|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
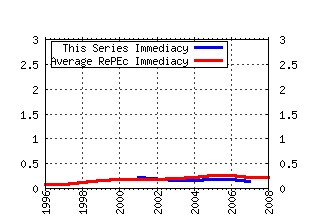
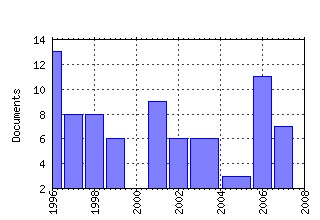
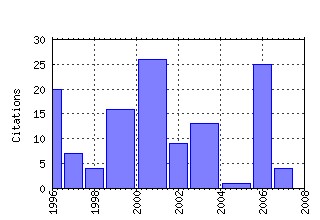
Suntory and Toyota International Centres for Economics and Related Disciplines, LSE / STICERD - Distributional Analysis Research Programme Papers Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Recent citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:cep:stidar:86 Inequality: Measurement (2006). (2) RePEc:cep:stidar:58 The Wild Bootstrap, Tamed at Last (2001). (3) RePEc:cep:stidar:44 Estimating the Intergenerational Correlation of Incomes: An Errors in Variables Framework (1999). (4) RePEc:cep:stidar:60 Sensitivity of Inequality Measures to Extreme Values (2002). (5) RePEc:cep:stidar:69 Convergence Club Empirics: Some Dynamics and Explanations of Unequal Growth across Indian States (2003). (6) RePEc:cep:stidar:32 Prediction and Determination of Household Permanent Income (1997). (7) RePEc:cep:stidar:68 Sticks and Carrots (2003). (8) RePEc:cep:stidar:25 Estimation of Inequality Indices (1996). (9) RePEc:cep:stidar:09 Identifying the Poor: A Multiple Indicator Approach (1994). (10) RePEc:cep:stidar:56 Attitudes towards Risk and Inequality: A Questionnaire-Experimental Approach (2001). (11) RePEc:cep:stidar:51 Distributional Dominance with Dirty Data (2001). (12) RePEc:cep:stidar:20 Modelling Income Distribution in Spain: A Robust Parametric Approach (1996). (13) RePEc:cep:stidar:47 Statistical Inference for Welfare under Complete and Incomplete Information (1999). (14) RePEc:cep:stidar:13 Welfare Judgements in the Presence Contaminated Data (1996). (15) RePEc:cep:stidar:52 Education, Inequality and Income Inequality (2001). (16) RePEc:cep:stidar:83 Decomposition of Bivariate Inequality Indicesby Attributes (2006). (17) RePEc:cep:stidar:21 Income Distribution in Brazil 1981-1990: Parametric and Non-Parametric Approaches (1996). (18) RePEc:cep:stidar:17 Income Mobility in Germany: Evidence from Panel Data (1996). (19) RePEc:cep:stidar:53 Galtonian Regression of Intergenerational Income Linkages: Biased Procedures, a New Estimator and Mean-Square Error Comparisons (2001). (20) RePEc:cep:stidar:92 Inequality Measurement forOrdered Response Health Data (2007). (21) RePEc:cep:stidar:55 Risk and Inequality Perceptions (2001). (22) RePEc:cep:stidar:43 Choices in Egalitarian Distribution: Inequality Aversion versus Risk Aversion (1999). (23) RePEc:cep:stidar:67 Theil, Inequality and the Structure of Income Distribution (2003). (24) RePEc:cep:stidar:50 Robust Lorenz Curves: A Semiparametric Approach (2001). (25) RePEc:cep:stidar:46 Responsibility-Sensitive Fair Compensation in Different Cultures (1999). (26) RePEc:cep:stidar:85 To Be or not To Be Involved:A Questionnaire-Experimental View on HarsanyiâsUtilitarian Ethics (2006). (27) RePEc:cep:stidar:12 Family Instability, Family Incomes and Inequality (1996). (28) RePEc:cep:stidar:04 Robust estimation of personal income distribution models (1993). (29) RePEc:cep:stidar:39 Inequality in Greece: An Analysis by Income Source (1998). (30) RePEc:cep:stidar:95 Redistributive Taxation and PublicExpenditures (2007). (31) RePEc:cep:stidar:76 Income Fluctuation, Poverty and Well-Being Over Time: Theory and Application to Argentina (2005). (32) RePEc:cep:stidar:34 Inheritance and the Distribution of Wealth (1998). (33) RePEc:cep:stidar:16 Income Distribution and Inequality in Germany: Evidence from Panel Data (1996). (34) RePEc:cep:stidar:45 Income Inequality Comparisons with Dirty Data: The UK and Spain during the 1980s (1999). (35) RePEc:cep:stidar:28 On the Performance of Social Benefit Systems (1997). (36) RePEc:cep:stidar:40 Happiness in Transition: The Case of Kyrgyzstan (1998). (37) RePEc:cep:stidar:61 Complaints and Inequality (2002). (38) RePEc:cep:stidar:78 Understanding Inequality Trends:Microsimulation Decomposition for Italy (2006). (39) RePEc:cep:stidar:35 Statistical Inference for Lorenz Curves with Censored Data (1998). (40) RePEc:cep:stidar:59 Measuring Inequality by Counting Complaints: Theory and Empirics (2002). (41) RePEc:cep:stidar:93 Distributional Orderings: An Approach with Seven Flavours (2007). (42) RePEc:cep:stidar:71 Argentinas Crises and the Poor, 1995-2002 (2003). (43) RePEc:cep:stidar:87 Growth and inequality: a demographicexplanation (2006). (44) RePEc:cep:stidar:15 Poverty Dynamics in Spain: A study of transitions in the 1990s (1996). (45) RePEc:cep:stidar:27 Equivalence of Scales and Inequality (published in Income Inequality Measurement:From Theory to Practice, J Silber (ed), Dewenter: Kluver (1999) (1997). (46) RePEc:cep:stidar:42 Evaluation via Extended Orderings: Empirical Findings from West and East (1999). (47) RePEc:cep:stidar:62 Intergenerational Mobility in Britain: Revisiting the Prediction Approach of Dearden, Machin and Reed (2002). (48) RePEc:cep:stidar:22 Workers or Employers: Who is Shaping Wage Inequality in Portugal? (1996). (49) RePEc:cep:stidar:81 Tax Compliance and Firmsâ StrategicInterdependence (2006). Recent citations received in: | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 Recent citations received in: 2008 Recent citations received in: 2007 (1) RePEc:rut:rutres:200706 A Positive Theory of Income Taxation (2007). Rutgers University, Department of Economics / Departmental Working Papers Recent citations received in: 2006 (1) RePEc:cep:stidar:82 Rethinking Inequality Decomposition:Comment (2006). Suntory and Toyota International Centres for Economics and Related Disciplines, LSE / STICERD - Distributional Analysis Research Programme Papers (2) RePEc:mlb:wpaper:971 EVALUATING POLICY: WELFARE WEIGHTS AND VALUE JUDGEMENTS (2006). The University of Melbourne / Department of Economics - Working Papers Series Recent citations received in: 2005 Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||