|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
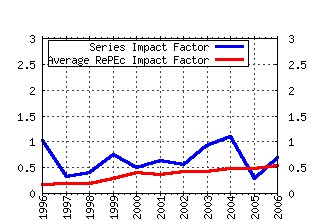
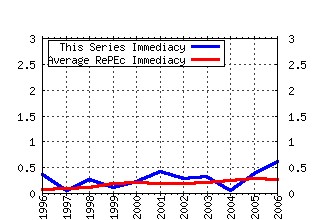
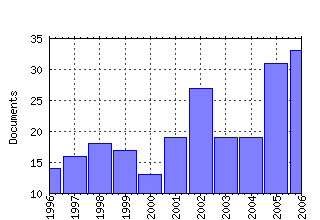
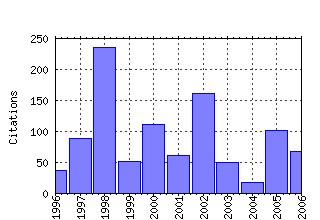
Center for Economic Studies, U.S. Census Bureau / Working Papers Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Recent citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:cen:wpaper:98-12 Aggregate Productivity Growth: Lessons From Microeconomic Evidence (1998). (2) RePEc:cen:wpaper:00-08 Plants and productivity in international trade (2000). (3) RePEc:cen:wpaper:98-3 Geographic Concentration as a Dynamic Process (1997). (4) RePEc:cen:wpaper:02-18 The Link Between Aggregate and Micro Productivity Growth: Evidence from Retail Trade (2002). (5) RePEc:cen:wpaper:88-2 The Longitudinal Research Database (LRD): Status And Research Possibilities (1988). (6) RePEc:cen:wpaper:01-05 Why Some Firms Export (2001). (7) RePEc:cen:wpaper:02-17 The Longitudinal Business Database (2002). (8) RePEc:cen:wpaper:94-10 Evidence on the Employer Size-Wage Premium From Worker-Establishment Matched Data (1994). (9) RePEc:cen:wpaper:02-15 The Deaths of Manufacturing Plants (2002). (10) RePEc:cen:wpaper:07-14 Firms in International Trade (2007). (11) RePEc:cen:wpaper:99-11 Do Conglomerate Firms Allocate Resources Inefficiently? (1999). (12) RePEc:cen:wpaper:06-17 Volatility and Dispersion in Business Growth Rates: Publicly Traded Versus Privately Held Firms (2006). (13) RePEc:cen:wpaper:05-11 Reallocation, Firm Turnover, and Efficiency: Selection on Productivity or Profitability? (2005). (14) RePEc:cen:wpaper:94-11 Capital Adjustment Patterns in Manufacturing Plants (1994). (15) RePEc:cen:wpaper:05-20 Importers, Exporters, and Multinationals: A Portrait of Firms in the U.S. that Trade Goods (2005). (16) RePEc:cen:wpaper:95-4 Capital Structure and Product Market Behavior: An Examination of Plant Exit and Investment Decisions (1995). (17) RePEc:cen:wpaper:92-2 The Dynamics Of Productivity In The Telecommunications Equipment Industry (1992). (18) RePEc:cen:wpaper:92-13 Gender Segregation Small Firms (1993). (19) RePEc:cen:wpaper:05-04 Immigration, Skill Mix, and the Choice of Technique (2005). (20) RePEc:cen:wpaper:95-10 The Worker-Establishment Characteristics Database (1995). (21) RePEc:cen:wpaper:96-7 Technology and Jobs: Secular Changes and Cyclical Dynamics (1996). (22) RePEc:cen:wpaper:05-23 Place of Work and Place of Residence: Informal Hiring Networks and Labor Market Outcomes (2005). (23) RePEc:cen:wpaper:94-7 The Span of the Effect of R&D in the Firm and Industry (1994). (24) RePEc:cen:wpaper:06-07 The Effects of Outsourcing on the Elasticity of Labor Demand (2006). (25) RePEc:cen:wpaper:93-6 Environmental Regulation And Manufacturing Productivity At The Plant Level (1993). (26) RePEc:cen:wpaper:02-19 Interactions, Neighborhood Selection, and Housing Demand (2002). (27) RePEc:cen:wpaper:98-9 Longitudinal Establishment And Enterprise Microdata (LEEM) Documentation (1998). (28) RePEc:cen:wpaper:91-1 Published Versus Sample Statistics From The ASM: Implications For The LRD (1991). (29) RePEc:cen:wpaper:97-8 Manufacturing Plant Location: Does State Pollution Regulation Matter? (1997). (30) RePEc:cen:wpaper:07-27 A Unified Framework for Measuring Preferences for Schools and Neighborhoods (2007). (31) RePEc:cen:wpaper:90-2 An Analysis of Small Business Size and Rate of Discontinuance (1990). (32) RePEc:cen:wpaper:95-3 Capital Structure And Product Market Rivalry: How Do We Reconcile Theory And Evidence? (1995). (33) RePEc:cen:wpaper:99-12 The Market for Corporate Assets: Who Engages in Mergers and Asset Sales and are there Efficiency Gains? (1999). (34) RePEc:cen:wpaper:04-02 The Agglomeration of Headquarters (2004). (35) RePEc:cen:wpaper:96-4 Sex Segregation in U.S. Manufacturing (1996). (36) RePEc:cen:wpaper:05-02 Micro and Macro Data Integration: The Case of Capital (2005). (37) RePEc:cen:wpaper:94-4 Downsizing and Productivity Growth: Myth or Reality? (1994). (38) RePEc:cen:wpaper:07-04 Do Employment Protections Reduce Productivity? Evidence from U.S. States (2007). (39) RePEc:cen:wpaper:94-2 A Comparison of Job Creation and Job Destruction in Canada and the United States (1994). (40) RePEc:cen:wpaper:91-5 The Structure Of Production Technology Productivity And Aggregation Effects (1991). (41) RePEc:cen:wpaper:98-11 Job Reallocation And The Business Cycle: New Facts An Old Debate (1998). (42) RePEc:cen:wpaper:95-5 Whittling Away At Productivity Dispersion (1995). (43) RePEc:cen:wpaper:91-7 Technology Usage in U.S. Manufacturing Industries: New Evidence from the Survey of Manufacturing Technology (1991). (44) RePEc:cen:wpaper:98-16 THE MANUFACTURING PLANT OWNERSHIP CHANGE DATABASE: ITS CONSTRUCTION AND USEFULNESS (1998). (45) RePEc:cen:wpaper:93-7 Asymmetric Learning Spillovers (1993). (46) RePEc:cen:wpaper:92-7 The Characteristics of Business Owners Database (1992). (47) RePEc:cen:wpaper:03-06 Productivity, Investment in ICT and Market Experimentation: Micro Evidence from Germany and the U.S. (2003). (48) RePEc:cen:wpaper:03-02 Endogenous Growth and Entrepreneurial Activity in Cities (2003). (49) RePEc:cen:wpaper:06-08 Plant Turnover and Demand Fluctuations in the Ready-Mix Concrete Industry (2006). (50) RePEc:cen:wpaper:02-08 The Distributional Effects of an Investment-Based Social Security System (2002). Recent citations received in: | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 Recent citations received in: 2006 (1) RePEc:cen:wpaper:06-02 Outstanding Outsourcers: A Firm- and Plant-Level Analysis of Production Sharing (2006). Center for Economic Studies, U.S. Census Bureau / Working Papers (2) RePEc:cen:wpaper:06-08 Plant Turnover and Demand Fluctuations in the Ready-Mix Concrete Industry (2006). Center for Economic Studies, U.S. Census Bureau / Working Papers (3) RePEc:cen:wpaper:06-12 Impacts of Trade on Wage Inequality in Los Angeles: Analysis Using Matched Employer-Employee Data (2006). Center for Economic Studies, U.S. Census Bureau / Working Papers (4) RePEc:cen:wpaper:06-17 Volatility and Dispersion in Business Growth Rates: Publicly Traded Versus Privately Held Firms (2006). Center for Economic Studies, U.S. Census Bureau / Working Papers (5) RePEc:cen:wpaper:06-24 Why Are Plant Deaths Countercyclical: Reallocation Timing or Fragility? (2006). Center for Economic Studies, U.S. Census Bureau / Working Papers (6) RePEc:cen:wpaper:06-30 Gross Job Flows for the U.S. Manufacturing Sector: Measurement from the Longitudinal Research Database (2006). Center for Economic Studies, U.S. Census Bureau / Working Papers (7) RePEc:cep:cepdps:dp0736 Multi-Product Firms and Product Switching (2006). Centre for Economic Performance, LSE / CEP Discussion Papers (8) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5708 Multi-Product Firms and Product Switching (2006). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (9) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5903 Contractual Institutions, Financial Development and Vertical Integration: Theory and Evidence (2006). C.E.P.R. Discussion Papers / CEPR Discussion Papers (10) RePEc:fip:fedfpr:y:2006:i:nov:x:2 Financial innovation and the Great Moderation: what do household data say? (2006). Proceedings (11) RePEc:fip:fedgfe:2006-04 Outstanding outsourcers: a firm- and plant-level analysis of production sharing (2006). Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (U.S.) / Finance and Economics Discussion Series (12) RePEc:fip:fedgfe:2006-31 Why are plant deaths countercyclical: reallocation timing or fragility? (2006). Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (U.S.) / Finance and Economics Discussion Series (13) RePEc:fip:fedhep:y:2006:i:qiii:p:14-27:n:v.30no.3 The self-employment duration of younger men over the business cycle (2006). Economic Perspectives (14) RePEc:fip:fedkcc:y:2006:i:jul:p:91-155 Stumbling blocks to entrepreneurship in low-and-moderate income communities (2006). Proceedings Community Affairs Dept. Conferences (15) RePEc:fip:fedkpr:y:2006:p:1-14 The new economic geography: opening remarks (2006). Proceedings (16) RePEc:mpc:wpaper:16 Diverging Trends in Aggregate and Firm-Level Volatility in the UK (2006). Monetary Policy Committee Unit, Bank of England / Discussion Papers (17) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:12167 The Flow Approach to Labor Markets: New Data Sources and Micro-Macro Links (2006). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (18) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:12293 Multi-Product Firms and Product Switching (2006). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (19) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:12354 Volatility and Dispersion in Business Growth Rates: Publicly Traded versus Privately Held Firms (2006). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (20) RePEc:ste:nystbu:06-12 Aggregate Shocks or Aggregate Information? Costly Information and Business Cycle Comovement (2006). New York University, Leonard N. Stern School of Business, Department of Economics / Working Papers Recent citations received in: 2005 (1) RePEc:cen:wpaper:05-01 Computer Investment, Computer Networks and Productivity (2005). Center for Economic Studies, U.S. Census Bureau / Working Papers (2) RePEc:cen:wpaper:05-15 Networking Off Madison Avenue (2005). Center for Economic Studies, U.S. Census Bureau / Working Papers (3) RePEc:cen:wpaper:05-16 Quality Sorting and Networking: Evidence from the Advertising Agency Industry (2005). Center for Economic Studies, U.S. Census Bureau / Working Papers (4) RePEc:cen:wpaper:05-18 Firm Structure, Multinationals, and Manufacturing Plant Deaths (2005). Center for Economic Studies, U.S. Census Bureau / Working Papers (5) RePEc:fip:fednep:y:2005:i:dec:p:25-27:n:v.11no.2 Commentary on Urban colossus: why is New York Americas largest city? (2005). Economic Policy Review (6) RePEc:fip:fednep:y:2005:i:dec:p:29-53:n:v.11no.2 The geography of entrepreneurship in the New York metropolitan area (2005). Economic Policy Review (7) RePEc:gat:wpaper:0505 Neighborhood effects, public housing and unemployment in France (2005). Groupe d'Analyse et de Théorie Economique (GATE), Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS), Université Lyon 2, Ecole Normale Supérieure / W (8) RePEc:irv:wpaper:050609 The Scarring Effect of Recessions (2005). University of California-Irvine, Department of Economics / Working Papers (9) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:11294 Why Do Public Firms Issue Private and Public Securities? (2005). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (10) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:11631 The Law and Economics of Antidiscrimination Law (2005). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (11) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:11825 Surviving Andersonville: The Benefits of Social Networks in POW Camps (2005). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (12) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:11839 Firm Fragmentation and Urban Patterns (2005). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers Recent citations received in: 2004 (1) RePEc:cen:wpaper:04-08 Productivity Growth Patterns in U.S. Food Manufacturing: Case of Dairy Products Industry (2004). Center for Economic Studies, U.S. Census Bureau / Working Papers Recent citations received in: 2003 (1) RePEc:egc:wpaper:872 A Unified Framework for Estimating Preferences for Schools and Neighborhoods (2003). Economic Growth Center, Yale University / Working Papers (2) RePEc:fip:fedfap:2003-23 Whats driving the new economy?: the benefits of workplace innovation (2003). Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco / Working Papers in Applied Economic Theory (3) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp895 Transitions in Welfare Participation and Female Headship (2003). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (4) RePEc:pra:mprapa:2854 Efectos de la aglomeración y los encadenamientos industriales en el patrón de crecimiento manufacturero en México (2003). University Library of Munich, Germany / MPRA Paper (5) RePEc:ube:dpvwib:dp0311 Income Segregation and Local Progressive Taxation: Empirical Evidence from Switzerland (2003). Universitat Bern, Volkswirtschaftliches Institut / Diskussionsschriften (6) RePEc:wdi:papers:2003-609 Job Flows and Establishment Characteristics: Variations Across U.S. Metropolitan Areas (2003). William Davidson Institute at the University of Michigan Stephen M. Ross Business School / William Davidson Institute Working Papers Series Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||