|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
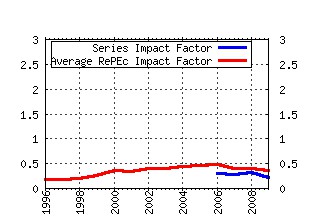
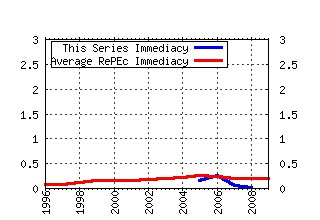
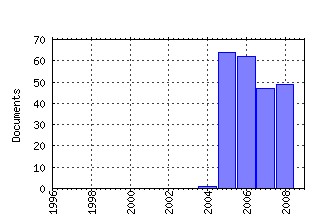
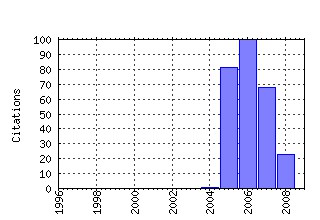
Discussion Papers (ECON - Département des Sciences Economiques) Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Recent citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2007004 Brain drain in developing countries (2007). (2) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006023 Brain drain and human capital formation in developing countries : winners and losers (2006). (3) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2007045 A gendered assessment of the brain drain (2007). (4) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005034 Counseling the unemployed : does it lower unemployment duration and recurrence ? (2005). (5) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005004 Involuntary Unemployment : the Elusive Quest for a Theory (2005). (6) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006014 Vintage Capital (2006). (7) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006039 Modelling Financial High Frequency Data Using Point Processes (2006). (8) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006006 Regime switching GARCH models (2006). (9) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2007029 Income Growth in the 21st century : forecasts with an overlapping generations model (2007). (10) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006010 Employment subsidies and substitutable skills : An equilibrium matching approach (2006). (11) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005038 Decentralization and Electoral Accountability : Incentives, Separation and Vote Welfare (2005). (12) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2007024 A Panel Data Analysis of the Brain Gain (2007). (13) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005007 Equilibrium Evaluation of Active Labor Market Programmes Enhancing Matching Effectiveness (2005). (14) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006057 Growth, public investment and corruption with failing institutions (2006). (15) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006021 The Growth economics of epidemics (2006). (16) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006061 Dynamics and monetary policy in a fair wage model of the business cycle (2006). (17) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2007022 A theory of dynamics and inequalities under epidemics (2007). (18) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005056 Gender and private returns to education : a cross-European analysis (2005). (19) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006046 Farsightedly stable networks (2006). (20) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005023 Early Literacy Achievements, Population Density and the Transition to Modern Growth (2005). (21) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005058 Bayesian inference for the mixed conditional heteroskedasticity model (2005). (22) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006025 A Theory of Medecine Effectiveness, Differential Mortality, Income Inequality and Growth for Pre-Industrial England (2006). (23) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005014 Commonalities in the order book (2005). (24) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006038 Bridging the Gap between Growth Theory and the New Economic Geography : The Spatial Ramsey Model (2006). (25) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2008048 Financial constraints in China : firm-level evidence (2008). (26) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005018 Oligopolistic Competition as a Common Agency Game (2005). (27) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006001 Complementarities and substitutabilities in matching models (2006). (28) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006036 Skilled Migration and Business Networks (2006). (29) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006008 Incentives to innovate in oligopolies (2006). (30) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006042 Incumbentsâ Interests, Votersâ Bias and Gender Quotas (2006). (31) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005009 Natural volatility, welfare and taxation (2005). (32) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005021 When All is Said and Done, How Should You Play and What Should You Expect ? (2005). (33) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2008010 Data games. Sharing public goods with exclusion (2008). (34) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2008008 Diaspora Externalities and Technology Diffusion (2008). (35) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2007033 Theory and inference for a Markov switching GARCH model (2007). (36) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2008017 Optimal firm behavior under environmental constraints (2008). (37) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006059 Endogenous Discounting via Wealth, Twin-Peaks and the Role of Technology (2006). (38) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2007005 Easter Islandâs Collapse : A Tale of a Population Race (2007). (39) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005013 Regional inequality and product variety (2005). (40) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005024 Multiple Lending and Constrained Efficiency in the Credit Market (2005). (41) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2008015 Mixed duopoly, privatization and the shadow cost of public funds (2008). (42) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005055 What Does it Take to Achieve Equality of Opportunity in Education ?
An Empirical Investigation Based on Brazilian Data (2005). (43) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006009 The Global Chilling Effects of Antidumping Proliferation (2006). (44) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2007016 IIs the Notification of Monitoring a Threat to the Unemployed ? A Regression Discontinuity Approach (2007). (45) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005017 A simple model of economic geography à la Helpman-Tabuchi (2005). (46) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006043 Virtual Nash implementation with admissible support (2006). (47) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2008028 On investment decisions in liberalized electricity markets : the impact of price caps at the spot market (2008). (48) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005062 Fiscal competition, revenue sharing, and policy-induced agglomeration (2005). (49) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005011 Did the market-clearing postulate pre-exist new classical economics ? The case of Marshallian theory (2005). (50) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2005043 Exchange Rate Volatility and the Mixture of Distribution Hypothesis (2005). Recent citations received in: | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 Recent citations received in: 2009 Recent citations received in: 2008 (1) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2008034 Estimating the Dynamics of R&D-based Growth Models (2008). Discussion Papers (ECON - Département des Sciences Economiques) Recent citations received in: 2007 (1) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2007024 A Panel Data Analysis of the Brain Gain (2007). Discussion Papers (ECON - Département des Sciences Economiques) (2) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2007045 A gendered assessment of the brain drain (2007). Discussion Papers (ECON - Département des Sciences Economiques) (3) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp3235 A Gendered Assessment of the Brain Drain (2007). IZA Discussion Papers Recent citations received in: 2006 (1) RePEc:cor:louvco:2006080 Modelling financial high frequency data using point processes (2006). CORE Discussion Papers (2) RePEc:cor:louvco:2006103 On optimality, endogenous discounting and wealth accumulation (2006). CORE Discussion Papers (3) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006010 Employment subsidies and substitutable skills : An equilibrium matching approach (2006). Discussion Papers (ECON - Département des Sciences Economiques) (4) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006039 Modelling Financial High Frequency Data Using Point Processes (2006). Discussion Papers (ECON - Département des Sciences Economiques) (5) RePEc:ctl:louvec:2006058 On optimality, endogeneous discounting and wealth accumulation (2006). Discussion Papers (ECON - Département des Sciences Economiques) (6) RePEc:dgr:kubcen:200661 Does Antidumping Use Contribute to Trade Liberalization? An Empirical Analysis (2006). Discussion Paper (7) RePEc:dgr:umamet:2006024 Price Manipulation in an Experimental Asset Market (2006). Research Memoranda (8) RePEc:diw:diwwpp:dp614 Competitive Screening in Insurance Markets with Endogenous Labor Supply (2006). Discussion Papers of DIW Berlin (9) RePEc:fda:fdaddt:2006-10 Secondhand market and the lifetime of durable goods (2006). Working Papers (10) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2073 Employment Subsidies and Substitutable Skills: An Equilibrium Matching Approach (2006). IZA Discussion Papers (11) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2440 Brain Drain and Inequality Across Nations (2006). IZA Discussion Papers (12) RePEc:kie:kieliw:1302 Comparing the Effectiveness of Employment Subsidies (2006). Kiel Working Papers (13) RePEc:mse:wpsorb:v06080 Education, corruption and growth in developing countries. (2006). Cahiers de la Maison des Sciences Economiques (14) RePEc:pra:mprapa:34241 Institutionally Induced Human Capital Vintages and Economic Growth in Transition (2006). MPRA Paper (15) RePEc:sce:scecfa:209 Medium term dynamics and inequalities under epidemics (2006). Computing in Economics and Finance 2006 (16) RePEc:van:wpaper:0614 Strategic Basins of Attraction, the Path Dominance Core, and Network Formation Games (2006). Working Papers Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||