|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
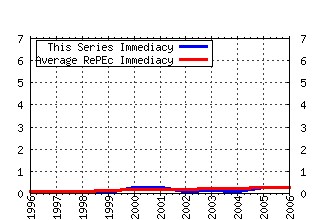
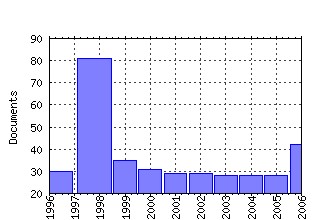
International Journal of Game Theory Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Recent citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:26:y:1997:i:3:p:335-351 Ternary Voting Games (1998). (2) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:27:y:1998:i:2:p:269-299 Dictator game giving: Rules of fairness versus acts of kindness (1998). (3) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:27:y:1998:i:2:p:245-256 Link formation in cooperative situations (1998). (4) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:25:y:1996:i:3:p:289-301 On Expectations and the Monetary Stakes in Ultimatum Games. (1996). (5) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:22:y:1993:i:2:p:171-98 Experimental Results on Ultimatum Games with Incomplete Information. (1993). (6) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:24:y:1995:i:4:p:323-44 An Evolutionary Approach to Explaining Cooperative Behavior by Reciprocal Incentives. (1995). (7) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:15:y:1986:i:3:p:187-200 On the Reduced Game Property and Its Converse. (1986). (8) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:19:y:1990:i:1:p:59-89 Evolutionary Selection Dynamics in Games: Convergence and Limit Properties. (1990). (9) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:27:y:1998:i:3:p:375-392 Population uncertainty and Poisson games (1998). (10) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:26:y:1997:i:3:p:379-401 The Core of an Economy with Multilateral Environmental Externalities (1998). (11) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:18:y:1989:i:3:p:273-91 A Bounded-Rationality Approach to the Study of Noncooperative Games. (1989). (12) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:25:y:1996:i:3:p:303-27 Expectations and Fairness in a Simple Bargaining Experiment. (1996). (13) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:20:y:1992:i:3:p:277-93 Games with Permission Structures: The Conjunctive Approach. (1992). (14) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:28:y:1999:i:1:p:131-152 Does observation of others affect learning in strategic environments? An experimental study (1999). (15) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:28:y:1999:i:3:p:263-300 Interactive epistemology I: Knowledge (1999). (16) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:20:y:1992:i:4:p:419-27 Strongly Balanced Cooperative Games. (1992). (17) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:25:y:1996:i:3:p:385-406 Voter Turnout as a Participation Game: An Experimental Investigation. (1996). (18) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:18:y:1989:i:4:p:389-407 The Consistent Shapley Value for Hyperplane Games. (1989). (19) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:21:y:1992:i:3:p:249-66 The Shapley Value for Cooperative Games under Precedence Constraints. (1992). (20) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:20:y:1992:i:4:p:393-418 Characterization and Computation of Nash-Equilibria for Auctions with Incomplete Information. (1992). (21) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:25:y:1996:i:2:p:245-58 The Nonemptiness of the f-Core of a Game without Side Payments. (1996). (22) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:18:y:1989:i:1:p:37-44 A Set of Axioms for a Value for Partition Function Games. (1989). (23) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:28:y:1999:i:4:p:511-520 Equivalence of axioms for bankruptcy problems (1999). (24) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:23:y:1994:i:1:p:75-83 Strategy-Proofness and the Strict Core in a Market with Indivisibilities. (1994). (25) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:28:y:1999:i:2:p:241-252 Strategic behavior of experienced subjects in a common pool resource game (1999). (26) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:26:y:1997:i:1:p:113-136 Order of Play in Strategically Equivalent Games in Extensive Form (1998). (27) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:29:y:2000:i:2:p:269-287 Loss aversion equilibrium (2000). (28) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:18:y:1989:i:1:p:57-89 Lower Equilibrium Payoffs in Two-Player Repeated Games with Non-observable Actions. (1989). (29) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:29:y:2001:i:4:p:487-494 Stability in coalition formation games (2001). (30) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:26:y:1997:i:1:p:27-43 An Axiomatization of the Disjunctive Permission Value for Games with a Permission Structure (1998). (31) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:25:y:1996:i:3:p:269-87 An Experimental Study of Constant-Sum Centipede Games. (1996). (32) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:26:y:1997:i:2:p:223-227 Correlated Equilibrium and Potential Games (1998). (33) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:25:y:1996:i:2:p:177-88 Mediated Talk. (1996). (34) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:26:y:1997:i:1:p:61-73 The Nucleolus and Kernel of Veto-Rich Transferable Utility Games (1998). (35) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:18:y:1989:i:3:p:293-310 On Equilibria in Repeated Games with Absorbing States. (1989). (36) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:21:y:1992:i:1:p:27-39 Weighted Values and the Core. (1992). (37) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:33:y:2005:i:4:p:505-514 A characterization of the position value* (2005). (38) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:25:y:1996:i:1:p:13-34 The Consistency Principle for Games in Strategic Forms. (1996). (39) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:34:y:2006:i:3:p:399-424 Cores of non-atomic market games (2006). (40) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:17:y:1988:i:4:p:279-300 Bargaining in Cooperative Games. (1988). (41) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:17:y:1988:i:2:p:89-99 An Axiomatization of the Banzhaf Value. (1988). (42) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:19:y:1990:i:2:p:191-217 Nash Equilibria of n-Player Repeated Games with Semi-standard Information. (1990). (43) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:30:y:2001:i:2:p:209-220 Inferior players in simple games (2001). (44) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:18:y:1989:i:2:p:227-40 A Value for Cooperative Games with Levels Structure of Cooperation. (1989). (45) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:18:y:1989:i:2:p:185-87 Credible Coalitions and the Core. (1989). (46) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:22:y:1993:i:3:p:279-302 Adjustment Patterns and Equilibrium Selection in Experimental Signaling Games. (1993). (47) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:25:y:1996:i:4:p:475-94 Ultimatums in Two-Person Bargaining with One-Sided Uncertainty: Offer Games. (1996). (48) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:29:y:2000:i:1:p:23-38 The selectope for cooperative games (2000). (49) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:20:y:1992:i:3:p:211-26 On the Equilibrium Payoffs Set of Two Player Repeated Games with Imperfect Monitoring. (1992). (50) RePEc:spr:jogath:v:28:y:1999:i:1:p:111-130 Evidence based rules and learning in symmetric normal-form games (1999). Recent citations received in: | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 Recent citations received in: 2006 (1) RePEc:aub:autbar:668.06 Weighted Approval Voting (2006). Unitat de Fonaments de l'Anà lisi Econòmica (UAB) and Institut d'Anà lisi Econòmica (CSIC) / UFAE and IAE Working Papers (2) RePEc:cca:wpaper:23 Application Costs in Sequential Admission Mechanisms (2006). Collegio Carlo Alberto / Working Papers (3) RePEc:cca:wpaper:24 Implementation with State Dependent Feasible Sets and Preferences: A Renegotiation Approach (2006). Collegio Carlo Alberto / Working Papers (4) RePEc:cca:wpaper:30 Non mean reverting affne processes for stochastic mortality (2006). Collegio Carlo Alberto / Working Papers (5) RePEc:clt:sswopa:1258 Political reputations and campaign promises (2006). California Institute of Technology, Division of the Humanities and Social Sciences / Working Papers (6) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006046 Farsightedly stable networks (2006). Université catholique de Louvain, Département des Sciences Economiques / Université catholique de Louvain, Département des Sciences Economiques Workin (7) RePEc:dgr:kubcen:200643 On the core of routing games with revenues (2006). Tilburg University, Center for Economic Research / Discussion Paper (8) RePEc:dgr:umamet:2006038 Weighted Approval Voting (2006). Maastricht : METEOR, Maastricht Research School of Economics of Technology and Organization / Research Memoranda (9) RePEc:dgr:umamet:2006045 A genetic algorithm for the partial binary constraint satisfaction problem: an application to a frequency assignment problem (2006). Maastricht : METEOR, Maastricht Research School of Economics of Technology and Organization / Research Memoranda (10) RePEc:dgr:umamet:2006046 Farsightedly Stable Networks (2006). Maastricht : METEOR, Maastricht Research School of Economics of Technology and Organization / Research Memoranda (11) RePEc:roc:wallis:wp41 A Reputational Theory of Two Party Competition (2006). University of Rochester - Wallis Institute of Political Economy / Wallis Working Papers Recent citations received in: 2005 (1) RePEc:clu:wpaper:0506-10 Cores of non-atomic market games (2005). Columbia University, Department of Economics / Discussion Papers (2) RePEc:dgr:kubcen:2005117 Learning to be prepared (2005). Tilburg University, Center for Economic Research / Discussion Paper (3) RePEc:dgr:kubcen:2005127 The component fairness solution for cycle-free graph games (2005). Tilburg University, Center for Economic Research / Discussion Paper (4) RePEc:dgr:kubcen:200594 The cutting power of preparation (2005). Tilburg University, Center for Economic Research / Discussion Paper (5) RePEc:dgr:umamet:2005056 The Component Fairness Solution for Cycle- Free Graph Games (2005). Maastricht : METEOR, Maastricht Research School of Economics of Technology and Organization / Research Memoranda (6) RePEc:dgr:uvatin:20050114 The Component Fairness Solution for Cycle-free Graph Games (2005). Tinbergen Institute / Tinbergen Institute Discussion Papers (7) RePEc:mse:wpsorb:b05086 Uniform payoff security and Nash equilibrium in metric games. (2005). Université Panthéon-Sorbonne (Paris 1) / Cahiers de la Maison des Sciences Economiques (8) RePEc:ore:uoecwp:2005-16 Interval values for strategic games in which players cooperate (2005). University of Oregon Economics Department / University of Oregon Economics Department Working Papers Recent citations received in: 2004 (1) RePEc:mtl:montde:2004-14 Nearly Serial Sharing Methods (2004). Universite de Montreal, Departement de sciences economiques / Cahiers de recherche (2) RePEc:upf:upfgen:788 Global Nash Convergence of Foster and Youngs Regret Testing (2004). Department of Economics and Business, Universitat Pompeu Fabra / Economics Working Papers Recent citations received in: 2003 (1) RePEc:icr:wpmath:25-2003 Archimedean Copulae and Positive Dependence. (2003). ICER - International Centre for Economic Research / ICER Working Papers - Applied Mathematics Series (2) RePEc:icr:wpmath:28-2003 Some Counterexamples in Positive Dependence. (2003). ICER - International Centre for Economic Research / ICER Working Papers - Applied Mathematics Series (3) RePEc:wpa:wuwpex:0310003 Learning about Learning in Games through Experimental Control of Strategic Interdependence (2003). EconWPA / Experimental (4) RePEc:wpa:wuwpga:0312004 A Wide Range No-Regret Theorem (2003). EconWPA / Game Theory and Information Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||