|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
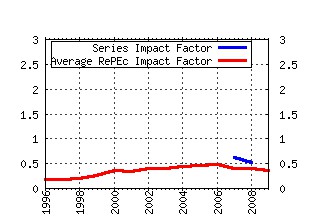
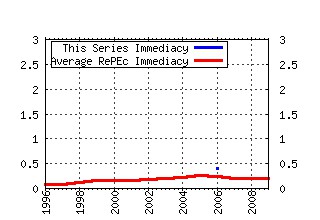
2006 Meeting Papers Raw citation data, Impact Factor, Immediacy Index, Published documents, Citations received, , Most cited papers , Recent citations and documents published in this series in EconPapers.
Most cited documents in this series: (1) RePEc:red:sed006:512 The Bank Capital Channel of Monetary Policy (2006). (2) RePEc:red:sed006:894 An Equilibrium Model of Global Imbalances and Low Interest Rates (2006). (3) RePEc:red:sed006:353 The Time Varying Volatility of Macroeconomic Fluctuations (2006). (4) RePEc:red:sed006:46 Differential Mortality, Uncertain Medical Expenses, and the Saving of Elderly Singles (2006). (5) RePEc:red:sed006:300 Price Setting during Low and High Inflation: Evidence from Mexico (2006). (6) RePEc:red:sed006:864 The Returns to Currency Speculation (2006). (7) RePEc:red:sed006:496 The Rise of the Service Economy (2006). (8) RePEc:red:sed006:31 Can News About the Future Drive the Business Cycle? (2006). (9) RePEc:red:sed006:207 Capital Deepening and Non-Balanced Economic Growth (2006). (10) repec:red:sed006:355 (). (11) RePEc:red:sed006:792 Financial Frictions and the Persistence of History (2006). (12) RePEc:red:sed006:479 Can Structural Small Open Economy Models Account for the Influence of Foreign Disturbances? (2006). (13) RePEc:red:sed006:45 A Model of Money and Credit, with Application to the Credit Card Debt Puzzle (2006). (14) RePEc:red:sed006:252 Could capital gains smooth a current account rebalancing? (2006). (15) RePEc:red:sed006:733 How Important is the New Goods Margin in International Trade? (2006). (16) RePEc:red:sed006:256 Structural Transformation and the Labor Market (2006). (17) RePEc:red:sed006:61 Death and Development (2006). (18) RePEc:red:sed006:796 Imports and Productivity (2006). (19) RePEc:red:sed006:518 Why Has CEO Pay Increased So Much? (2006). (20) RePEc:red:sed006:195 The Valuation Channel of External Adjustment (2006). (21) RePEc:red:sed006:5 On-the-job Search, Productivity Shocks, and the Individual Earnings Process (2006). (22) RePEc:red:sed006:43 Investment in Schooling and the Marriage Market (2006). (23) RePEc:red:sed006:544 Identifying the Role of Labor Markets for Monetary Policy in an Estimated DSGE Model (2006). (24) RePEc:red:sed006:371 Financial Integration and International Risk Sharing (2006). (25) RePEc:red:sed006:502 Inefficient Policies, Inefficient Institutions and Trade (2006). (26) RePEc:red:sed006:660 The Empirical Content of Models with Multiple Equilibria (2006). (27) RePEc:red:sed006:304 Which Sectors Make the Poor Countries so Unproductive? (2006). (28) RePEc:red:sed006:504 Career Choice and Wage Growth (2006). (29) RePEc:red:sed006:445 Why are Married Men Working So Much? (2006). (30) RePEc:red:sed006:773 Wage Rigidity and Job Creation (2006). (31) RePEc:red:sed006:679 A Feasible Equilibrium Search Model of Individual Wage Dynamics with Experience Accumulation (2006). (32) RePEc:red:sed006:775 Lumpy Investment in Dynamic General Equilibrium (2006). (33) RePEc:red:sed006:10 On the extent of job-to-job transitions (2006). (34) RePEc:red:sed006:313 Business cycle accounting for the Japanese economy (2006). (35) RePEc:red:sed006:15 The Diffusion of Wal-Mart and Economies of Density (2006). (36) RePEc:red:sed006:361 Knowing what others Know: Coordination motives in information acquisition (2006). (37) RePEc:red:sed006:299 Default and the Term Structure in Sovereign Bonds (2006). (38) RePEc:red:sed006:455 Capital Taxation (2006). (39) RePEc:red:sed006:565 Sovereign Risk and Secondary Markets (2006). (40) RePEc:red:sed006:9 The Costs of Environmental Regulation in a Concentrated Industry (2006). (41) RePEc:red:sed006:468 A Dynamic Analysis of Cooperative Research in the Semiconductor Industry (2006). (42) RePEc:red:sed006:8 Gold rush fever in business cycles (2006). (43) RePEc:red:sed006:368 The distribution of wealth and redistributive policies (2006). (44) RePEc:red:sed006:411 Gender roles and technological progress (2006). (45) RePEc:red:sed006:210 Time Consistent Debt (2006). (46) RePEc:red:sed006:410 Social Security, Life Insurance and Annuities for Families (2006). (47) RePEc:red:sed006:206 The Dynamic (In)efficiency of Monetary Policy by Committee (2006). (48) RePEc:red:sed006:137 On-the-Job Search and Precautionary Savings: Theory and Empirics of Earnings and Wealth Inequality (2006). (49) RePEc:red:sed006:29 Reconciling the Return Predictability Evidence (2006). (50) RePEc:red:sed006:56 Trends in Hours and Economic Growth (2006). Recent citations received in: | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 Recent citations received in: 2009 Recent citations received in: 2008 Recent citations received in: 2007 Recent citations received in: 2006 (1) RePEc:aah:aarhec:2006-10 Educational Homogamy: Preferences or Opportunities? (2006). Economics Working Papers (2) RePEc:ags:iaae06:25279 The Physical, Social, and Cultural Determinants of Obesity: An Empirical Study of the U.S. (2006). 2006 Annual Meeting, August 12-18, 2006, Queensland, Australia (3) RePEc:bca:bocawp:06-5 Are Currency Crises Low-State Equilibria? An Empirical, Three-Interest-Rate Model (2006). Working Papers (4) RePEc:bde:wpaper:0602 Social Security Reform with Uninsurable Income Risk and Endogenous Borrowing Constraints (2006). Banco de España Working Papers (5) RePEc:bde:wpaper:0633 Inefficient policies, inefficient institutions and trade (2006). Banco de España Working Papers (6) RePEc:bde:wpaper:0634 Genetic algorithm estimation of interest rate term structure (2006). Banco de España Working Papers (7) RePEc:bis:biswps:222 An equilibrum model of global imbalances and low interest rates (2006). BIS Working Papers (8) RePEc:boe:boeewp:301 The welfare benefits of stable and efficient payment systems (2006). Bank of England working papers (9) RePEc:bos:wpaper:wp2006-020 Managerial Preferences, Corporate Governance, and Financial Structure (2006). Boston University - Department of Economics - Working Papers Series (10) RePEc:cep:cepdps:dp0746 Trends in Hours and Economic Growth (2006). CEP Discussion Papers (11) RePEc:cep:cepdps:dp0757 Unemployment and Hours of Work: The North Atlantic Divide Revisited (2006). CEP Discussion Papers (12) RePEc:cep:cepdps:dp0762 An R&D-Based Model of Multi-Sector Growth (2006). CEP Discussion Papers (13) RePEc:ces:ceswps:_1697 Optimal Central Bank Design: Benchmarks for the ECB (2006). CESifo Working Paper Series (14) RePEc:ces:ceswps:_1739 Monetary Transmission Mechanism in Transition Economies: Surveying the Surveyable (2006). CESifo Working Paper Series (15) RePEc:chb:bcchwp:359 The Consumption-Real Exchange Rate Anomaly: Non-Traded Goods, Incomplete Markets and Distribution Services (2006). Working Papers Central Bank of Chile (16) RePEc:cje:issued:v:39:y:2006:i:4:p:1041-1072 The spectre of deflation: a review of empirical evidence (2006). Canadian Journal of Economics (17) RePEc:col:000094:002032 Assortative Matching and the Education Gap (2006). BORRADORES DE ECONOMIA (18) RePEc:cor:louvco:2006088 International stock return predictability: statistical evidence and economic significance (2006). CORE Discussion Papers (19) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5489 Civic Attitudes and the Design of Labour Market Institutions: Which Countries Can Implement the Danish Flexicurity Model? (2006). CEPR Discussion Papers (20) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5503 Are Specific Skills an Obstacle to Labour Market Adjustment? Theory and an Application to the EU Enlargement (2006). CEPR Discussion Papers (21) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5512 International Portfolio Equilibrium and the Current Account (2006). CEPR Discussion Papers (22) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5513 Estimating Macroeconomic Models: A Likelihood Approach (2006). CEPR Discussion Papers (23) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5713 CEO Compensation and Strategy Inertia (2006). CEPR Discussion Papers (24) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5770 Predictability in Financial Markets: What Do Survey Expectations Tell Us? (2006). CEPR Discussion Papers (25) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5772 How Robust is the New Conventional Wisdom? The Surprising Fragility of the Theoretical Foundations of Inflation Targeting and Central Bank Independence (2006). CEPR Discussion Papers (26) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5878 The Structural Dynamics of Output Growth and Inflation: Some International Evidence (2006). CEPR Discussion Papers (27) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5881 Heterogenous Life-Cycle Profiles, Income Risk and Consumption Inequality (2006). CEPR Discussion Papers (28) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5909 Behavioural Theories of the Business Cycle (2006). CEPR Discussion Papers (29) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5935 Frictional Wage Dispersion in Search Models: A Quantitative Approach (2006). CEPR Discussion Papers (30) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5950 Globalization and the Provision of Incentives Inside the Firm (2006). CEPR Discussion Papers (31) RePEc:cpr:ceprdp:5957 Euro-Dollar Real Exchange Rate Dynamics in an Estimated Two-Country Model: What is Important and What is Not (2006). CEPR Discussion Papers (32) RePEc:deg:conpap:c011_020 Indias Service Sector Growth - A New Revolution (2006). DEGIT Conference Papers (33) RePEc:deg:conpap:c011_030 When Does Domestic Saving Matter for Economic Growth? (2006). DEGIT Conference Papers (34) RePEc:deg:conpap:c011_034 Investment in Schooling and the Marriage Market (2006). DEGIT Conference Papers (35) RePEc:dgr:kubcen:200657 Why do Worker-Firm Matches Dissolve? (2006). Discussion Paper (36) RePEc:ebl:ecbull:v:15:y:2006:i:10:p:1-6 Distribution services and economic growth (2006). Economics Bulletin (37) RePEc:ecb:ecbwps:20060585 Are specific skills an obstacle to labor market adjustment? Theory and an application to the EU enlargement. (2006). Working Paper Series (38) RePEc:ecb:ecbwps:20060625 Sectoral explanations of employment in Europe - the role of services. (2006). Working Paper Series (39) RePEc:ecb:ecbwps:20060635 Identifying the role of labor markets for monetary policy in an estimated DSGE model. (2006). Working Paper Series (40) RePEc:ecb:ecbwps:20060669 Regular adjustment - theory and practice. (2006). Working Paper Series (41) RePEc:ecb:ecbwps:20060684 Inflation dynamics and regime shifts (2006). Working Paper Series (42) RePEc:ecl:harjfk:rwp06-003 Global Imbalances or Bad Accounting? The Missing Dark Matter in the Wealth of Nations (2006). Working Paper Series (43) RePEc:eui:euiwps:eco2006/35 Employment Protection, Firm Selection, and Growth (2006). (44) RePEc:eui:euiwps:eco2006/36 S-Curve Redux: On the International Transmission of Technology Shocks. (2006). (45) RePEc:fip:fedawp:2006-25 Credit and the no-surcharge rule (2006). Working Paper (46) RePEc:fip:fedcwp:0610 Adaptive learning, endogenous inattention, and changes in monetary policy (2006). Working Paper (47) RePEc:fip:fedfel:y:2006:i:dec1:n:2006-33-34 Economic inequality in the United States (2006). FRBSF Economic Letter (48) RePEc:fip:fedfer:y:2006:p:31-45 Current account adjustment with high financial integration: a scenario analysis (2006). Economic Review (49) RePEc:fip:fedfpr:y:2006:i:jun:x:2 The U.S. current account deficit and the expected share of world output (2006). Proceedings (50) RePEc:fip:fedfpr:y:2006:i:jun:x:8 The international financial integration of China and India (2006). Proceedings (51) RePEc:fip:fedfwp:2006-03 Could capital gains smooth a current account rebalancing? (2006). Working Paper Series (52) RePEc:fip:fedfwp:2006-26 Aggregate shocks or aggregate information? costly information and business cycle comovement (2006). Working Paper Series (53) RePEc:fip:fedfwp:2006-38 The U.S. current account deficit and the expected share of world output (2006). Working Paper Series (54) RePEc:fip:fedgfe:2007-15 Learning by investing--embodied technology and business cycles (2006). Finance and Economics Discussion Series (55) RePEc:fip:fedhep:y:2006:i:qiii:p:2-13:n:v.30no.3 Right before the end: asset decumulation at the end of life (2006). Economic Perspectives (56) RePEc:fip:fedhep:y:2006:i:qiv:p:2-21:n:v.30no.4 Policymakers, researchers, and practitioners discuss the role of central counterparties (2006). Economic Perspectives (57) RePEc:fip:fedkpr:y:2006:p:265-305 Impact of globalization on monetary policy (2006). Proceedings (58) RePEc:fip:fedkpw:psrwp06-01 Microfoundations of two-sided markets: the payment card example (2006). Payments System Research Working Paper (59) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2005-026 Is value premium a proxy for time-varying investment opportunities: some time series evidence (2006). Working Papers (60) RePEc:fip:fedlwp:2006-019 Understanding stock return predictability (2006). Working Papers (61) RePEc:fip:fedmsr:376 Modern macroeconomics in practice: how theory is shaping policy (2006). Staff Report (62) RePEc:fip:fedmwp:645 Consumer search and firm growth (2006). Working Papers (63) RePEc:fip:fednsr:237 Could capital gains smooth a current account rebalancing? (2006). Staff Reports (64) RePEc:fip:fednsr:249 Expectations and contagion in self-fulfilling currency attacks (2006). Staff Reports (65) RePEc:fip:fednsr:263 Payment networks in a search model of money (2006). Staff Reports (66) RePEc:fip:fedreq:y:2006:i:sum:p:195-223:n:v.92no.3 The productivity of nations (2006). Economic Quarterly (67) RePEc:fip:fedrwp:06-05 The Lucas critique and the stability of empirical models (2006). Working Paper (68) RePEc:fip:fedrwp:06-07 Frictional wage dispersion in search models: a quantitative assessment (2006). Working Paper (69) RePEc:fip:fedrwp:06-11 Computing business cycles in emerging economy models (2006). Working Paper (70) RePEc:geo:guwopa:gueconwpa~06-06-12 Assortative Matching and the Education Gap (2006). Working Papers (71) RePEc:geo:guwopa:gueconwpa~06-06-13 Financial Integration, Macroeconomic Volatility and Welfare (2006). Working Papers (72) RePEc:hal:cesptp:halshs-00115622 Banks procyclicality behavior : does provisioning matter ? (2006). Université Paris1 Panthéon-Sorbonne (Post-Print and Working Papers) (73) RePEc:has:discpr:0602 Social Security Reform in the US: Lessons from Hungary (2006). IEHAS Discussion Papers (74) RePEc:has:discpr:0603 Why do (or do not) banks share customer information? A comparison of mature private credit markets and markets in transition (2006). IEHAS Discussion Papers (75) RePEc:hhs:aareco:2006_009 Job Mobility and Wage Dynamics (2006). Working Papers (76) RePEc:hkm:wpaper:172006 Currency Appreciation and Current Account Adjustment (2006). Working Papers (77) RePEc:hum:wpaper:sfb649dp2006-023 How Far Are We From The Slippery Slope? The Laffer Curve Revisited (2006). SFB 649 Discussion Papers (78) RePEc:iei:wpaper:0604 Human Capital Inequality, Life Expectancy and Economic Growth (2006). Working Papers (79) RePEc:ifs:ifsewp:06/08 Dynamic models for policy evaluation (2006). IFS Working Papers (80) RePEc:igi:igierp:316 Monetary Policy in a Small Open Economy with a Preference for Robustness (2006). Working Papers (81) RePEc:imf:imfwpa:06/160 U.S. Dollar Risk Premiums and Capital Flows (2006). IMF Working Papers (82) RePEc:imf:imfwpa:06/281 Central Bank Boards Around the World: Why Does Membership Size Differ? (2006). IMF Working Papers (83) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp1928 Civic Attitudes and the Design of Labor Market Institutions: Which Countries Can Implement the Danish Flexicurity Model? (2006). IZA Discussion Papers (84) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2065 Capital Deepening and Wage Differentials: Germany vs. US (2006). IZA Discussion Papers (85) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2165 Why Do Worker-Firm Matches Dissolve? (2006). IZA Discussion Papers (86) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2257 Sectoral Explanations of Employment in Europe: The Role of Services (2006). IZA Discussion Papers (87) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2260 Career Progression and Formal versus On-the-Job Training (2006). IZA Discussion Papers (88) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2271 Educational Homogamy: Preferences or Opportunities? (2006). IZA Discussion Papers (89) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2331 Differences in Wage Growth by Education Level: Do Less-Educated Workers Gain Less from Work Experience? (2006). IZA Discussion Papers (90) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2339 Aggregate Shocks or Aggregate Information? Costly Information and Business Cycle Comovement (2006). IZA Discussion Papers (91) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2408 Globalization and the Provision of Incentives Inside the Firm: The Effect of Foreign Competition (2006). IZA Discussion Papers (92) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2454 Investment in Schooling and the Marriage Market (2006). IZA Discussion Papers (93) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2485 How General Is Specific Human Capital? (2006). IZA Discussion Papers (94) RePEc:iza:izadps:dp2528 Nominal Wage Rigidities in a New Keynesian Model with Frictional Unemployment (2006). IZA Discussion Papers (95) RePEc:kie:kieliw:1303 Banks Regulatory Buffers, Liquidity Networks and Monetary Policy Transmission (2006). Kiel Working Papers (96) RePEc:kln:owiwdp:dp_03_2006 The final blow to the Stability Pact? EMU enlargement and government debt (2006). Otto-Wolff-Institut Discussion Paper Series (97) RePEc:lev:levysa:sa_nov_06 Can Global Imbalances Continue?: Policies for the U.S. Economy (2006). Economics Strategic Analysis Archive (98) RePEc:lev:wrkpap:wp_486 Global Imbalances, Bretton Woods II, and Eurolands Role in All This (2006). Economics Working Paper Archive (99) RePEc:mib:wpaper:103 Market Leaders and Industrial Policy (2006). Working Papers (100) RePEc:mse:wpsorb:bla06035 Banksprocyclicality behavior : does provisioning matter ?. (2006). Cahiers de la Maison des Sciences Economiques More than 100 citations. List broken... Warning!! This is still an experimental service. The results of this service should be interpreted with care, especially in research assessment exercises. The processing of documents is automatic. There still are errors and omissions in the identification of references. We are working to improve the software to increase the accuracy of the results. Source data used to compute the impact factor of RePEc series. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||