|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
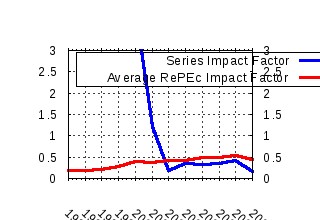
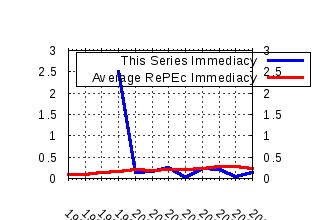
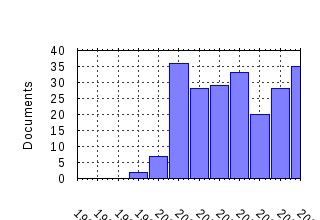
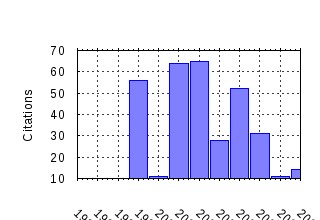
Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research, The University of Melbourne / Melbourne Institute Working Paper Series Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Recent citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp1999n13 Dissecting the Cycle (1999). (2) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp1999n12 Knowing the Cycle (1999). (3) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2002n24 Estimation of Labour Supply Models for Four Separate Groups in the Australian Population (2002). (4) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2002n08 Estimation of Wage Equations in Australia: Allowing for Censored Observations of Labour Supply (2002). (5) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2002n26 Estimation of Wage Equations in Australia: Allowing for Censored Observations of Labour Supply (2002). (6) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2001n06 Simulating the Behavioural Effects of Welfare Reforms among Sole Parents in Australia (2001). (7) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2003n24 Investigating the Role of Neighbourhood Characteristics in Determining Life Satisfaction (2003). (8) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2004n03 The Effects of Wealth and Income on Subjective Well-Being and Ill-Being (2004). (9) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2001n03 The Growth of Jobless Households in Australia (2001). (10) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2004n15 Money Doesnt Buy Happiness ⦠or Does It? A Reconsideration Based on the Combined Effects of Wealth, Income and Consumption (2004). (11) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2002n21 Regime Switches in GDP Growth and Volatility: Some International Evidence and Implications for Modelling Business Cycles (2002). (12) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2000n09 Import Competition and Labour Productivity (2001). (13) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2001n16 The Melbourne Institute Tax and Transfer Simulator (MITTS) (2001). (14) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2002n17 Intransigencies in the Labour Supply Choice (2002). (15) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2004n06 Demands for Childcare and Household Labour Supply in Australia (2004). (16) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2005n04 The Effects on Firm Profits of the Stock of Intellectual Property Rights (2005). (17) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2005n05 Patent Application Outcomes across the Trilateral Patent Offices (2005). (18) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2005n03 Transitions to Retirement: A Review (2005). (19) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2004n04 Health Status and Labour Force Participation: Evidence from the HILDA Data (2004). (20) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2000n06 Dynamic Relationships in the Australian Labour Market: Heterogeneity and State Dependence (2001). (21) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2003n28 The Role of the Unit of Analysis in Tax Policy Reform Evaluations (2003). (22) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2004n12 The Structure and Distribution of Household Wealth in Australia (2004). (23) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2002n25 The Effect of a Reduced Allowance and Pension Taper Rate: Policy Simulations Using the Melbourne Institute Tax and Transfer Simulator (2002). (24) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2003n02 Labour Market Outcomes and Welfare Dependence of Persons with Disabilities in Australia (2003). (25) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2005n09 Health Status and Labour Force Status of Older Working-Age Australian Men (2005). (26) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2006n10 Effects of Household Joblessness on Subjective Well-Being (2006). (27) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2004n10 Examining Biases in Measures of Firm Innovation (2004). (28) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2001n15 Aggregating Labour Supply and Feedback Effects in Microsimulation (2001). (29) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2002n03 The Dynamic Performance of Australian Enterprises (2002). (30) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2003n09 Effects of the Australian New Tax System on Government Expenditure With and Without Behavioural Changes (2003). (31) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2003n27 How Do Administrative Arrangements Affect Exit from Unemployment Payments? The Case of the Job Seeker Diary in Australia (2003). (32) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2004n24 Effect of Family Structure on Life Satisfaction: Australian Evidence (2004). (33) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2003n15 The Characteristics of Casual and Fixed-Term Employment: Evidence from the HILDA Survey (2003). (34) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2004n19 Female Breadwinner Families: Their Existence, Persistence and Sources (2004). (35) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2004n02 Patterns of Trademarking Activity in Australia (2004). (36) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2005n02 Behavioural Microsimulation Modelling for Tax Policy Analysis in Australia: Experience and Prospects (2005). (37) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2001n08 Enterprise Bargaining and Productivity: Evidence from the Business Longitudinal Survey (2001). (38) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2002n09 Employment Polarisation in Australia (2002). (39) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2004n14 Does Work for the Dole Work? (2004). (40) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2005n07 Preferred vs Actual Working Hours in Couple Households (2005). (41) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2002n14 New Estimates of the Private Rate of Return to University Education in Australia (2002). (42) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2007n19 The Changing Distribution of Working Hours in Australia (2007). (43) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2000n07 Union Wage Effects in the Presence of Enterprise Bargaining (2000). (44) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2000n16 Disaggregated Models of Unemployment in Australia (2001). (45) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2002n04 Industrial Relations Reform and Business Performance: An Introduction (2002). (46) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2005n06 Determinants of International Patent Examination Outcomes (2005). (47) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2007n02 Effects of Health on Wages of Australian Men (2007). (48) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2000n10 Analysing Firm-Level Labour Productivity Using Survey Data (2000). (49) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2001n14 How Segmented Are Skilled and Unskilled Labour Markets: The Case of Beveridge Curves (2001). (50) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2007n21 Comparing Welfare Change Measures with Income Change Measures in Behavioural Policy Simulations (2007). Recent citations received in: | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 Recent citations received in: 2007 (1) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2007n15 Children, Labour Supply and Childcare: Challenges for Empirical Analysis (2007). Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research, The University of Melbourne / Melbourne Institute Working Paper Series (2) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2007n23 The Macroeconomic Content of Equity Market Factors (2007). Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research, The University of Melbourne / Melbourne Institute Working Paper Series (3) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2007n25 Co-movement and Integration among Developed Equity Markets (2007). Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research, The University of Melbourne / Melbourne Institute Working Paper Series (4) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2007n29 Working Time Mismatch and Subjective Well-Being (2007). Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research, The University of Melbourne / Melbourne Institute Working Paper Series (5) RePEc:mlb:wpaper:1022 Hours of Work: A Demand Perspective (2007). The University of Melbourne / Department of Economics - Working Papers Series Recent citations received in: 2006 (1) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2475 Entrepreneurship and the Process of Firmsââ¬â¢ Entry, Survival and Growth (2006). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers Recent citations received in: 2005 (1) RePEc:auu:dpaper:499 Improving the Modeling of Couples Labour Supply (2005). Centre for Economic Policy Research, RSSS, ANU / Discussion Papers (2) RePEc:dgr:vuarem:2005-12 A microsimulation analysis of the 2006 regime change in the Dutch disability scheme (2005). Free University Amsterdam, Faculty of Economics, Business Administration and Econometrics / Serie Research Memoranda (3) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2005n17 Trade Liberalisation, Poverty and Inequality in South Africa: A CGE-Microsimulation Analysis (2005). Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research, The University of Melbourne / Melbourne Institute Working Paper Series (4) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1773 Improving the Modeling of Couples Labour Supply (2005). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers Recent citations received in: 2004 (1) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2004n03 The Effects of Wealth and Income on Subjective Well-Being and Ill-Being (2004). Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research, The University of Melbourne / Melbourne Institute Working Paper Series (2) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2004n17 SMEs and Their Use of Intellectual Property Rights in Australia (2004). Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research, The University of Melbourne / Melbourne Institute Working Paper Series (3) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2004n19 Female Breadwinner Families: Their Existence, Persistence and Sources (2004). Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research, The University of Melbourne / Melbourne Institute Working Paper Series (4) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2004n20 Effects of Recent Carrot-and-Stick Policy Initiatives on Private Health Insurance Coverage in Australia (2004). Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research, The University of Melbourne / Melbourne Institute Working Paper Series (5) RePEc:iae:iaewps:wp2004n27 The Determinants of Research and Development and Intellectual Property Usage among Australian Companies, 1989 to 2002 (2004). Melbourne Institute of Applied Economic and Social Research, The University of Melbourne / Melbourne Institute Working Paper Series (6) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1175 Income and Happiness: New Results from Generalized Threshold and Sequential Models (2004). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (7) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1308 Female Breadwinner Families: Their Existence, Persistence and Sources (2004). Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) / IZA Discussion Papers (8) RePEc:soz:wpaper:0407 Income and Happiness: New Results from Generalized Threshold and Sequential Models (2004). University of Zurich, Socioeconomic Institute / Working Papers Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||