|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
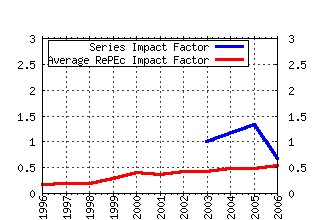
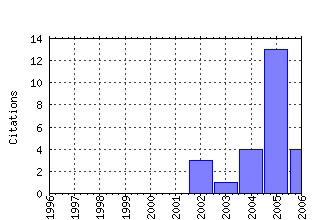
Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City / Payments System Research Working Paper Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Recent citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:fip:fedkpw:psrwp05-01 Interchange fees in various countries: developments and determinants (2005). (2) RePEc:fip:fedkpw:psrwp05-05 Internet banking: an exploration in technology diffusion and impact (2005). (3) RePEc:fip:fedkpw:psrwp04-02 A puzzle of card payment pricing : why are merchants still accepting card payments? (2004). (4) RePEc:fip:fedkpw:psrwp02-02 Nonbanks in the payments system (2002). (5) RePEc:fip:fedkpw:psrwp04-01 Income distribution, market size and the evolution of industry (2007). (6) RePEc:fip:fedkpw:psrwp06-02 Payment card rewards programs and consumer payment choice (2006). (7) RePEc:fip:fedkpw:psrwp05-02 Technological innovation and market turbulence: the dot-com experience (2005). (8) RePEc:fip:fedkpw:psrwp04-03 The supervisory framework surrounding nonbank participation in the U.S. retail payments system : an overview (2006). (9) RePEc:fip:fedkpw:psrwp03-01 Financial innovation, strategic real options and endogenous competition : theory and an application to Internet banking (2003). (10) RePEc:fip:fedkpw:psrwp06-01 Microfoundations of two-sided markets: the payment card example (2006). Recent citations received in: | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 Recent citations received in: 2006 (1) RePEc:fip:fedkpw:psrwp06-03 Pricing and welfare implications of payment card network competition (2006). Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City / Payments System Research Working Paper Recent citations received in: 2005 (1) RePEc:fip:fedkpc:y:2005:i:may:p:121-137 What do we know about interchange fees and what does it mean for public policy? : commentary on Evans and Schmalensee (2005). Proceedings Payments System Research Conferences (2) RePEc:fip:fedkpc:y:2005:i:may:p:51-64 Interchange fees in various countries : developments and determinants : commentary on Weiner and Wright (2005). Proceedings Payments System Research Conferences (3) RePEc:fip:fedkpw:psrwp05-02 Technological innovation and market turbulence: the dot-com experience (2005). Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City / Payments System Research Working Paper (4) RePEc:fip:fedkpw:psrwp05-05 Internet banking: an exploration in technology diffusion and impact (2005). Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City / Payments System Research Working Paper Recent citations received in: 2004 Recent citations received in: 2003 Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||