|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
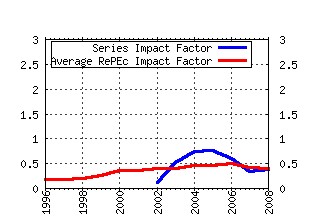
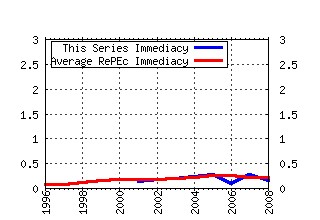
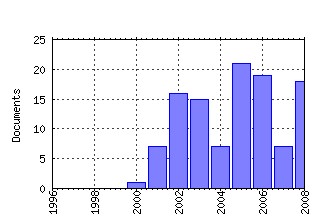
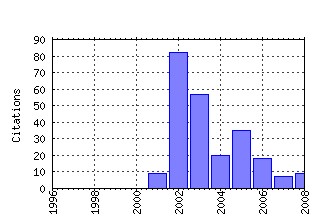
The School of Economic Studies, The Univeristy of Manchester / Centre for Growth and Business Cycle Research Discussion Paper Series Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Recent citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:10 Asymmetric Interest Rate Effects for the UK Real Economy (2002). (2) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:25 Growth, volatility and learning (2003). (3) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:03 A Tale of Two Cycles: Co-fluctuations Between UK Regions and the Euro Zone (2002). (4) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:37 The International Business Cycle in a Changing World: Volatility and the Propagation of Shocks (2003). (5) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:18 Nonlinearity in the Feds Monetary Policy Rule (2002). (6) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:29 Business Cycle Affiliations in the Context of European Integration (2003). (7) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:36 Testing for Volatility Changes in US Macroeconomic Time Series (2003). (8) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:12 Growth, Cycles and Stabilisation Policy (2002). (9) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:52 The Analytics of Segmented Labor Markets (2005). (10) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:16 Changes in Variability of the Business Cycle in the G7 Countries (2002). (11) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:76 Credit Market Imperfections and the Monetary Transmission Mechanism Part I: Fixed Exchange Rates (2006). (12) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:13 Endogenous Life Expectancy in a Simple Model of Growth (2002). (13) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:59 Fiscal Policy and Endogenous Growth with Public Infrastructure (2005). (14) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:62 Health and Infrastructure in Models of Endogenous Growth (2005). (15) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:11 Domestic and International Influences on Business Cycle Regimes in Europe (2002). (16) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:08 Short-term Volatility versus Long-term Growth: Evidence in US Macroeconomic Time Series (2001). (17) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:43 The Macroeconomics of Poverty Reduction (2004). (18) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:44 Nonlinearity and Structural Change in Interest Rate Reaction Functions for the US, UK and Germany (2004). (19) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:34 The Incidence and Persistence of Corruption in Economic Development (2003). (20) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:42 Distribution and Development in a Model of Misgovernance (2004). (21) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:47 Infrastructure, Public Education and Growth with Congestion Costs (2005). (22) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:22 Endogenous Corruption in Economic Development (2002). (23) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:50 Business Cycle Linkages for the G7 Countries:Does the US Lead the World? (2005). (24) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:73 The Tyranny of Rules: Fiscal Discipline, Productive Spending, and Growth (2006). (25) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:01 On the Relationship Between Growth and Volatility in Learning-by-Doing Economies (2001). (26) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:64 Spillovers and Correlations between US and Major European Stock Markets: The Role of the Euro (2005). (27) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:17 Dating the Business Cycle in Britain (2002). (28) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:15 The Prediction of Business Cycle Phases: Financial Variables and International Linkages (2002). (29) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:46 Modelling UK Inflation: Persistence, Seasonality and Monetary Policy (2004). (30) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:98 Public Investment and Growth: The Role of Corruption (2008). (31) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:61 Schooling and Public Capital in a Model of Endogenous Growth (2005). (32) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:109 Identifying Changes in Mean, Seasonality, Persistence and Volatility for G7 and Euro Area Inflation (2008). (33) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:74 Human Capital Accumulation in a Stochastic Environment: Some New Results on the Relationship Between Growth and Volatility (2006). (34) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:55 Public Expenditures, Bureaucratic Corruption and Economic Development (2005). (35) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:87 Credit Market Imperfections and the Monetary Transmission Mechanism Part II: Flexible Exchange Rates (2007). (36) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:53 Public Expenditures, Bureaucratic Corruption and Economic Development (2005). (37) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:93 Monetary Policy and External Shocks in a Dollarized Economy with Credit Market Imperfections (2007). (38) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:60 Infrastructure Investment and Maintenance Expenditure: Optimal Allocation Rules in a Growing Economy (2005). (39) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:48 Growth, Uncertainty and Finance. (2005). (40) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:128 Entrepreneurs, Legal Institutions and Firm Dynamics (2009). (41) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:35 Modelling Real Exchange Rate Effects on Output Performance in Latin America (2004). (42) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:54 Public Expenditures, Bureaucratic Corruption and Economic Development (2005). (43) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:95 Aid Allocation, Growth and Welfare with Productive Public Goods (2008). (44) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:111 The UK Intranational Trade Cycle (2008). (45) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:31 Public Investment in Transportation and Communication and Growth:A Dynamic Panel Approach* (2003). (46) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:79 Observed Inflation Forecasts and the New Keynesian Phillips Curve (2006). (47) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:40 The effect of nominal shock uncertainty on output growth (2003). (48) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:92 Business Cycle Synchronization of the Euro Area with the New and Negotiating Member Countries (2007). (49) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:49 Policy Variability in Models of Endogenous Growth with Productive Spending. (2005). (50) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:38 The Extent of Seasonal/Business Cycle Interactions in European Industrial Production (2003). Recent citations received in: | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 Recent citations received in: 2008 (1) RePEc:imf:imfwpa:08/256 Creating Sustainable Fiscal Space for Infrastructure: The Case of Tanzania (2008). International Monetary Fund / IMF Working Papers (2) RePEc:kob:dpaper:232 Globalization and Business Cycle Transmission (2008). Research Institute for Economics & Business Administration, Kobe University / Discussion Paper Series (3) RePEc:san:cdmawp:0806 Long-Term Growth and Short-Term Volatility: The Labour Market Nexus (2008). Centre for Dynamic Macroeconomic Analysis / CDMA Working Paper Series Recent citations received in: 2007 (1) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:90 Monetary Policy Analysis in a Small Open Credit-Based Economy (2007). The School of Economic Studies, The Univeristy of Manchester / Centre for Growth and Business Cycle Research Discussion Paper Series (2) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:93 Monetary Policy and External Shocks in a Dollarized Economy with Credit Market Imperfections (2007). The School of Economic Studies, The Univeristy of Manchester / Centre for Growth and Business Cycle Research Discussion Paper Series Recent citations received in: 2006 (1) RePEc:lbo:lbowps:2006_19 On stabilisation policy: Are there conflicting implications for growth and welfare? (2006). Economics Dept, Loughborough University / Discussion Paper Series (2) RePEc:wbk:wbrwps:4064 Public infrastructure and growth : new channels and policy implications (2006). The World Bank / Policy Research Working Paper Series Recent citations received in: 2005 (1) RePEc:fip:fedfwp:2006-36 Dual labor markets and business cycles (2005). Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco / Working Paper Series (2) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:47 Infrastructure, Public Education and Growth with Congestion Costs (2005). The School of Economic Studies, The Univeristy of Manchester / Centre for Growth and Business Cycle Research Discussion Paper Series (3) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:60 Infrastructure Investment and Maintenance Expenditure: Optimal Allocation Rules in a Growing Economy (2005). The School of Economic Studies, The Univeristy of Manchester / Centre for Growth and Business Cycle Research Discussion Paper Series (4) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:61 Schooling and Public Capital in a Model of Endogenous Growth (2005). The School of Economic Studies, The Univeristy of Manchester / Centre for Growth and Business Cycle Research Discussion Paper Series (5) RePEc:man:cgbcrp:62 Health and Infrastructure in Models of Endogenous Growth (2005). The School of Economic Studies, The Univeristy of Manchester / Centre for Growth and Business Cycle Research Discussion Paper Series (6) RePEc:man:sespap:0524 Infrastructure, Public Education and Growth with Congestion Costs (2005). School of Economics, The University of Manchester / The School of Economics Discussion Paper Series Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||