|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
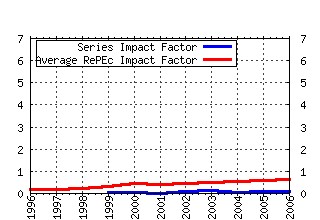
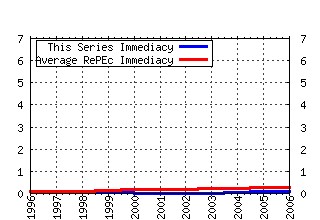
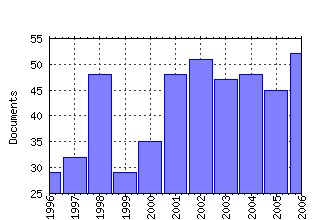
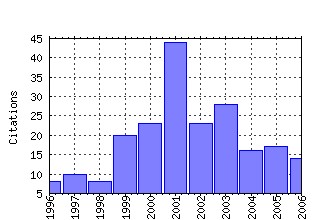
Transportation Research Part B: Methodological Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Recent citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:eee:transb:v:35:y:2001:i:7:p:677-693 Quasi-random maximum simulated likelihood estimation of the mixed multinomial logit model (2001). (2) RePEc:eee:transb:v:25:y:1991:i:1:p:1-12 Estimability in the multinomial probit model (1991). (3) RePEc:eee:transb:v:26:y:1992:i:2:p:155-170 Generalized autoregressive errors in the multinomial probit model (1992). (4) RePEc:eee:transb:v:34:y:2000:i:5:p:315-338 Joint mixed logit models of stated and revealed preferences for alternative-fuel vehicles (2000). (5) RePEc:eee:transb:v:19:y:1985:i:6:p:526-528 Parameter estimability in the multinomial probit model (1985). (6) RePEc:eee:transb:v:37:y:2003:i:9:p:837-855 Simulation estimation of mixed discrete choice models using randomized and scrambled Halton sequences (2003). (7) RePEc:eee:transb:v:37:y:2003:i:8:p:681-698 A latent class model for discrete choice analysis: contrasts with mixed logit (2003). (8) RePEc:eee:transb:v:21:y:1987:i:5:p:413-431 The economics of road safety (1987). (9) RePEc:eee:transb:v:36:y:2002:i:8:p:707-729 Second-best congestion pricing in general networks. Heuristic algorithms for finding second-best optimal toll levels and toll points (2002). (10) RePEc:eee:transb:v:29:y:1995:i:6:p:471-483 A heteroscedastic extreme value model of intercity travel mode choice (1995). (11) RePEc:eee:transb:v:33:y:1999:i:1:p:63-79 A practical technique to estimate multinomial probit models in transportation (1999). (12) RePEc:eee:transb:v:19:y:1985:i:4:p:275-285 A nested logit model of automobile holdings for one vehicle households (1985). (13) RePEc:eee:transb:v:35:y:2001:i:10:p:903-928 A non-compensatory choice model incorporating attribute cutoffs (2001). (14) RePEc:eee:transb:v:40:y:2006:i:8:p:688-707 Investigating the distribution of the value of travel time savings (2006). (15) RePEc:eee:transb:v:39:y:2005:i:7:p:621-640 Assessing the influence of design dimensions on stated choice experiment estimates (2005). (16) RePEc:eee:transb:v:24:y:1990:i:1:p:27-43 Airline competition in a hub-dominated environment: An application of noncooperative game theory (1990). (17) RePEc:eee:transb:v:13:y:1979:i:2:p:105-111 The dogit model (1979). (18) RePEc:eee:transb:v:34:y:2000:i:1:p:1-15 Distinguishing taste variation from error structure in discrete choice data (2000). (19) RePEc:eee:transb:v:36:y:2002:i:1:p:1-17 Specification and estimation of the nested logit model: alternative normalisations (2002). (20) RePEc:eee:transb:v:17:y:1983:i:1:p:13-23 Discrete choice theory, information theory and the multinomial logit and gravity models (1983). (21) RePEc:eee:transb:v:24:y:1990:i:3:p:209-228 Departure time and route choice for the morning commute (1990). (22) RePEc:eee:transb:v:33:y:1999:i:7:p:473-494 Ex ante heuristic measures of schedule reliability (1999). (23) RePEc:eee:transb:v:37:y:2003:i:8:p:699-718 Airline deregulation and external costs: a welfare analysis (2003). (24) RePEc:eee:transb:v:26:y:1992:i:2:p:97-114 A duration model of automobile ownership (1992). (25) RePEc:eee:transb:v:30:y:1996:i:1:p:19-30 A Monte Carlo study of tests for the independence of irrelevant alternatives property (1996). (26) RePEc:eee:transb:v:38:y:2004:i:7:p:613-633 A learning-based transportation oriented simulation system (2004). (27) RePEc:eee:transb:v:31:y:1997:i:1:p:11-21 Covariance heterogeneity in nested logit models: Econometric structure and application to intercity travel (1997). (28) RePEc:eee:transb:v:33:y:1999:i:3:p:157-188 Economic efficiency of second-best congestion pricing schemes in urban highway systems (1999). (29) RePEc:eee:transb:v:21:y:1987:i:2:p:91-102 Incorporating random constraints in discrete models of choice set generation (1987). (30) RePEc:eee:transb:v:40:y:2006:i:2:p:147-163 On the use of a Modified Latin Hypercube Sampling (MLHS) method in the estimation of a Mixed Logit Model for vehicle choice (2006). (31) RePEc:eee:transb:v:33:y:1999:i:1:p:25-42 Some traffic features at freeway bottlenecks (1999). (32) RePEc:eee:transb:v:34:y:2000:i:2:p:107-121 Solving the pickup and delivery problem with time windows using reactive tabu search (2000). (33) RePEc:eee:transb:v:36:y:2002:i:9:p:755-778 Operational car assignment at VIA Rail Canada (2002). (34) RePEc:eee:transb:v:36:y:2002:i:7:p:593-616 A unified mixed logit framework for modeling revealed and stated preferences: formulation and application to congestion pricing analysis in the San Francisco Bay area (2002). (35) RePEc:eee:transb:v:18:y:1984:i:4-5:p:339-355 Dynamic model of peak period congestion (1984). (36) RePEc:eee:transb:v:34:y:2000:i:2:p:147-156 Fictitious play for finding system optimal routings in dynamic traffic networks (2000). (37) RePEc:eee:transb:v:40:y:2006:i:1:p:75-92 Accounting for heterogeneity in the variance of unobserved effects in mixed logit models (2006). (38) RePEc:eee:transb:v:38:y:2004:i:10:p:889-904 A parameterized consideration set model for airport choice: an application to the San Francisco Bay Area (2004). (39) RePEc:eee:transb:v:35:y:2001:i:7:p:643-666 Choice set generation within the generalized extreme value family of discrete choice models (2001). (40) RePEc:eee:transb:v:24:y:1990:i:1:p:73-77 Consumers surplus and the value of travel time savings (1990). (41) RePEc:eee:transb:v:15:y:1981:i:6:p:453-462 Properties of a traffic control policy which ensure the existence of a traffic equilibrium consistent with the policy (1981). (42) RePEc:eee:transb:v:28:y:1994:i:5:p:365-375 Traffic jams and the congestion toll (1994). (43) RePEc:eee:transb:v:39:y:2005:i:9:p:825-853 Incorporating variance and covariance heterogeneity in the Generalized Nested Logit model: an application to modeling long distance travel choice behavior (2005). (44) RePEc:eee:transb:v:19:y:1985:i:5:p:397-407 Physical distribution from a warehouse: Vehicle coverage and inventory levels (1985). (45) RePEc:eee:transb:v:38:y:2004:i:9:p:767-787 A mixed multinomial logit model analysis of weekend recreational episode type choice (2004). (46) RePEc:eee:transb:v:20:y:1986:i:5:p:403-414 A model for the structure of lane-changing decisions (1986). (47) RePEc:eee:transb:v:39:y:2005:i:8:p:679-707 A multiple discrete-continuous extreme value model: formulation and application to discretionary time-use decisions (2005). (48) RePEc:eee:transb:v:40:y:2006:i:9:p:807-825 A discrete choice model incorporating thresholds for perception in attribute values (2006). (49) RePEc:eee:transb:v:29:y:1995:i:2:p:139-154 A pareto optimum congestion reduction scheme (1995). (50) RePEc:eee:transb:v:38:y:2004:i:4:p:313-327 Quasi-random simulation of discrete choice models (2004). Recent citations received in: | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 Recent citations received in: 2006 (1) RePEc:ant:wpaper:2006034 Discrete choices and the trade off between money and time: Another test of the theory of reference dependent preferences (2006). University of Antwerp, Faculty of Applied Economics / Working Papers (2) RePEc:fem:femwpa:2006.128 Lexicographic Preferences in Discrete Choice Experiments: Consequences on Individual-Specific Willingness to Pay Estimates (2006). Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei / Working Papers (3) RePEc:fem:femwpa:2006.26 Using Discrete Choice Experiments to Derive Individual-Specific WTP Estimates for Landscape Improvements under Agri-Environmental Schemes: Evidence from the Rural Environment Protection Scheme in Irel (2006). Fondazione Eni Enrico Mattei / Working Papers (4) RePEc:lmu:muenec:916 Estimation with Numerical Integration on Sparse Grids (2006). University of Munich, Department of Economics / Discussion Papers in Economics (5) RePEc:wai:econwp:06/15 Utility in WTP Space: A Tool to Address Confounding Random Scale Effects in Destination Choice to the Alps (2006). University of Waikato, Department of Economics / Working Papers in Economics Recent citations received in: 2005 (1) RePEc:nbr:nberwo:11553 Vehicle Choices, Miles Driven, and Pollution Policies (2005). National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc / NBER Working Papers (2) RePEc:wai:econwp:05/08 Experimental Designs for Environmental Valuation with Choice-Experiments: A Monte-Carlo Investigation (2005). University of Waikato, Department of Economics / Working Papers in Economics (3) RePEc:wiw:wiwrsa:ersa05p375 Random Covariance Heterogeneity in Discrete Choice Models (2005). European Regional Science Association / ERSA conference papers Recent citations received in: 2004 (1) RePEc:ags:aaea04:20170 MODELING SPATIAL ACCESSIBILITY WITHIN DISCRETE CHOICE FRAMEWORK (2004). American Agricultural Economics Association (New Name 2008: Agricultural and Applied Economics Association) / 2004 Annual meeting, August 1-4, Denver, (2) RePEc:rne:rneart:v:3:y:2004:i:4:p:401-414 Second-Best Congestion Pricing in Urban Space: Cordon Pricing and Its Alternatives (2004). Review of Network Economics Recent citations received in: 2003 (1) RePEc:jae:japmet:v:18:y:2003:i:3:p:379-383 Discrete choice methods with simulation, Kenneth E. Train, Cambridge University Press, 2003, ISBN: 0-521-81696-3, pp. 334 (2003). Journal of Applied Econometrics Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||