrahousehold strategic weight differentials and their distributional outcomes. (2005). (15) RePEc:pse:psecon:2006-46 Solving heterogeneous-agent models with parameterized cross-sectional distributions (2006). (16) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-01 The emergence of large shareholders in mass privatized firms: Evidence from Poland and the Czech Republic. (2005). (17) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-38 Separating selection and incentive effects in health insurance. (2005). (18) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-12 The political economy of job protection and income redistribution. (2005). (19) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-25 Collusive market-sharing and corruption in procurement. (2005). (20) RePEc:pse:psecon:2006-19 Consensus building: How to persuade a group (2006). (21) RePEc:pse:psecon:2007-12 Education inequalities and the Kuznets curves: a global perspective since 1870 (2007). (22) RePEc:pse:psecon:2006-16 Institutions, unemployment and inactivity in the OECD countries. (2006). (23) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-03 Education, redistributive taxation and confidence. (2005). (24) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-40 Strategic analysis of petty corruption: Entrepreneurs and bureaucrats. (2005). (25) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-21 Subsidy competition in integrating economies. (2005). (26) RePEc:pse:psecon:2006-29 The curved relationship between subjective well-being and age. (2006). (27) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-51 The real effect of inflation in liquidity constrained models. (2005). (28) RePEc:pse:psecon:2007-25 Rationalizability in games with a continuum of players (2007). (29) RePEc:pse:psecon:2006-23 A note on unhappiness and unemployment duration (2006). (30) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-09 Dynamic analysis of bankruptcy and economic waves. (2005). (31) RePEc:pse:psecon:2007-15 Optimality conditions and comparative static properties of non-linear income taxes revisited (2007). (32) RePEc:pse:psecon:2006-17 Differentiated duopoly with Elimination by Aspects (2006). (33) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-41 Do people really adapt to marriage? (2005). (34) RePEc:pse:psecon:2006-09 Income-related reporting heterogeneity in self-assessed health: evidence from France. (2006). (35) RePEc:pse:psecon:2006-35 Born to be mild? Cohort effects dont explain why well-being is U-shaped in age. (2006). (36) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-49 Competitiveness, market power and price stickiness: A paradox and a resolution. (2005). (37) RePEc:pse:psecon:2007-23 Job satisfaction and co-worker wages: Status or signal? (2007). (38) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-08 The void at the heart of rules: routines in the context of rule-following. (2005). (39) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-42 Concentration, agglomeration and the size of plants. (2005). (40) RePEc:pse:psecon:2006-38 The strategy structure of some coalition formation games (2006). Latest citations received in: | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 | 2002 Latest citations received in: 2005 (1) RePEc:bri:cmpowp:05/132 Transparency, Recuitment and Retention in the Public Sector (2005). Department of Economics, University of Bristol, UK / The Centre for Market and Public Organisation (2) RePEc:cep:cepdps:dp0697 You Cant Always Get What You Want: the Impact of the Jobseekers Allowance (2005). Centre for Economic Performance, LSE / CEP Discussion Papers (3) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005007 Equilibrium Evaluation of Active Labor Market Programmes Enhancing Matching Effectiveness (2005). Université catholique de Louvain, Département des Sciences Economiques / Université catholique de Louvain, Département des Sciences Economiques Workin (4) RePEc:dgr:umamer:2005022 The Division of Labour, Worker Organisation, and Technological Change (2005). Maastricht : MERIT, Maastricht Economic Research Institute on Innovation and Technology / Research Memoranda (5) RePEc:dgr:umaror:2005005 The Division of Labour, Worker Organisation, and Technological Change (2005). Maastricht : ROA, Researchcentrum voor Onderwijs en Arbeidsmarkt / Research Memoranda (6) RePEc:dgr:vuarem:2005-12 A microsimulation analysis of the 2006 regime change in the Dutch disability scheme (2005). Free University Amsterdam, Faculty of Economics, Business Administration and Econometrics / Serie Research Memoranda (7) RePEc:ese:emodwp:em8/05 Micro-level analysis of the European Social Agenda: Combating poverty and social exclusion through changes in social and fiscal policy - Final Report (2005). EUROMOD at the Institute for Social and Economic Research / EUROMOD Working Papers (8) RePEc:fda:fdaddt:2005-14 Discrete choice models of labour Supply, behavioural microsimulation and the Spanish tax reforms (2005). FEDEA / Working Papers (9) RePEc:fda:fdaddt:2005-15 Measuring Changes in Health Capital (2005). FEDEA / Working Papers (10) RePEc:fda:fdaddt:2005-17 Life Satisfaction among Spanish Workers: Importance of Intangible Job Characteristics (2005). FEDEA / Working Papers (11) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1526 Equilibrium Evaluation of Active Labor Market Programmes Enhancing Matching Effectiveness (2005). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (12) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1709 The Division of Labour, Worker Organisation, and Technological Change (2005). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (13) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1810 Welfare Reform in European Countries: A Microsimulation Analysis (2005). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (14) RePEc:lea:leawpi:0506 Nouvelles Technologies et Nouvelles Formes dOrganisation du Travail : Quelles conséquences pour lemploi des salariés âgés ? (2005). Laboratoire d'Economie Appliquee, INRA / Research Unit Working Papers (15) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:11576 Insuring Consumption and Happiness Through Religious Organizations (2005). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (16) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-04 Sharing resources within the household: a multi-country microsimulation analysis of the determinants of intrahousehold strategic weight differentials and their distributional outcomes. (2005). PSE (Ecole normale supérieure) / PSE Working Papers (17) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-13 Discrete choice models of labour supply, behavioural microsimulation and the Spanish tax reform. (2005). PSE (Ecole normale supérieure) / PSE Working Papers (18) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-19 Nouvelles technologies et nouvelles formes dorganisation du travail : quelles conséquences pour lemploi des salariés âges ? (2005). PSE (Ecole normale supérieure) / PSE Working Papers (19) RePEc:pse:psecon:2005-45 Monetary policy with heterogenous agents and credit constraints. (2005). PSE (Ecole normale supérieure) / PSE Working Papers (20) RePEc:shr:wpaper:05-03 Horizontal and Vertical Redistribution and Micro-simulation. (2005). Departement d'Economique de la Faculte d'administration à l'Universite de Sherbrooke / Cahiers de recherche (21) RePEc:shr:wpaper:05-12 Impact Analysis of the Liberalization of Groundnut Production in Senegal: A Multi-household Computable General Equilibrium Model (2005). Departement d'Economique de la Faculte d'administration à l'Universite de Sherbrooke / Cahiers de recherche (22) RePEc:shr:wpaper:05-13 A Poverty and Inequality Impact Assessment of Liberalization of Water Utility in Senegal: A Macro-Micro Analysis (2005). Departement d'Economique de la Faculte d'administration à l'Universite de Sherbrooke / Cahiers de recherche (23) RePEc:zbw:zewdip:3283 The Effects of Changes in the Unemployment Compensation System on the Adoption of IT by Older Workers (2005). ZEW - Zentrum für Europäische Wirtschaftsforschung / Center for European Economic Research / ZEW Discussion Papers Latest citations received in: 2004 Latest citations received in: 2003 Latest citations received in: 2002 Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |