|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
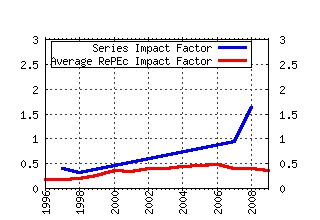
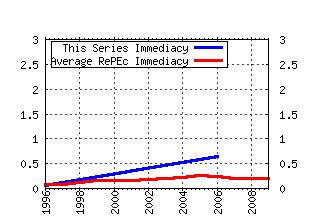
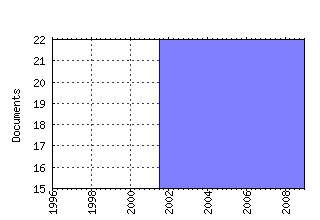
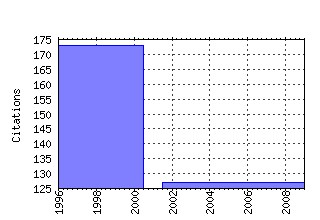
Handbook of Computational Economics Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Recent citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:eee:hecchp:2-23 Heterogeneous Agent Models in Economics and Finance (2006). (2) RePEc:eee:hecchp:1-14 Numerical dynamic programming in economics (1996). (3) RePEc:eee:hecchp:1-04 Mechanics of forming and estimating dynamic linear economies (1996). (4) RePEc:eee:hecchp:2-24 Agent-based Computational Finance (2006). (5) RePEc:eee:hecchp:1-15 Monte carlo simulation and numerical integration (1996). (6) RePEc:eee:hecchp:1-02 Computation of equilibria in finite games (1996). (7) RePEc:eee:hecchp:1-01 Computable general equilibrium modelling for policy analysis and forecasting (1996). (8) RePEc:eee:hecchp:2-16 Agent-Based Computational Economics: A Constructive Approach to Economic Theory (2006). (9) RePEc:eee:hecchp:2-18 Agent Learning Representation: Advice on Modelling Economic Learning (2006). (10) RePEc:eee:hecchp:2-25 Agent-based Models of Innovation and Technological Change (2006). (11) RePEc:eee:hecchp:2-19 Agent-Based Models and Human Subject Experiments (2006). (12) RePEc:eee:hecchp:1-12 Approximation, perturbation, and projection methods in economic analysis (1996). (13) RePEc:eee:hecchp:1-07 Parallel computation (1996). (14) RePEc:eee:hecchp:2-34 Remarks on the Foundations of Agent-Based Generative Social Science (2006). (15) RePEc:eee:hecchp:2-20 Economic Activity on Fixed Networks (2006). (16) RePEc:eee:hecchp:2-30 Governing Social-Ecological Systems (2006). (17) RePEc:eee:hecchp:1-13 Numerical methods for linear-quadratic models (1996). (18) RePEc:eee:hecchp:2-27 Market Design Using Agent-Based Models (2006). (19) RePEc:eee:hecchp:v:2-21 ACE Models of Endogenous Interactions (2006). (20) RePEc:eee:hecchp:2-32 Out-of-Equilibrium Economics and Agent-Based Modeling (2006). (21) RePEc:eee:hecchp:1-05 Nonlinear pricing and mechanism design (1996). (22) RePEc:eee:hecchp:2-28 Automated Markets and Trading Agents (2006). (23) RePEc:eee:hecchp:2-36 Agent-Based Macro (2006). (24) RePEc:eee:hecchp:2-17 Computationally Intensive Analyses in Economics (2006). (25) RePEc:eee:hecchp:2-37 Some Fun, Thirty-Five Years Ago (2006). (26) RePEc:eee:hecchp:1-03 Computational methods for macroeconometric models (1996). (27) RePEc:eee:hecchp:1-09 Neural networks for encoding and adapting in dynamic economies (1996). (28) RePEc:eee:hecchp:2-33 Agent-based Modeling as a Bridge Between Disciplines (2006). (29) RePEc:eee:hecchp:2-26 Agent-Based Models of Organizations (2006). Recent citations received in: | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 Recent citations received in: 2009 Recent citations received in: 2008 Recent citations received in: 2007 Recent citations received in: 2006 (1) RePEc:ams:ndfwpp:06-01 Interacting agents in finance, entry written for the New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics, Second Edition, edited by L. Blume and S. Durlauf, Palgrave Macmillan, forthcoming 2006. (2006). CeNDEF Working Papers (2) RePEc:ams:ndfwpp:06-02 Price and Wealth Dynamics in a Speculative Market with Generic Procedurally Rational Traders (2006). CeNDEF Working Papers (3) RePEc:ams:ndfwpp:06-11 Informational differences and learning in an asset market with boundedly rational agents (2006). CeNDEF Working Papers (4) RePEc:ams:ndfwpp:06-12 More hedging instruments may destabilize markets (2006). CeNDEF Working Papers (5) RePEc:ams:ndfwpp:06-15 E&F Chaos: a user friendly software package for nonlinear economic dynamics (2006). CeNDEF Working Papers (6) RePEc:dgr:uvatin:20060029 Interacting Agents in Finance (2006). Tinbergen Institute Discussion Papers (7) RePEc:isu:genres:12402 Agent-Based Computational Modeling And Macroeconomics (2006). Staff General Research Papers (8) RePEc:kap:compec:v:28:y:2006:i:1:p:51-69 On the Selection of Adaptive Algorithms in ABM: A Computational-Equivalence Approach (2006). Computational Economics (9) RePEc:kap:compec:v:28:y:2006:i:4:p:313-331 Republication: On the Selection of Adaptive Algorithms in ABM: A Computational-Equivalence Approach (2006). Computational Economics (10) RePEc:man:sespap:0623 Dynamic interaction models of economic equilibrium (2006). The School of Economics Discussion Paper Series (11) RePEc:pra:mprapa:1261 Memory and Asset Pricing Models with Heterogeneous Beliefs (2006). MPRA Paper (12) RePEc:sce:scecfa:225 Behavioral Consistent Market Equilibria under Procedural Rationality (2006). Computing in Economics and Finance 2006 (13) RePEc:spr:jeicoo:v:1:y:2006:i:2:p:189-214 Impact of investors varying risk aversion on the dynamics of asset price fluctuations (2006). Journal of Economic Interaction and Coordination (14) RePEc:ssa:lemwps:2006/14 Empirical Validation of Agent Based Models: A Critical Survey (2006). LEM Papers Series Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||